Top Microbiology News in 2018: There is a world we are not capable of seeing with the naked eye. It is the world of bacteria, archaea, and viruses. While previously we viewed those organisms solely as nasty pathogens, the scientific breakthroughs show us how complex this world is and how indispensable it is to our way of life.
Table of Contents
- Top 15 Microbiology News in 2018
- 1. A Breach in Viral Defenses
- 2. A New Educational Idea for Microbiology Students
- 3. Microorganisms as evidence in microbial forensics
- 4. New protection mechanism in Epstein – Barr viruses discovered
- 5. Speeding up bacteria detection with biosensors
- 6. IBD is associated with crucial changes in the gut microbiome
- 7. Collective bacterial defense against immunity
- 8. Some antibiotic-resistance genes are interconnected
- 9. Archaea and bacteria work together to destroy waste
- 10. Soil microorganisms can withstand drought
- 11. Scientists Discover 1000+ Chlorophyll-Containing Bacteria
- 12. Next-generation sequencing against corrosion in the oil industry
- 13. Bacteria can assist in counteracting climate change
- 14. The secret of aquaponics lies with microbes
- 15. Fighting mercury contamination with bacteria
Top 15 Microbiology News in 2018
1. A Breach in Viral Defenses
 There are five types of Ebola viruses – and all can cause lethal disease in humans. Now a weakness common to all five has been found.
There are five types of Ebola viruses – and all can cause lethal disease in humans. Now a weakness common to all five has been found.
- It is a conserved sequence that codes for a glycoprotein;
- The sequence is similar in all five members of the Ebola virus genus;
- The glycoprotein can be used as a part of a universal vaccine that would protect from the whole genus.
![]()
2. A New Educational Idea for Microbiology Students
 Usually, studying microbiology means mechanical memorization of multiple classes and species. A novel idea to use collaborative learning was proposed by educators at Sao Paolo University, Brazil.
Usually, studying microbiology means mechanical memorization of multiple classes and species. A novel idea to use collaborative learning was proposed by educators at Sao Paolo University, Brazil.
- Each student was told to “adopt” a certain genus of bacteria;
- Students were required to research information and make posts on Facebook about the “adopted” genus.
- Forums were launched to discuss findings.
- Students have reported that they enjoyed the activities and learned to use scientific resources.
- Students also learned more compared to the traditional approach.
![]()
3. Microorganisms as evidence in microbial forensics
 Novel genetic analysis has led to the development of the new discipline – microbial forensics.
Novel genetic analysis has led to the development of the new discipline – microbial forensics.
- It involves using massively parallel sequencing;
- Could be applied in the investigation of biocrime/bioterrorism cases;
- Can be used in epidemiological research;
- Helps establish the cause of death in criminal investigations;
- Can assist in microbiome-based human identification;
Unfortunately, until new standards are developed the application of this promising technology is limited.
![]()
4. New protection mechanism in Epstein – Barr viruses discovered
 A novel study has revealed how the Epstein – Barr virus protects itself from innate immunity in humans.
A novel study has revealed how the Epstein – Barr virus protects itself from innate immunity in humans.
- APOBEC enzymes block replication of single-stranded DNA viruses and are part of innate antiviral immunity;
- An Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) protein called BORF2 is responsible for blocking APOBEC;
- BORF2 both inhibits APOBEC activity and transports the protein out of the nucleus;
- Viruses without BORF2 were susceptible to APOBEC activity;
These findings provide us with insight as to how viruses protect themselves from the immune system activity, which in turn could help us find antiviral treatments.
![]()
5. Speeding up bacteria detection with biosensors
 Establishing the presence of pathogenic bacteria can be time-consuming and hampers treatment. A new biosensor that quickly detects bacteria was developed.
Establishing the presence of pathogenic bacteria can be time-consuming and hampers treatment. A new biosensor that quickly detects bacteria was developed.
- The biosensor is a microfluidic chip that can be injected with a sample and placed in the microwave resonator;
- Then bacteria can be detected in fluids with different pH;
- The sensor detects bacteria presence, concentration, and growth;
The new invention would make laboratory tests much quicker and provide a vast array of crucial information.
![]()
6. IBD is associated with crucial changes in the gut microbiome
 Metabolomic and metagenomic profiles of patients with IBD and Crohn’s disease were studied.
Metabolomic and metagenomic profiles of patients with IBD and Crohn’s disease were studied.
- IBD was associated with an increase in the production of sphingolipids and bile acids in the gut;
- It was established that around 122 changes in metabolism among different microbiome species were associated with IBD development;
- Certain parameters of microbiome composition and metabolic activity of gut microorganisms could be used as diagnostic markers of IBD;
These findings can potentially be used in IBD diagnosis and treatment.
![]()
7. Collective bacterial defense against immunity
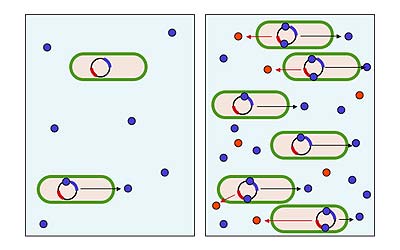 Quorum sensing in bacterial species allows many bacteria to act as one against threats. Properties of one of the molecules that induce quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa were studied.
Quorum sensing in bacterial species allows many bacteria to act as one against threats. Properties of one of the molecules that induce quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa were studied.
