Are you intrigued by the vast, mysterious world beneath the ocean surface and want to explore it for a living? Marine biologists delve into these depths daily, exploring how life thrives in our planet’s aquatic ecosystems.
BioExplorer demystifies their crucial role from studying intriguing marine creatures and plants to preserving precious underwater habitats. Hold your breath as we dive deep into the incredible world of Marine biology!
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Marine biologists play a crucial role in understanding climate change impacts, conserving biodiversity, and managing resources responsibly.
- Marine biologists study diverse sea creatures, from plankton to whales, and explore specialized fields such as phycology, ichthyology, invertebrate zoology, marine mammalogy, fishery biology, and marine ecology.
- They use diverse methods of ocean exploration, including high-frequency radars, sea gliders, animal telemetry, buoy systems, submersibles, scuba diving, drones, and satellites.
- Marine biologists study water chemistry, marine interactions, ocean floor geology, and act as guardians of marine life by protecting endangered species and their habitats.
- They collect underwater samples, discover unknown aquatic species, oversee fish populations, track marine mammal migrations, and innovate underwater research tools.
- Collaborating with other scientists and stakeholders is essential for making greater discoveries and implementing effective conservation strategies.
- Becoming a marine biologist requires a degree in marine biology or related fields, practical experience through internships and fieldwork, and continuous learning about marine ecosystems and research techniques.
- Career opportunities for marine biologists are available in academia, research institutions, government agencies, aquariums, conservation organizations, and private sector roles related to marine life and ecosystems.
![]()
What is Marine Biology?

Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms[1] inhabiting the ocean and other saltwater environments. As part of the broader marine sciences, it investigates how these aquatic species interact with their ecosystems under varying conditions.
This field is critical in understanding climate change impacts[2], conserving biodiversity, and managing resources[3] responsibly. Marine biologists are integral to this science, tasked with exploring complex underwater systems and puzzling mysteries hidden beneath surface waves.
Suggested Reading:
Top 15 Famous Marine Biologists
Definition and importance of studying marine biology
Marine biology is about studying sea life. This includes creatures and plants in oceans, wetlands, and estuaries. Marine biologists dig deep to learn how the ocean impacts where organisms live.

They look at how marine life acts, lives, and plays with the environment. Their focus? All parts of sea life! It’s key for us to study this field. The reason is that we need to understand oceans’ processes and systems better.
Also, we can see clearly when human activity harms these areas.
![]()
Role of marine biologists in understanding marine ecosystems
Marine biologists do critical work. They shed light on the hidden world beneath the ocean’s surface. Their task is to study marine life and the way it acts. They eye everything from small fish to big whales.
Also, they keep an eye on plants that live underwater. Testing the water for chemicals is also a part of their job.
Their aim? To find out what lives in our oceans and how it reacts to change.
They spot shifts in where animals choose to go and live. Doing this helps us foresee changes that might happen because of human actions. Many marine biologists focus on new species, too! Unseen life forms can tell us much about how our saltwater ecosystems work.
These scientists are true friends of Earth’s watery places! With their work, we stand a better chance at keeping these habitats safe and full of life.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Best Marine Biology Colleges
What Do Marine Biologists Do?
Here are top 25 things that marine biologists on their day-to-day lives.
1. Studying Diverse Sea Creatures

Marine biologists dive into the ocean to learn about lots of sea life. They look at big animals like whales and small ones like plankton. But there is so much more.
Some marine biologists are keenly interested in special fish or coral types. Others like to find out about weird creatures that live deep down on the ocean floor. For example, George Brown Goode made a name for himself by collecting different fish species.
This work helps us understand how each creature fits into the big picture of life underwater.
2. Exploring the World of Plankton

Marine biologists dive deep to study the tiny world of plankton. These small water-dwelling creatures may seem simple, but they hold big secrets about our oceans. You can see many of them in places like the Barents Sea, where they come together in large groups called blooms.
Studying these blooms tells us more about our marine ecosystems’ health and movement. This shows that even the smallest life forms have a big role to play in our world under the waves!
3. Observing Majestic Whales

Not many sights match a whale breaching the ocean’s surface. Seeing this is part of a marine biologist’s work. Whales are big sea animals, reaching over 100 feet in size. Marine biologists spend time studying these large beings.
They watch how whales live and interact with each other. Some whales stay together in groups for long periods, showing social behaviors. These scientists want to understand why they do this.
What sound does a whale make? They sing complex songs that wow people who hear them! It is another area marine biologists study about whales.
Then there are questions about how these giant creatures see us humans. We still don’t know if whales see humans as only black and white or in color, too!
Suggested Reading:
What Do Killer Whales Eat?
4. Choosing Specialized Fields

