
Top Anatomy News in 2018: We think that we know everything about the human body. We know where everything is located and all the theory about how our organs work. However, do we really? The advances in clinical medicine show us that our bodies still hold many secrets.
Table of Contents
- Top Anatomy News in 2018
- 1. Restoring sight for the blind
- 2. Growing animal body parts in Lab
- 3. Minimally invasive heart surgery
- 4. Intestine on a chip: a novel way to study our digestive system
- 5. A new approach to monitoring bone healing (Smartbone)
- 6. Computer nerves: Dueling Neural Networks
- 7. A new system for respiratory monitoring
- 8. AR comes to the OR: new techniques to help the surgeons.
- 9. The complex emotions of a new face: face transplants
- 10. An injectable agent for the optical nerve cells regeneration
- 11. Brain Signals to Audible Speech
- 12. Getting the grip: hand surgery for tetraplegic patients.
- 13. A novel nanoparticle to assist in cancer surgery
- 14. An RNA map of the intestine
- 15. NCPAP: A safe way to treat infants in respiratory distress
- 16. A new approach for evaluation of preterm infants’ prognosis
- 17. Different types of nerve cells can produce misfolded proteins
- 18. Growing the brain in 3D
- 19. The wonder wall that protects the brain: blood-brain barrier
- 20. Viruses for the nerve cells treatment
- 21. Taste is created by the brain
- 22. The novel way to study the central nervous system
- 23. Eye of the truth: how irises can detect health problems
- 24.Understanding chronic pain for prevention and better treatment
- 25. Hidden camera in the intestine
- 26. Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine for 2018
Top Anatomy News in 2018
Here are the top 26 discoveries and breakthroughs in anatomy for 2018 (not listed in any particular order). Let us begin.
1. Restoring sight for the blind
 Until now, rapidly developing blindness left the patients without any no options.
Until now, rapidly developing blindness left the patients without any no options.
- Once even surgery could not help – there was only darkness. However, recently it was established that unique azonobenzene compounds could activate the nerve cells in the eyes of the completely blind mice and make them transmit impulses in response to the light.
- These compounds act as photoswitches and are chemical prostheses for the blind. They can potentially be used in humans too.
![]()
2. Growing animal body parts in Lab
 A steak grown in a lab is not a prop from science-fiction anymore.
A steak grown in a lab is not a prop from science-fiction anymore.
- The first attempts were made as early as 2013; in 2018 there are already several start-ups around the world developing better and cleaner methods of synthetic meat cultivation.
- Their founders are sure that once they overcome the problems with taste and safety, as well as debate appropriate policies with authorities, such meat can help overcome world hunger and partially counteract the greenhouse effect.
![]()
3. Minimally invasive heart surgery
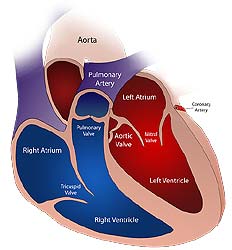 Sometimes an aneurysm forms right at the root of the aorta. In such patients, surgeons utilize a method called a David procedure.
Sometimes an aneurysm forms right at the root of the aorta. In such patients, surgeons utilize a method called a David procedure.
- They leave the aortic valve intact but replace the damaged area of the vessel. This procedure can be risky in elderly and weakened patients, but the risk can be reduced if the incision is smaller and less invasive.
- A new minimal invasion protocol for David procedure helps reduce blood loss, adverse effects, and mortality in cardiac patients.
![]()
4. Intestine on a chip: a novel way to study our digestive system
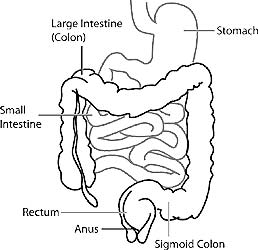 Our gastrointestinal system seems simple, but it is still a terra incognita for scientists.
Our gastrointestinal system seems simple, but it is still a terra incognita for scientists.
- It is possible to make cellular cultures of different types of cells that compose it, but such cultures do not explain how the cells that form the intestinal tract interact with each other in health and pathology.
- It is now possible to produce small, so-called organoid systems that include all the necessary tissues on a much smaller scale – say, the size of a chip. Such systems are more comfortable to study and allow observation of intestinal pathologies in 3D.
- It can ultimately lead to innovative and more effective treatments.
![]()
5. A new approach to monitoring bone healing (Smartbone)
 It is often hard to evaluate if the fractured bone heals properly.
It is often hard to evaluate if the fractured bone heals properly.
- The most commonly used tool is X-ray – but it can help only after the bone mineralizes.
- A new approach was successfully tested in mice with individual implants that are inserted into the site of the fracture.
- The implants emit signals that can be read with EIS microscopy, allowing real-time monitoring of the process of bone healing.
- This approach is much less invasive and can detect problems at early stages after the surgery.
![]()
6. Computer nerves: Dueling Neural Networks
 Computers have changed our methods in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Computers have changed our methods in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
- However, developments in neurophysiology and anatomy have in their turn led to the development of nerve-like computer algorithms that makes deep computer learning significantly more effective.