- N-(3-oxo-dodecanoyl) homoserine lactone is a signal molecule that induces LasI-LasR circuitry in P. aeruginosa;
- This circuitry is responsible for quorum sensing in the species;
- It was found that these signal molecules also cause cell death in lymphocytes.
This finding can be the basis for a new treatment strategy aimed at quorum sensing signaling.
![]()
8. Some antibiotic-resistance genes are interconnected
 Many antibiotic resistance genes influence each other, forming epistatic pairs. A study to find epistatic pairs of antibiotic resistance genes was undertaken.
Many antibiotic resistance genes influence each other, forming epistatic pairs. A study to find epistatic pairs of antibiotic resistance genes was undertaken.
- A new approach was used that simplified the search for this type of genes;
- 38 loci and 240 epistatic pairs of antibiotic resistance genes were found in Neisseria gonorrhoeae as a result;
The new study opens up a way to understand antibiotic resistant better and establish new studies aimed at finding epistatic relationships in the course of genome-wide studies.
![]()
9. Archaea and bacteria work together to destroy waste
 A new player in the process of nitrogen removal from wastewater was discovered.
A new player in the process of nitrogen removal from wastewater was discovered.
- It was found that ammonia-oxidizing archaea can remove nitrogen from waste along with bacteria;
- Archaea can work under different environmental conditions, including low temperatures and low oxygen environment;
- The interactions and activity of this group of microorganisms is not sufficiently studied at the moment;
Archaea could replace bacteria at wastewater plants when scientists would know more about them.
![]()
10. Soil microorganisms can withstand drought
 A study to evaluate the changes in soil microorganisms and fungi after a prolonged drought was undertaken.
A study to evaluate the changes in soil microorganisms and fungi after a prolonged drought was undertaken.
- Microbial communities in areas with minimal tillage were compared to the ones with conventional tillage systems;
- Areas with minimal tillage were characterized by higher diversity of microorganisms, fungi, and prokaryotes;
- Communities in both areas were severely affected by drought;
- Both communities were restored after drought has ended, regardless of the tillage system.
These findings could be used to recommending proper measures in agriculture.
![]()
11. Scientists Discover 1000+ Chlorophyll-Containing Bacteria
 Genomics studies have revealed the presence of chlorophototrophic bacteria in multiple genera.
Genomics studies have revealed the presence of chlorophototrophic bacteria in multiple genera.
- There are currently seven bacterial phyla that are known for chlorophyll-based phototrophy;
- In the course of the last 20 years, around 1,100 chlorophototrophic species were found with the help of genome sequencing;
- Scientists estimate that unknown species that produce chlorophyll and other photo chemicals can still be discovered in the future;
Genomic studies not only have helped us understand photosynthesis better; they also helped in understanding symbiosis and the roles of photosynthetic bacteria in ecosystems.
![]()
12. Next-generation sequencing against corrosion in the oil industry
 Efficacy of detection of H2S producing bacteria on North Sea oil stations with the help of next-generation sequencing was evaluated in two separate studies.
Efficacy of detection of H2S producing bacteria on North Sea oil stations with the help of next-generation sequencing was evaluated in two separate studies.
- H2S – producing bacteria pose a significant danger to oil stations, as they cause metal corrosion;
- Both quantitative polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing were used for bacteria identification and localization;
- Both methods helped in identification of machine parts and fluids that contained the highest concentration of corrosion-inducing bacteria.
Based on these discoveries, sequencing of bacterial species genomes can also have application in industry.
![]()
13. Bacteria can assist in counteracting climate change
 Bacteria participate in the cycles that involve greenhouse gases, such as CH4 and N2O.
Bacteria participate in the cycles that involve greenhouse gases, such as CH4 and N2O.
- CH4 and N2O are the major greenhouse gases produced through agriculture;
- Both gases are regulated by the activity of methanotrophs and nitrogen-fixing bacteria;
- Genetic manipulation of these species, as well as certain agricultural practices, could increase methane uptake and nitrous oxide reduction.
![]()
14. The secret of aquaponics lies with microbes
 Aquaponics involves cultivation of plants together with fish in the water. It was found that aquaponics success dramatically depends on microbe-plant interactions.
Aquaponics involves cultivation of plants together with fish in the water. It was found that aquaponics success dramatically depends on microbe-plant interactions.
- Mycorrhizal fungi and Rhizobia bacteria are crucial for root health in plants grown in water-based systems;
- Microfungi may consume bacteria necessary for normal plant growth in such environments;
- Bacteria may compete with plants for iron and other microelements;
In conclusion, bacteria and plants interact in complex ways even in soil-free conditions. Aquaponics systems cannot succeed without considering this fact.
![]()
15. Fighting mercury contamination with bacteria
 A search for mercury resistant bacteria that can be used in bioremediation was undertaken.
A search for mercury resistant bacteria that can be used in bioremediation was undertaken.
- 28 mercury resistant strains were isolated from polluted metal sites;
- Two isolates among them were able both to resist mercury and remove it;
- The strains belonged to P. aeruginosa and B. licheniformis;
- Both strains worked best at pH 6 and temperature of 35°C.
The discovered strains can be used for successful bioremediation of the areas polluted with mercury.
![]()
Bacteria and viruses influence all areas of our life, from causing diseases to contributing to climate change. In order to move forward, we need to understand our miniscule companions better!
![]()






