Marine biologists dive into detailed areas of marine life. They pick a specialized field.
- They study one part of the ocean world.
- Some become experts in phycology, the study of seaweed and algae.
- Others might choose ichthyology and learn all about fish.
- The strange world of squids and octopuses pulls in some. They become experts in invertebrate zoology.
- Studying whales, Seals, and dolphins is called marine mammalogy.
- Fishery biology is another choice for them. It’s good if you want to help manage our fish stocks.
- There’s marine ecology for those who love to see how everything fits together.
- Special fields give these scientists powerful tools to help sea life.
- Each field allows them to explore how specific plants or animals live.
- These experts find new facts about sea creatures every day.
Suggested Reading:
What Do Dolphins Eat?
5. Diverse Methods of Ocean Exploration
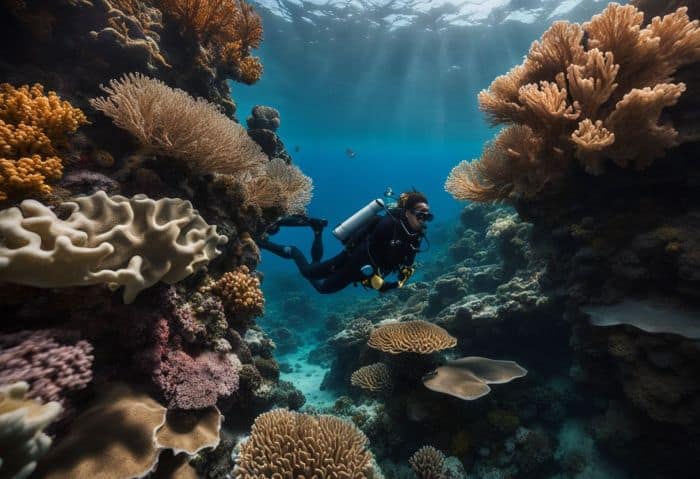

Marine biologists use many unique ways to study the underwater world. They explore oceans in a lot of ways.
- They use high-frequency radars[6]. This helps them map the ocean floor.
- Sea gliders glide through the water. They collect data about the ocean.
- Animal telemetry tracks marine animals. This tells us where the animals go and why.
- Marine biologists also deploy buoy systems at sea, collecting data about tides, currents, and weather changes.
- They even use submersibles. These are special vehicles that can dive very deep into the ocean.
- Some marine biologists like to get up close; they scuba dive to observe or collect marine samples.
- Others use drones or satellites for large-scale monitoring and mapping of marine environments.
Suggested Reading:
Explore 15 Remarkable Adaptations of Ocean Inhabitants
6. Deciphering Celestial Effects on Tides

Marine biologists find out why tides move. They look at the moon and stars to see how they pull on the seas. The pull of gravity from these bodies makes sea levels rise and fall. This is called a tide.
Even volcanoes can be tied to tides, scientists say! Marine biologists use what they learn from natural patterns to help them study sea life better.
Suggested Reading:
16 Immortal Animals Who Defy Death
7. Diving into Water Chemistry
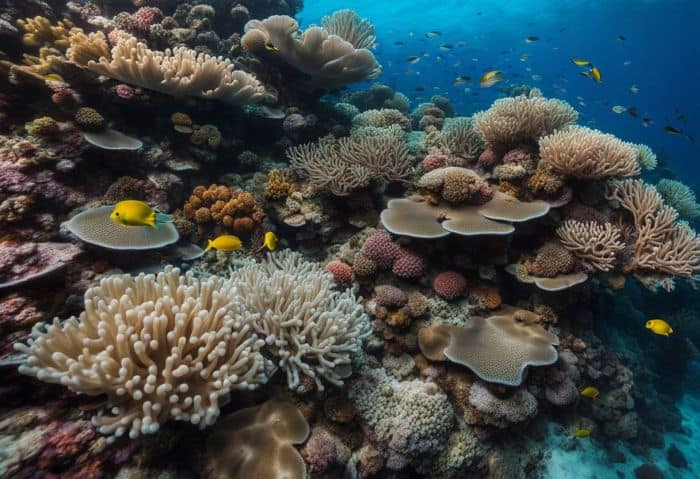

