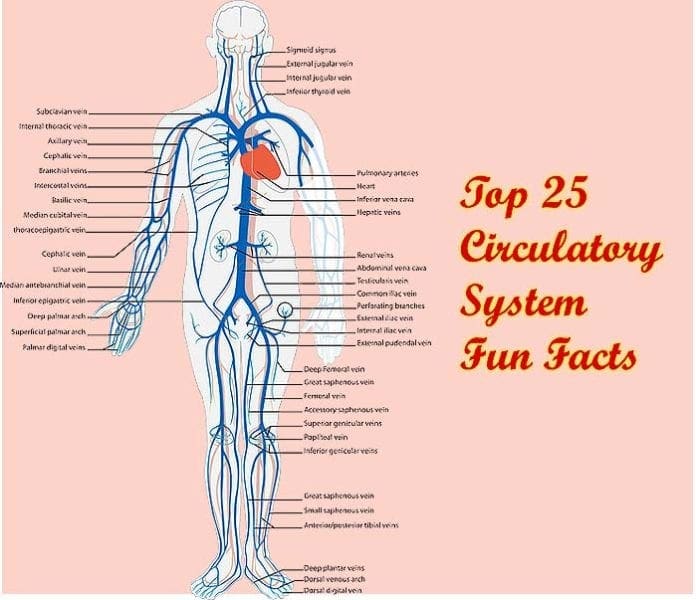
Circulatory System Fun Facts: The heart is the central functional unit of the human body, without which all other organ systems fail to function. The pumping action of the fist-sized heart helps transport oxygen dissolved in the blood to every tissue and organ system of the body.
So, it would be appropriate to say that the heart is the only organ that works tirelessly to ensure the proper functioning of the human body. The heart is at the center of the circulatory system, comprising blood, blood vessels, lymph, and lymphatic vessels. Its primary function is transporting oxygen-carrying blood toward the other tissues and organs and bringing deoxygenated blood back from the tissues and organs toward the heart.
This cycle of events keeps the human body functioning. Individually, the cardiovascular or circulatory system also plays a vital role in the development and governance of the Immune system which is responsible for fighting infections and establishing defense mechanisms of the human body.
Table of Contents
- Top 25 Circulatory System Fun Facts
- 1. Circulatory System Length is about 100,000 kms
- 2. The RBCs are 8 Microns Size.
- 3. Larger Mammals = Slow Heart Rate
- 4. The Heart can beat around 3 to 5 mins outside the body
- 5. RBCs Have No Nuclei
- 6. Blood Comes in Varying Shades of Red
- 7. Total Heartbeat count is about 2.5 Billion Times
- 8. Resting Heart rate can detect heart diseases
- 9. The Heart pumps 2,000 Gallons of Blood/Day
- 10. Two Circulatory Systems
- 11. The Cornea has Zero Blood Vessels
- 12. 8 Million Blood Cells Die/Born Every second
- 13. Blood Travels in Both Arteries and Veins.
- 14. Brain’s First Line of Defense = Blood Vessels
- 15. Weather controls Blood Vessels
- 16. Brain Freeze is Caused by Blood Vessels
- 17. Chocolate Reduces the Risk of Heart Diseases
- 18. Obesity Affects Blood Vessels’ Health
- 19. Cardiac Conduction System Functions the Heart
- 20. Heart and Blood Vessels Begin to Develop from Embryonic Stage
- 21. Laughing Reduces the Risk of Heart Disease
- 22. Sympathetic Nervous system Innervates Blood Vessels
- 23. Blood Vessels are Made of 1 Muscle Cell Type Only
- 24. 2 Types of Arteries
- 25. Venules are Mediators Between Capillaries & Veins
Top 25 Circulatory System Fun Facts
The following are the top 25 circulatory system fun facts:
1. Circulatory System Length is about 100,000 kms
 The circulatory system has a length equivalent to 100,000 kms.
The circulatory system has a length equivalent to 100,000 kms.
