Cell Biology News in 2017: Cell biology is the branch of biology that studies the cell structure, its organization of the organelles, their metabolic processes, their physiological properties, signaling pathways, life cycle, and interactions with their environment.
In the field of cell biology, there are several technological advancements and innovations every year.
In this article, we will focus on top 12 cell biology news, breakthroughs and research studies in 2017.
Table of Contents
- Top 12 Cell Biology News in 2017
- Recreation of Mammalian Tissues By Developmental Biology Study
- German Researchers Find Selenium’s Role in Enzyme GPX
- Study Confirms CTL-1 Protein’s Role in Choline Transport
- Cure For Genetic Deafness Using Genome Editing Agent
- DNA Origami Inside Living Cells For Optimal Drug Delivery
- Discovery of Dicer Protein in Fruit Fly To Kill Viruses
- Keeping VEGF Levels In Check Prevents Blindness
- Discovery of Kidney Stones via Calcium Ion Channel – TRPV5
- Scripps Institute Explains The Structure of Piezo1 Protein
- Avoidance of Cell Death in Diabetes by Cellular Reprogramming
- Better E-coli Antibiotics From A New Research
- Study Explains “Force Detection” Process At The Cellular Level
Top 12 Cell Biology News in 2017
Recreation of Mammalian Tissues By Developmental Biology Study
Recent studies in developmental biology revealed that complex folded shapes that eventually become mammalian tissues could be recreated. This technique involves creating patterns of human or mouse cells on extracellular fiber layers. The cells then fold into different shapes that can eventually give rise to tissues.
![]()
German Researchers Find Selenium’s Role in Enzyme GPX
Researchers in Germany elucidated the central role Selenium plays in mammalian development. Selenium forms a part of the enzyme GPX as selenocysteine. This enzyme protects interneurons in the brain.
![]()
Study Confirms CTL-1 Protein’s Role in Choline Transport
A recent study published in the PLOS journal revealed the role of a protein called CTL-1 involved in choline transport. This protein was found to be a major contributor in cellular processes such as vesicle trafficking, ion homeostasis, and the development and growth of plants.
![]()
Cure For Genetic Deafness Using Genome Editing Agent
Scientists at the Howard Hughes medical institute discovered that genetic deafness in mice could be cured by treatment with a genome editing agent. This technology could one day be used to cure certain variant forms of deafness in humans. See the autosomal recessive inheritance page for more details.
![]()
DNA Origami Inside Living Cells For Optimal Drug Delivery

Researchers at the Arizona State University succeeded in creating a single long strand of DNA or RNA that can self-fold to form large complex structures. This technique, known as DNA origami can be carried out inside living cells and used for drug delivery at the nanoscale.
![]()
Discovery of Dicer Protein in Fruit Fly To Kill Viruses

A recent study carried out at the University of Utah revealed a tiny cellular machine that is capable of killing viruses. A protein found in the fruit fly, called Dicer, is found to have anti-viral properties. As the virus releases its DNA into the target cell, the Dicer protein catches hold of this DNA and chops it off, thus eliminating the viral particle and preventing infection.
![]()
Keeping VEGF Levels In Check Prevents Blindness
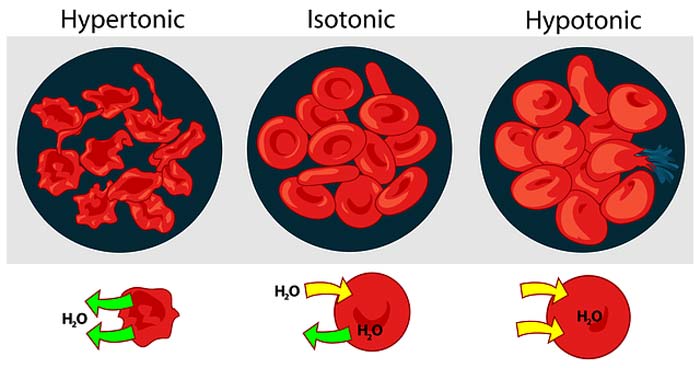
John Hopkins researchers identified a cell signaling pathway involved in diabetic retinopathy. A growth factor known as VEGF was found at high levels in the retina, which attracts white blood cells and clogs the blood vessels, reducing blood flow, leading to blindness. Reducing VEGF levels may restore blood flow to the retina thus preventing blindness.
![]()
Discovery of Kidney Stones via Calcium Ion Channel – TRPV5
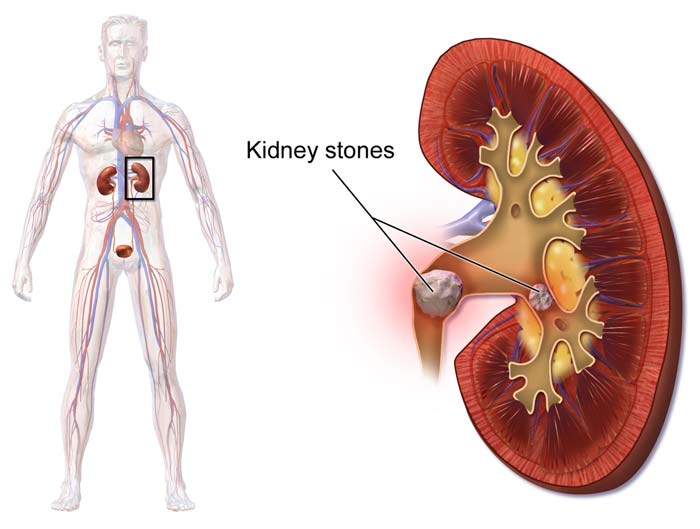
A study published in Nature Structural and molecular biology elucidated the structure of a calcium ion channel called TRPV5 found in the kidney cell membrane. Inhibitors bind to the calcium channel thereby inactivating it. This cause calcium to remain in the kidney and form kidney stones.
![]()
Scripps Institute Explains The Structure of Piezo1 Protein