As a marine biologist, you dive deep into water chemistry. You study the mix of salt and other things in the ocean. This helps you know how sea plants and animals survive. Changes in water chemistry can hurt or help marine life forms.
With this knowledge, You devise ways to aid them when needed. Scuba diving lets you take samples from different ocean depths for testing. All of these tasks make your work day fun! Each dive brings new findings about the secret life under the waves.
Suggested Reading:
What Do Walruses Eat?
8. Understanding Marine Interactions
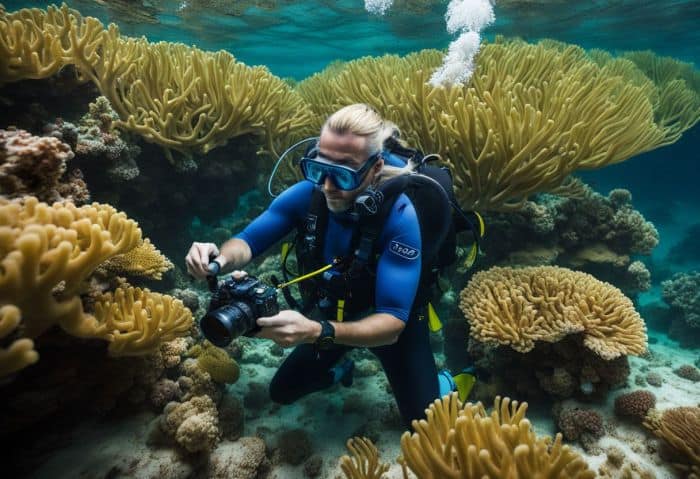

Marine biologists dive deep to figure out how sea life gets along. They examine all connections between water plants, fish, and marine animals. This part of marine biology is called biological oceanography.
Aristotle once studied the same things! He helped shape our view of interacting marine species. Marine biologists today still gather samples from the sea for study in labs, just like he did in ancient times.
This research helps them learn all about the underwater world and helps us understand it, too!
Suggested Reading:
How Long Do Jellyfish Live Or Are They Really Immortal?
9. Unearthing Ocean Floor Geology

Marine biologists dig deep into the ocean’s bedrock. They use special tools to uncover mysteries beneath the surface. This includes looking at sea bed rocks, soil, and sand layers.
It needs a lot of careful work! Studying what’s under the water tells us about times past. Unseen fossils or stones may tell tales from thousands of years ago! Many marine scientists give all their time to this study area.
More research helps us learn more about our planet’s history. Marine biologists aim to better understand how we can best protect our oceans now and in the future.
Suggested Reading:
The Domain Archaea: Finding Life’s Extremists
10. Guardians of Marine Life

Marine biologists act as guardians of marine life. They keep sea animals safe and help those in danger. Over 5, 000 new species were found by them in a hidden part of the Pacific Ocean.
Jobs may include saving water creatures that are close to being lost forever. The work they do guides plans to protect sea life and use ocean resources wisely. These scientists ensure our oceans are full of many different kinds of fish and other sea animals daily.
This is not just good for the ocean, but it helps people, too.
Suggested Reading:
What Do Manatees Eat?
11. Bird-Watching by the Shore

Bird-watching by the shore is a key task of a marine biologist. They spot, identify, and track birds near the sea. This helps them study how these birds interact with their environment.
This work tells marine biologists about changes in fish numbers or types. Why? When there are fewer or different fish, seabirds change their habits, too. It’s important to protect all parts of our ecosystems!
Suggested Reading:
Order Charadriiformes / Shorebirds
12. Studying Coastal Land Creatures

Marine biologists study animals that live on the coast, too. These land creatures often rely on food from the sea. They find food washed up on the shore or where water meets the land.
This work helps them understand more about marine life and how everything is linked in an ecosystem. Studying these coastal dwellers is a key part of conserving our oceans and keeping them healthy for every creature, big or small.
Suggested Reading:
What Do Turtles Eat?
13. A Day of Varied Marine Tasks
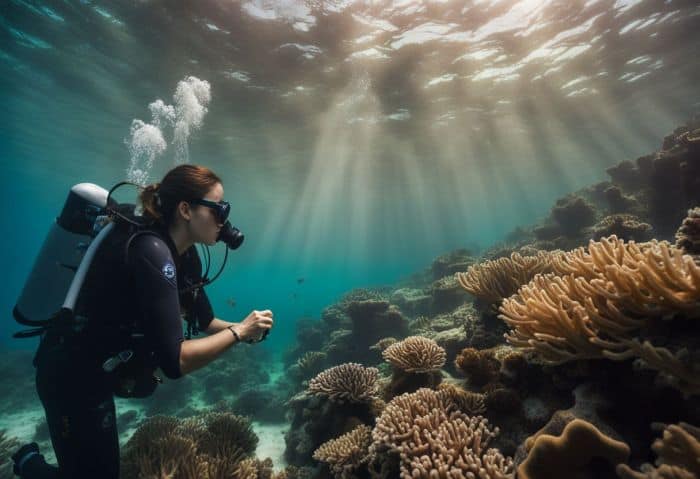