- The circulatory system comprises blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries running throughout the length of the human body.
- If laid end to end, the entire circulatory system could run a span of about 60,000 miles.
- Most of this length would be comprised of the tiniest blood vessels that link arteries and veins, called the capillaries.
![]()
2. The RBCs are 8 Microns Size.
 The RBCs move in a single file, one after the other, in capillaries.
The RBCs move in a single file, one after the other, in capillaries.
- The RBCs are small in size, and the diameter of the capillaries is even smaller, measuring about 8 microns.
- To move through the capillaries, the RBCs have to squeeze themselves and move in a single file, one after the other.
- The RBCs also change shape when moving through capillaries. A calcium-mediated signaling pathway is thought to be causing this distortion in shape.
![]()
3. Larger Mammals = Slow Heart Rate
 Higher body mass or size is related to slower heart rate.
Higher body mass or size is related to slower heart rate.
- Throughout the animal kingdom and mammals, in particular, body size is inversely proportional to the heart rate of the organism.
- Young children have a heartbeat higher than that of adults. This changes as they grow over time.
- Larger animals also have larger hearts to transport blood to every body part.
![]()
4. The Heart can beat around 3 to 5 mins outside the body
 The heart can beat outside the body for a short period.
The heart can beat outside the body for a short period.
- Technically, the heart creates its electrical signals and impulses, which cause it to beat.
- Due to this feature, if separated from the body, it continues to beat for a short period.
- Usually, a heart can beat for around 3-5 minutes outside the body, until it runs out of energy. However, in a medical facility, it can probably survive up to 4 hours.
![]()
5. RBCs Have No Nuclei
 Red Blood cells do not contain nuclei.
Red Blood cells do not contain nuclei.
- The red blood cells are primarily oxygen-carrying cells, which impart a red color to the blood due to the presence of heme.
- Red blood cells are devoid of any nucleus, and therefore, do not have any genetic material.
- The absence of nuclei ensures that the red blood cells can carry oxygen molecules to the best of their ability by providing enough space for the heme-oxygen moiety.
![]()
6. Blood Comes in Varying Shades of Red
 Blood flowing through the body is found in varying shades of red.
Blood flowing through the body is found in varying shades of red.
- Blood flowing towards the cells from the heart is rich in oxygen and is called oxygenated blood. This blood is bright red.
- Blood that flows towards the heart, from the tissues, contains carbon dioxide (CO2) and is called de-oxygenated blood. The deoxygenated blood is darker in color than the oxygenated blood.
- This behavior differs from other species, such as mollusks and arthropods, where the color of oxygenated blood is blue.
![]()
7. Total Heartbeat count is about 2.5 Billion Times
 On an average, the heart beats around 2.5 billion times in a person’s lifetime.
On an average, the heart beats around 2.5 billion times in a person’s lifetime.
- The heart is an organ that never tires and beats continuously to supply blood and oxygen to every part of the human body.
- The heartbeat of an average human being would be around 70-78 beats per minute. Although, this would differ during rest and exercise.
![]()
8. Resting Heart rate can detect heart diseases
 The resting heart rate can predict heart disease risk in women.
The resting heart rate can predict heart disease risk in women.
- Heartbeat measured at rest is also known as the resting heart rate, and it is typically found to be between 50 and 100 bpm.
- However, a lower resting heart rate indicates efficient cardiovascular function and is associated with good heart function.
- A resting heart rate higher than 76 beats per minute, especially in women, is associated with an increased likelihood of heart disease.
![]()
9. The Heart pumps 2,000 Gallons of Blood/Day
 The heart pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood in a day.
The heart pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood in a day.
- Every minute, the heart pumps around five quarts of blood throughout the body.
- On average, blood takes around 20 seconds to circulate through the entire vascular system in the resting state.
- In a day, blood travels approximately an equivalent of 12,000 miles throughout the human body.