![]()
7. A new system for respiratory monitoring
 A new device called triboelectric nanogenerator or TENG helps in monitoring and registering the changes in breathing.
A new device called triboelectric nanogenerator or TENG helps in monitoring and registering the changes in breathing.
- With the help of a special thin film made of nanoparticles placed in an acrylic tube, the device transforms the air flow into electric signals that can be recorded.
- It also triggers an alarm in case of any critical change in breathing.
ACS Nano 2018 12 (6), 6156-6162. Accessed February 22, 2019. Link.
![]()
8. AR comes to the OR: new techniques to help the surgeons.
 Today, surgeons have even more instruments at their disposal than before.
Today, surgeons have even more instruments at their disposal than before.
- New approaches allow using new imaging techniques to help surgeons make better decisions during a surgery – for instance, new fluorescent dyes, special lighting and even augmented reality based on ultrasound probes.
- Such imaging techniques also lead to less invasive procedures – it is possible to have a smaller incision with all the supplementing images of the operating field from other sources.
![]()
9. The complex emotions of a new face: face transplants
 When a person gets a complete face transplant, many difficult problems lie ahead during rehabilitation.
When a person gets a complete face transplant, many difficult problems lie ahead during rehabilitation.
- One of them was somewhat overlooked before: expressions. When scientists compared the expressions of emotions between healthy subjects and the face transplant recipients, it was proven that the latter has problems with certain emotional expressions.
- As our ability to show emotion is essential for communication, this aspect of rehabilitation should be improved upon.
![]()
10. An injectable agent for the optical nerve cells regeneration
 Though we know now that some nerve cells can regenerate, it still does not happen often.
Though we know now that some nerve cells can regenerate, it still does not happen often.
- That is why it is better to prevent any damage beforehand. A new agent was tested in mice with damages to the optical nerve.
- The agent could be easily injected into the eye and helped both in regenerating retinal cells, as well as protecting them from further damage.
- This new agent has a promising future in the treatment of patients with eye diseases.
![]()
11. Brain Signals to Audible Speech
 A new technology was developed that transforms brain signals into speech. All the words we say are appearing first in our brains, in the form of electrical signals between the nerve cells.
A new technology was developed that transforms brain signals into speech. All the words we say are appearing first in our brains, in the form of electrical signals between the nerve cells.
- We have special structures that transform these signals into speech using other organs, such as vocal cords. However, brain strokes can deactivate natural middlemen.
- For these patients, a new neural decoder was presented in 2018. The devices do the same as brain structures – translates the neural electric signals into sounds.
- Moreover, it can be trained to produce intelligible, understandable speech. If this device is successful, many patients rendered mute by the disease can get their thoughts voiced at last.
![]()
12. Getting the grip: hand surgery for tetraplegic patients.
 It is now possible to undertake a reconstructive surgery that will allow patients suffering from paralysis of both upper and lower limbs to have use of their hands again.
It is now possible to undertake a reconstructive surgery that will allow patients suffering from paralysis of both upper and lower limbs to have use of their hands again.
- This surgery together prolonged rehabilitation can return the patient the ability to grasp objects and move their hands.
- A trial has also confirmed that this operation can be successful even if the patients suffer from severe pain before the surgery.
![]()
13. A novel nanoparticle to assist in cancer surgery
 Fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging are both excellent tools that allow to find different aspects of tumor structure.
Fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging are both excellent tools that allow to find different aspects of tumor structure.
- A group of researchers has successfully tested a nanoparticle that can combine both imaging methods due to the ability to change its form in response to a certain light trigger.
- This new agent can be used both before and during cancer surgery – this way the oncologist can ensure how the tumor looks and also be sure it was removed safely.
![]()
14. An RNA map of the intestine
 Single-cell RNA and DNA sequencing have opened new horizons in studying various processes in the body.
Single-cell RNA and DNA sequencing have opened new horizons in studying various processes in the body.
- A group of scientists has utilized RNA sequencing in order to observe the processes taking place during the development of the intestinal tract in human embryos and adults.
- This approach allows led to the creation of a complex roadmap of multiple interactions that influence the development and differentiation of the intestine and its tissues.
![]()
15. NCPAP: A safe way to treat infants in respiratory distress
 Sometimes a newborn inhales meconium by accident during birth. Such accidents can lead to severe lung problems.
Sometimes a newborn inhales meconium by accident during birth. Such accidents can lead to severe lung problems.
- Usually, such infants are put on mechanical ventilation. However, there is proven a better alternative.
- Instead of ventilation, such babies can be prescribed NCPAP- a method when air bubbles under pressure are inhaled through the nose with the help of a mask.
- This method is often used for the treatment of obstructive apnea, but it helps in newborns as well.
- Babies that received NCPAP did not need mechanical ventilation as often, had lower sepsis risk and got better faster.
![]()
16. A new approach for evaluation of preterm infants’ prognosis
 In preterm infants with meager weight at birth, problems with breathing are the main risk.
In preterm infants with meager weight at birth, problems with breathing are the main risk.
- A new approach of evaluation of lung activity called FOT (Forced Oscillatory Technique) can help predict which babies would be most likely to be at such a risk.