Scripps Institute researchers succeeded in elucidating the structure of a protein called Piezo1. This protein is responsible for converting physical stimuli such as touch into chemical signals. The results from this study can be used to find a cure for diseases that are caused by a dysfunctional or mutated Peizo1 protein.
![]()
Avoidance of Cell Death in Diabetes by Cellular Reprogramming
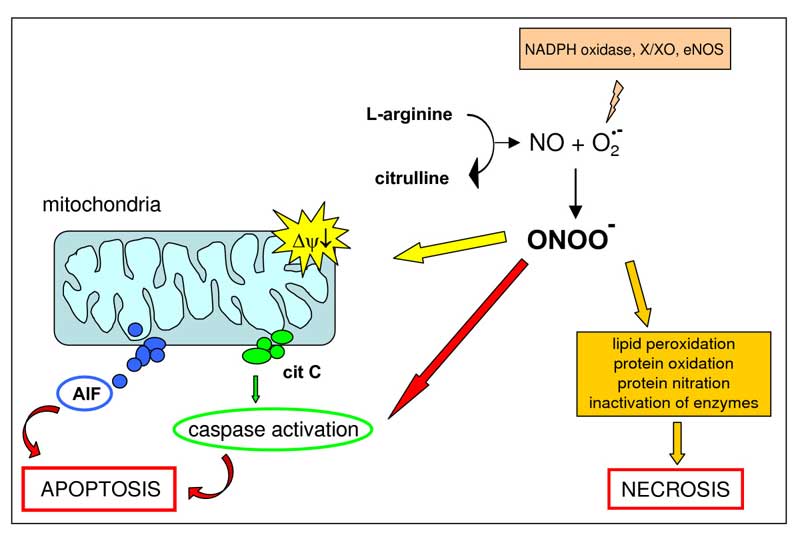
A recent study published in ‘Cell Reports’ demonstrated how cells function and adapt to stress factors. By re-programming their internal cellular networks and signaling pathways, they avoid cell death under stressful conditions such as water loss. The results from this study can be used to design therapeutics to prevent cell death in diseases such as diabetes.
![]()
Better E-coli Antibiotics From A New Research
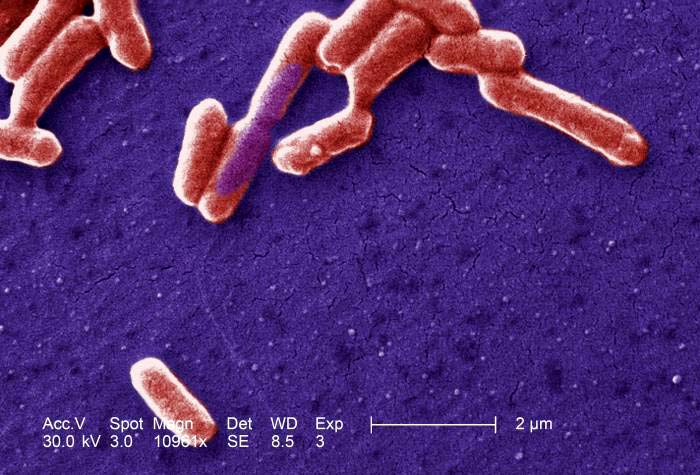
Scientists at the OIST graduate University have further understood the process of cell division in E.coli. This type of bacteria can cause a host of different illnesses like pneumonia and diarrhea. The findings from this study can help gain new insights into the design of antibiotics for these diseases.
![]()
Study Explains “Force Detection” Process At The Cellular Level
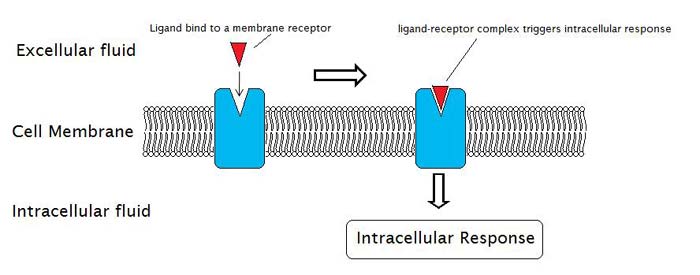
A recent study published in nature described how a cell senses its environment and position of molecules in its environment. The process is called force detection, and it occurs when ligands join together, cells apply a force according to the ligand’s position in the environment, and this allows the cell to detect its surroundings.
![]()






