![]()
10. Two Circulatory Systems
 The human body has two circulatory systems.
The human body has two circulatory systems.
- The human body has two interconnected circulatory systems: the systemic and the pulmonary.
- The systemic circulatory system takes oxygen-carrying blood from the heart toward the tissues and organ systems.
- The pulmonary circulatory system carries oxygen from the external environment and enters the blood through the lungs. At the same time, the blood carrying carbon dioxide generated from the tissues is released out into the external environment.
![]()
11. The Cornea has Zero Blood Vessels
 The cornea is the only tissue in the body that does not have blood vessels.
The cornea is the only tissue in the body that does not have blood vessels.
- The cornea in the eye does not receive any blood supply and thus does not receive any protection from the immune cells in the blood.
- The cornea receives its nourishment through the tears and the aqueous humor.
- One of the reasons for this exception is that the cornea best functions in its transparent state. Abnormal blood vessel growth or any injury that clouds the cornea’s surface can lead to vision impairment.
![]()
12. 8 Million Blood Cells Die/Born Every second
 Eight million blood cells die every second in the human body and about the same are born as well.
Eight million blood cells die every second in the human body and about the same are born as well.
- The red blood cells are formed from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. They live for about 4 months and are finally destroyed in the spleen.
- In a tiny drop of blood, about 5 million blood cells exist.
- Each blood cell takes about 20 seconds to travel throughout the body and usually takes about 200,000 trips in its entire lifespan.
![]()
13. Blood Travels in Both Arteries and Veins.
 Blood travels in both arteries and veins in the body, depending on where it is originating from.
Blood travels in both arteries and veins in the body, depending on where it is originating from.
- Oxygen-carrying blood traveling from the left side of the heart is carried in arteries towards the tissues and organ systems.
- De-oxygenated blood traveling from the tissues towards the right side of the heart that eventually reaches the lungs travels through the Veins.
- Capillaries are tiny blood vessels found on the ends of arteries and veins that help the blood to move into or out of the larger blood vessels.
![]()
14. Brain’s First Line of Defense = Blood Vessels
 Blood vessels act as a first line of defense for the brain.
Blood vessels act as a first line of defense for the brain.
- A network of blood vessels works together to keep harmful substances out of the brain.
- They act as a defense system known as the blood-brain barrier.
- The blood-brain barrier allows water and other molecules to pass through, filtering out microbes and pathogens and preventing them from entering the brain.
![]()
15. Weather controls Blood Vessels
 The weather affects the blood vessels.
The weather affects the blood vessels.
- The circulatory system is responsible for maintaining normal body temperature.
- In warmer weather conditions, the blood vessels expand to help release and dissipate heat from the body to cool it down.
- In colder weather conditions, the blood vessels constrict to prevent the release of heat from the body to keep it warm.
![]()
16. Brain Freeze is Caused by Blood Vessels
 Brain freeze is caused by the temperature control function of the blood vessels.
Brain freeze is caused by the temperature control function of the blood vessels.
- When a cold object such as a popsicle or ice cream touches the roof of the mouth, the blood vessels rapidly constrict, trying to minimize heat loss.
- Following this, they relax to restore the blood flow to the roof of the mouth.
- The swift response causes a short burst of pain that lingers for a few minutes. They are also called ice-cream headaches or brain freeze and are also commonly found in people with migraines.
![]()
17. Chocolate Reduces the Risk of Heart Diseases
 Eating chocolate helps in reducing the risk of heart disease.
Eating chocolate helps in reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Eating chocolates in moderation could be beneficial in preserving the health of blood vessels and the overall cardiovascular system.
- Dark chocolate contains flavonoids rich in antioxidants that help fight heart disease.
- It leads to a lower risk of heart disease and stroke.
![]()
18. Obesity Affects Blood Vessels’ Health
 Obesity leads to the risk of heart disease by affecting the health of the blood vessels.
Obesity leads to the risk of heart disease by affecting the health of the blood vessels.