- FOT can be quickly and painlessly applied in infants and help predict outcomes and therapy in such vulnerable patients.
![]()
17. Different types of nerve cells can produce misfolded proteins
 Some brain disorders are caused by the accumulation of a misfolded protein, α-synuclein.
Some brain disorders are caused by the accumulation of a misfolded protein, α-synuclein.
- The misfolded protein aggregates in the nerve cells, leading to pathology. Two types of misfolded α-synuclein were found: one causes milder disease with Lewy bodies (LBD), while others can lead to a more severe condition called multiple system atrophy (MSA).
- It was found that if misfolded α-synuclein is formed in oligodendrocytes, they are likely to “infect” the neighboring cells with the protein aggregates that cause the more severe condition, MSA.
- On the other hand, if the aggregates of the protein form in neurons, the “seeds” of protein they form are much less aggressive and lead to milder forms of brain degeneration.
![]()
18. Growing the brain in 3D
 With progress in establishing 3D cultures and reprogramming stem cells, it has become possible to grow small brain organoids.
With progress in establishing 3D cultures and reprogramming stem cells, it has become possible to grow small brain organoids.
- Unlike regular cultures, these are not only three-dimensional;
- They are also composed of different cell types and allow the researchers to observe events in brain development and cell-to-cell interactions.
![]()
19. The wonder wall that protects the brain: blood-brain barrier
 In the last decade, the barrier that prevents the passage of pathogens and complex molecules from the blood into the brain has been an object of extensive study.
In the last decade, the barrier that prevents the passage of pathogens and complex molecules from the blood into the brain has been an object of extensive study.
- It is now clear that this structure plays a crucial role in immunity and psychiatric disorders.
- Moreover, understanding the blood-brain barrier is crucial for successful brain diseases treatment.
- It is now a separate field of clinical research and has a series of journals explicitly dedicated to it.
![]()
20. Viruses for the nerve cells treatment
 Delivering medicines or gene therapy to the brain directly is a complex endeavor because of its complexity and the presence of the blood-brain barrier.
Delivering medicines or gene therapy to the brain directly is a complex endeavor because of its complexity and the presence of the blood-brain barrier.
- In the last year, particular viral vectors were developed based on the adeno-associated virus (AAV).
- The recombinant virus can carry various genes and as cargo and can be used to treat certain neuron types or all the cells in the body.
![]()
21. Taste is created by the brain
 When we eat, we perceive taste: some foods are bitter, some sweet, some acidic, and so on.
When we eat, we perceive taste: some foods are bitter, some sweet, some acidic, and so on.
- However, our real perceptions form not on the tongue, but in the brain that receives the information from the taste receptors.
- It was shown in mice that bitter and sweet perceptions of taste are determined in separate regions in the amygdala.
- It was even possible to manipulate the taste perceptions of the animals by interfering with these areas.
- This research is significant for understanding taste and eating behavior in humans as well.
![]()
22. The novel way to study the central nervous system
 Medical students spend much time in mortuaries, trying to understand the complexity of the human body.
Medical students spend much time in mortuaries, trying to understand the complexity of the human body.
- However, not all parts of human anatomy are equally easy to study. For instance, the central nervous system (CNS) in all its complexity is very hard to extract intact.
- As it takes time, it is often studied in separate parts. A novel dissection procedure was offered that can allow the teachers to extract the CNS as a whole, thus allowing the students to integrate their neuroanatomy knowledge.
![]()
23. Eye of the truth: how irises can detect health problems
 We know that the structure of the eye irises is highly individual.
We know that the structure of the eye irises is highly individual.
- That is why we use iris scans for identification in cases where a high level of security is crucial.
- However, irises can also change along with the changes in the human body and may reflect the pathologies present.
- Novel algorithms evaluating a various aspect of their structure can help in making a noninvasive health diagnosis.
![]()
24.Understanding chronic pain for prevention and better treatment
 Chronic pain is a problem faced by an increasing number of patients.
Chronic pain is a problem faced by an increasing number of patients.
- At present, researchers understand much better how and why acute pain becomes chronic and how to predict the likelihood of this transition in patients.
- It is also clear that new, non-opioid analgesics are crucial and necessary. In order to do that, the researchers study how pain is produced and subdued in nature, and it already leads to new therapeutic approaches.
![]()
25. Hidden camera in the intestine
 How to observe the changes in the body from the inside? Taking a look from the intestine is one of the solutions!
How to observe the changes in the body from the inside? Taking a look from the intestine is one of the solutions!
- Breakthroughs in material science and engineering can help in the development of small electric devices that can be ingested and used to observe the body as “insiders“.
- These devices can be used for testing the solutions in the GI tract, observing tissue changes, and even deliver target medicines.
![]()
26. Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine for 2018
James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo were the proud joint winners of Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine in 2018 for their discovery of cancer therapy by inhibition of negative immune regulation.
![]()
As you can see, there are multiple beautiful discoveries made in 2018. Which is your absolute favorite?
![]()






