A normal day for a marine biologist is full of different tasks. The sun rises, and they dive deep into the sea. They gather samples from different plants and creatures. Before noon, they are on their ship, looking at data from the ocean floor.
After lunch, time in the lab starts with checking tests from past experiments. A quick chat about ideas or problems with team members follows next. They watch birds near the coast by evening, noting changes since last seen.
Once back home, they end their day by logging all findings and planning for tomorrow’s search for new marine species!
Suggested Reading:
Biology Boomtowns: 10 Best US Cities for Job Opportunities
14. Observing in Natural Habitats
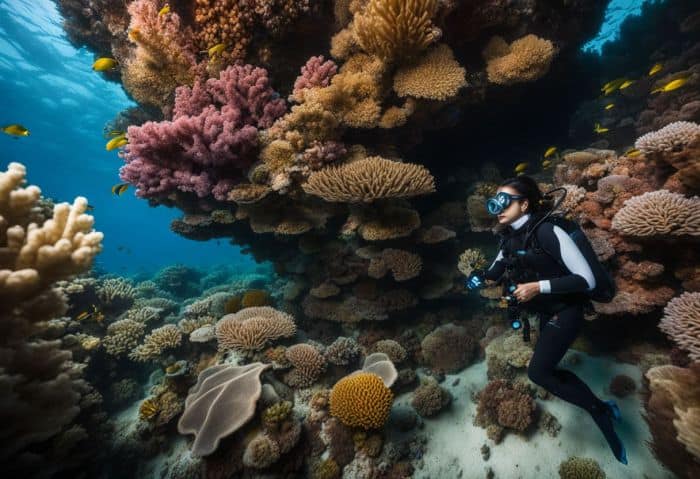

Marine biologists watch sea life in the places where they live. They look at how plants and animals interact with their home. This helps them know if the sea is healthy or sick. To get a close view, marine biologists dive underwater.
They use underwater cameras to take pictures of plants and animals in action. By looking closely, they learn new things about ocean life every day!
Suggested Reading:
What Do Starfish Eat?
15. Champions of Water Health
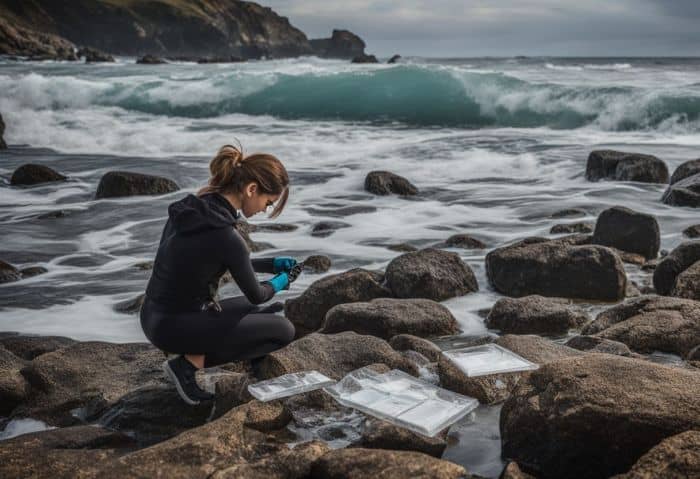

Marine biologists keep our water healthy. They test the water to find out how clean or dirty it is. Sea experts study harmful things in the ocean, like oil spills and waste. They figure out how these bad things hurt sea animals and plants.
Our oceans are home to so many creatures. Dirty water can make them sick or even kill them. Marine biologists guide others on ways to avoid polluting the ocean. Their work helps ensure safe homes for all sea life, now and in the future.
Suggested Reading:
Top 15 Current Environmental Issues in the US
16. Decoding Complex Water Systems
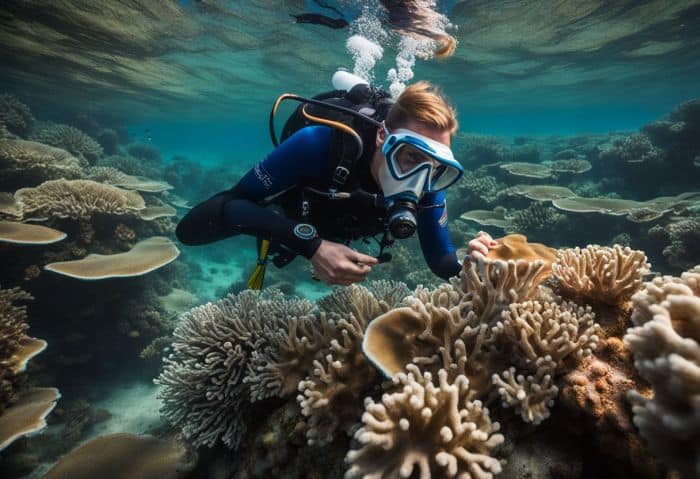