- Increased weight over the normal range can affect the health of the blood vessels.
- The added pressure on the blood vessels increases the burden on the heart to pump blood.
- It increases the risk of blockages inside blood vessels.
![]()
19. Cardiac Conduction System Functions the Heart
 The heart is powered by an electric system called the cardiac conduction system.
The heart is powered by an electric system called the cardiac conduction system.
- A cardiac conduction system is a specialized group of muscle cells in the heart’s wall that produce electrical signals.
- These electrical signals are responsible for creating the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart.
- The cardiac conduction system consists of the SA node, AV node, Purkinje Fibers, a bundle of His, and bundle branches.
![]()
20. Heart and Blood Vessels Begin to Develop from Embryonic Stage
 The development of the heart and the blood vessels begins in the embryonic stage.
The development of the heart and the blood vessels begins in the embryonic stage.
- Blood vessels generate from the mesodermal embryonic layer.
- The heart and blood vessels develop in the third week of gestation.
- The circulatory system starts functioning from the 8th week of life.
![]()
21. Laughing Reduces the Risk of Heart Disease
 Laughing helps to keep the heart healthy and reduces the risk of heart disease.
Laughing helps to keep the heart healthy and reduces the risk of heart disease.
- Laughter helps boost the immune system’s function and reduce stress by increasing blood circulation.
- By triggering the release of a substance known as endorphins into the bloodstream, it helps to relax the body and boost energy levels.
- It is beneficial overall for cardiovascular health and helps lower blood pressure.
![]()
22. Sympathetic Nervous system Innervates Blood Vessels
 The sympathetic nervous system innervates the blood vessels.
The sympathetic nervous system innervates the blood vessels.
- The Inner musculature of the blood vessels contains nervous receptors such as alpha-1, alpha-2, etc.
- The receptors present inside the blood vessels help transmit information regarding oxygen content and blood pressure.
- This information is then sent to the brain, which controls the dilation and constriction of the blood vessels.
![]()
23. Blood Vessels are Made of 1 Muscle Cell Type Only
 Blood vessels are made up of only one type of muscle cells.
Blood vessels are made up of only one type of muscle cells.
- The inner walls of the blood vessels contain only smooth muscle cells.
- The smooth muscles are found along with the connective tissue and the elastic fibers, bundled inside a region known as the tunica media.
- The skeletal muscles that aid movement also help move the blood from the periphery toward the heart.
![]()
24. 2 Types of Arteries
 There are two major types of arteries present in the cardiovascular system.
There are two major types of arteries present in the cardiovascular system.
- Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the heart toward the tissues and organs. They function under high pressure and, for this reason, contain high amounts of elastic fibers.
- There are two types of arteries present in the circulatory system: Elastic and Muscular.
- Muscular arteries contain more smooth muscle in their tunica media, whereas elastic arteries contain more elastic fibers in their tunica media. Elastic arteries are found closer to the heart and help maintain a constant pressure gradient.
![]()
25. Venules are Mediators Between Capillaries & Veins
 Venules are tiny vessels that connect capillaries to larger veins.
Venules are tiny vessels that connect capillaries to larger veins.
- Venules are thin-walled vessels that receive deoxygenated blood from the capillaries.
- Tiny sphincters at the end of capillaries help push blood into the venules.
- Venules open into larger veins that eventually carry blood toward the heart.
![]()
The circulatory system, comprising the heart and blood vessels that innervate the human body, is vital for any other organ system to function fully. It provides oxygen and nourishment to tissues and organs, thus keeping them alive and functional.
The functions of the circulatory system overlap with that of the respiratory system, which helps supply oxygen inhaled by the lungs, and give out carbon dioxide gathered as a by-product from tissues and organs, that is finally removed from the body through the process of exhalation.
The pumping action of the heart ensures that blood reaches every other organ system. Damage to blood vessels, cardiac muscle, or the heart’s function due to lifestyle or diet can increase the risk of heart disease.
![]()