Marine biologists love to solve water puzzles. They look at how streams, rivers, and oceans behave. Complex water systems can be hard to understand. But these scientists use patterns in the water to tell them what’s going on.
Water isn’t just wet stuff you drink or swim in. It’s a world full of life and things we don’t know yet. Each drop holds clues about our planet and its health. Marine biologists read those clues like a storybook.
They decode complex water systems as part of their job every day!
Suggested Reading:
Top 15 Best Marine Biology Books
17. Sustainable Marine Ecosystem Advocates
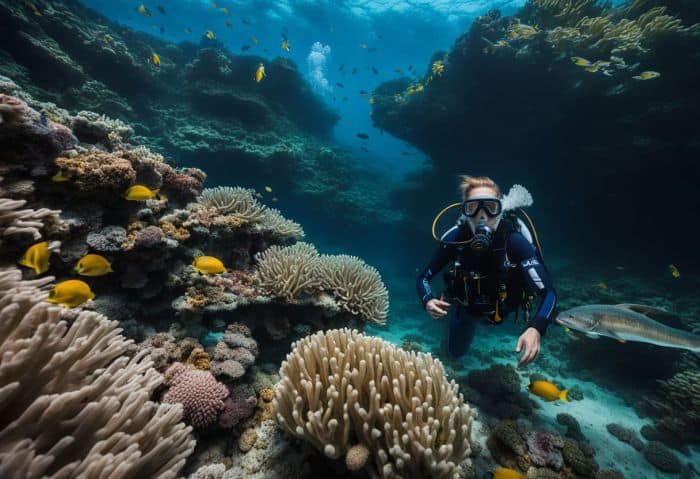

Marine biologists are loud voices for the sea. They fight for healthy oceans and seas. Jean Wiener, a man from Haiti, shows this well. He leads others to keep the ocean clean in his home country.
Like him, many marine biologists work hard to stop bad things like waste dumps and cruel fishing ways that hurt ocean life. They want recent rules to ensure sharks, dolphins, and other sea species do not die out or become lost forever.
The Earth is better off with our oceans safe and sound!
Suggested Reading:
Top 27 Biology-themed Movies
18. Highlighting Conservation Strategies
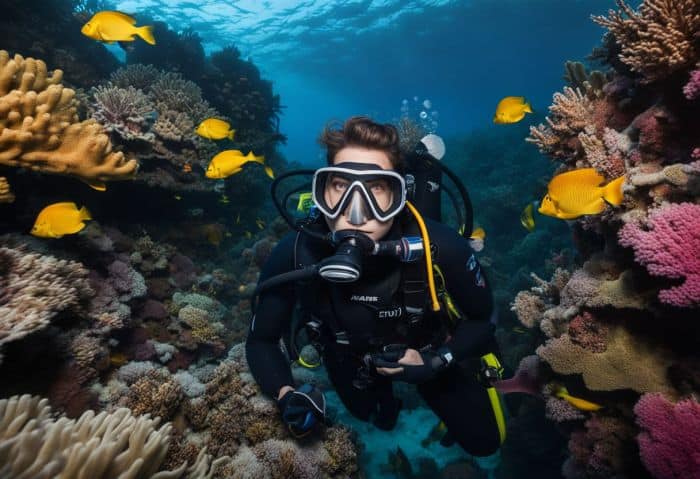

Marine biologists have many ways to help save our oceans. Here are a few:
- They learn about marine life. By studying the plants and animals in the sea, they can see what needs help the most.
- They look for issues. If a type of fish is nearly gone, or if some plants don’t grow anymore, they find out why.
- They use scientific facts when working on solutions. They make sure their plans will work in the real world.
- They help keep ocean places healthy, called “marine protected areas“. These are places where people do not harm sea life.
- They ensure fishermen catch fish in ways that won’t hurt other species.
- Often, they team up with others to plan for the best results. This could be other scientists, people who make rules, or those who live by the sea.
- Marine biologists also teach people how to protect ocean life. It’s an important part of their job, too.
- Tracking human impact on oceans assists conservation plans by understanding areas that need more protection from harmful activities.
- Sustainable practices like careful fishing helps keep all species safe and strong for future generations.
- Marine biologists strive for healthier oceans by making rules based on good scientific knowledge.
- Their research guides how to avoid wasting resources or unknowingly hurting sea life.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Discoveries in Ecology 2019
19. Adventures in Scuba Diving
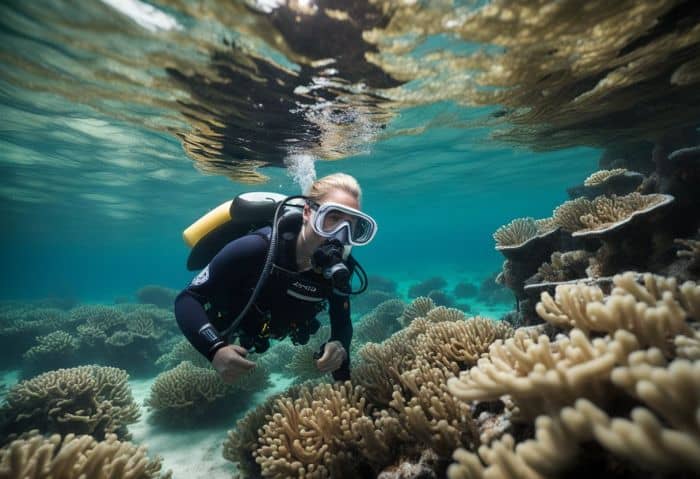

Scuba diving is a big part of a marine biologist’s job. They go deep into the ocean to see sea life up close. Doing this helps them learn more about what lives under the water.
Marine biologists also use scuba diving to collect samples from the ocean floor and take underwater photos. They may even get extra pay for their dive skills! Each dive can be different; it depends on the work they are doing at that time.
Suggested Reading:
Top 15 Evolutionary Biology News of 2021
20. Collecting Underwater Samples
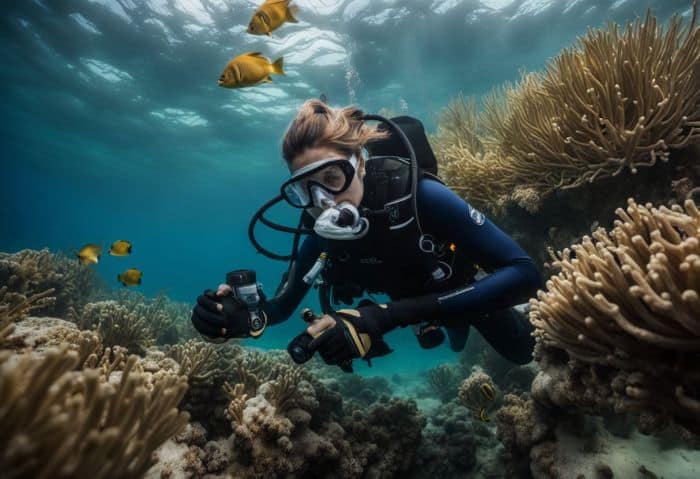

Marine biologists dive deep into the sea to get samples. They use these samples for many tests and studies. Diving can take place on reefs or from boats and ships. Sometimes, they pull a net through the water to gather things like little fish, crabs, or plants.
This is called trawling. Not everything happens in water, though! Once back on land, they study their findings and write reports about them. To do this right, marine biologists must be good at researching and analyzing facts.
21. Discovering Unknown Aquatic Species
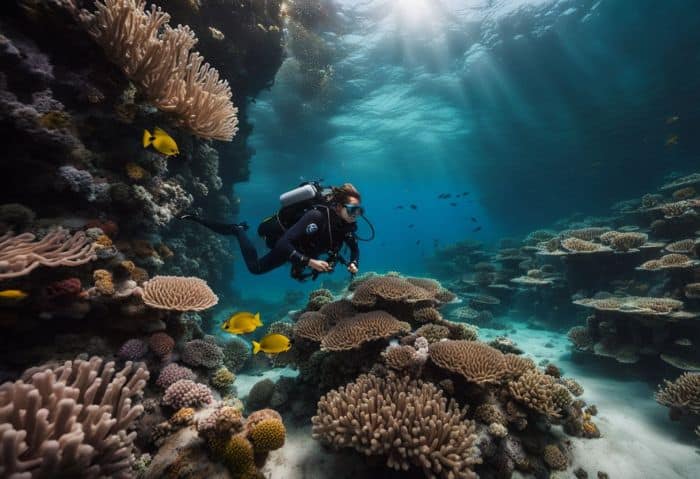

Marine biologists often find new sea life. They look deep in the ocean for these unknown creatures. These scientists act like detectives, using tools and tricks to help them search.
When they find a new species, they study it closely. This helps us know more about what lives in our world’s oceans. It is always an adventure! Each new finding brings joy and adds to our knowledge of marine science.
Suggested Reading:
What Do Salmons Eat?
22. Overseeing Fish Populations

Marine biologists have a big job. They watch over fish in the sea. This helps keep our oceans healthy and full of life. They count different types of fish and see how fast they grow, too.
All this data tells us if our marine ecosystems are well or not. Changes can be spotted early so action can be taken to protect the ecosystem. So, marine biologists don’t just study the ocean; they help save it!
23. Tracking Marine Mammal Migrations
Sea animals like whales, seals, and dolphins often move around in the sea. Marine biologists work to know where these animals go and why they travel. They use tools such as acoustic telemetry[7] to discover these silent voyages under the seawater.
When a marine animal swims in warm waters, its way of life changes too. It may start eating different food or have babies at a new time of year! This is worrying for some kinds because many are now less common than before.
Tracking their moves helps scientists make plans to keep them safe.
24. Innovating Underwater Research Tools

Marine biologists create new tools for underwater research. They use high-frequency radars to watch ocean currents. These help them understand the sea’s behavior on the coast. Autonomous underwater vehicles called SeaGliders gather data, too.
This includes information about water traits, currents, and marine creatures living beneath the waves. Sometimes, they stick electronic tags on sea animals to see where they go and what they do – this is known as animal telemetry! Buoy systems tell them many things about water, like how hot or cold it is, how much salt it has, and current motions in the deep sea.
Another tool used is clod cards! They are small tools stuck onto things underwater so marine organisms can be studied more closely.
25. Collaborating for Greater Discoveries

Teamwork is a big part of being a marine biologist. Working together can lead to bigger and better discoveries. Scientists may share ideas, tools, or areas they have studied before.
This sharing helps make new ideas in science come alive! One person might see something that another person missed. Big problems need many brains to solve them. The ocean holds much life that we still don’t know about yet.
More people working on the same task means more chances to find new things under the sea daily!
Suggested Reading:
25 Mind-Blowing Biology Breakthroughs That Shaped Our World!
Responsibilities of Marine Biologists
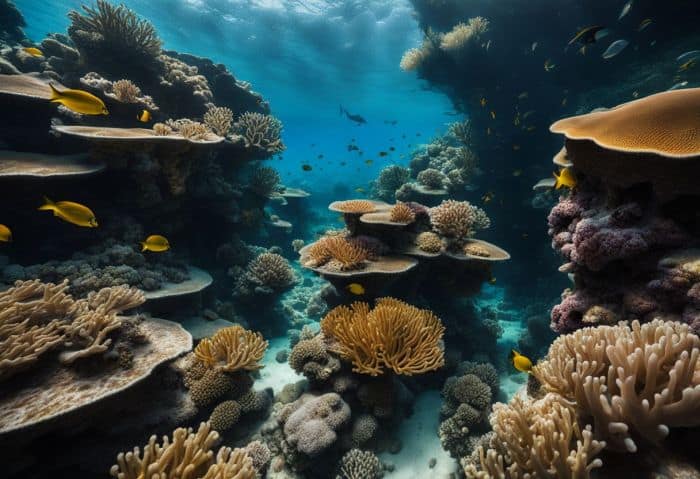

Marine biologists primarily carry out vital tasks such as conducting research and accumulating data[8] in the field. They also delve into detailed analysis and interpretation of collected data within laboratory environments.
Their work involves studying marine organisms[9], understanding their behaviors, and examining their interactions with various marine ecosystems.
Conducting research and collecting data in the field
Marine biologists go to the ocean to do their work. They study marine life in their own home. Their tools are nets, tags, and diving gear. They take notes on what they see. This is called fieldwork or research in the field.
It helps them learn how living things act in the sea. They look at animals, plants, and water conditions too. Often, they bring samples back to a lab for more tests.
![]()
Analyzing and interpreting data in the laboratory

Marine biologists use special computer tools to read and sort data. Data comes from taking samples at sea or tracking wild animals. The marine biologist uses this data to better understand life under the ocean.
Marine biologists sometimes write reports about what they learn from the data. It tells us how human steps change our oceans and water life. This work is key as it helps protect and keep all forms of sea life safe.
![]()
Studying marine organisms and their behaviors
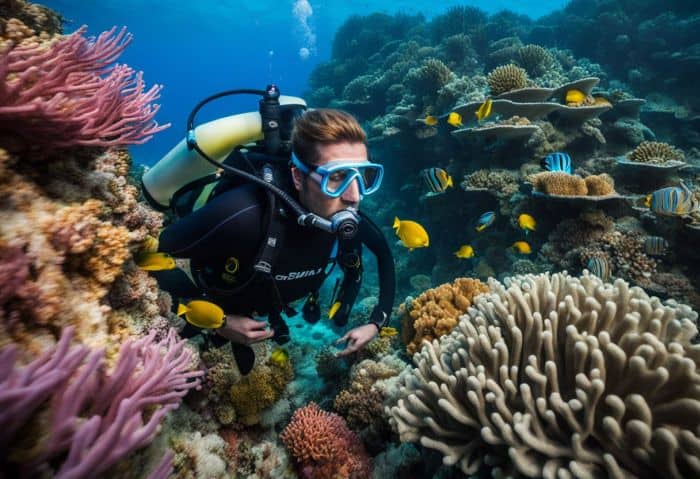

Marine biologists take a deep look at sea life. They study different types of animals, like whales and fish. They also focus on plants that grow in the ocean. These scientists learn how these organisms live day to day.
They watch carefully to see what they eat and where they go. This can help them determine why some species are more common than others, or some might be in danger. The goal is to better understand every part of marine life to keep our oceans healthy for many years.
![]()
Education and Career Path for Marine Biologists

Embarking on a career as a marine biologist requires specialized education, starting with degree courses highlighting marine life and ecosystems. Hunting for internships and fieldwork offers hands-on experience vital for honing research skills.
With myriad opportunities from academia to government agencies, the journey into becoming a marine biologist unfolds an extraordinary exploration of our oceans’ mysteries.
Find out more about how you can navigate this thrilling path!
![]()
Degree requirements and recommended courses
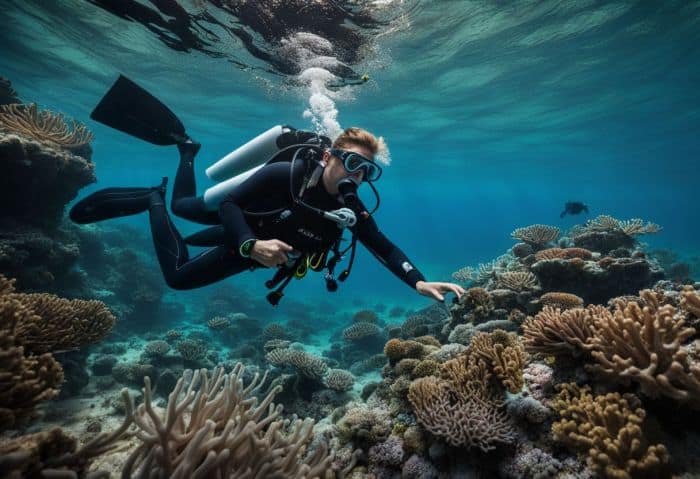

To become a marine biologist, you need the right school plan. This job needs a good understanding of math, physics, and science. Here are some courses you should think about:
- High school classes in earth science, chemistry, and biology.
- A university degree in marine biology or another related field like animal science or botany.
- More studies to get a master’s degree if you want to research.
![]()
Gaining practical experience through internships and fieldwork
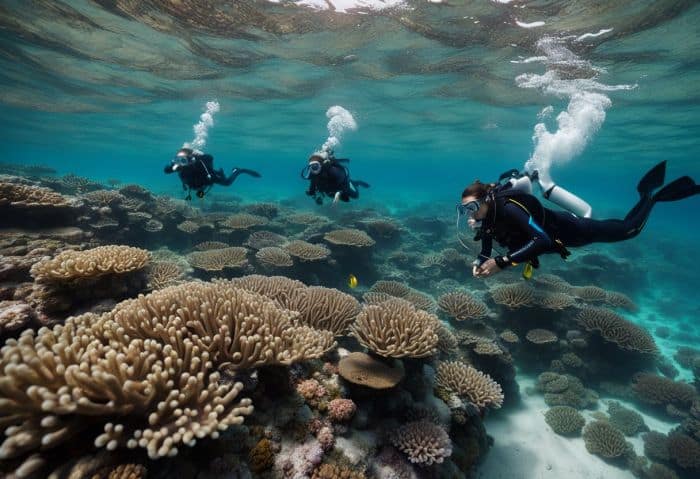

Starting out in marine biology means getting hands-on. You grow skills through internships and fieldwork. It all begins with you saying yes to working for free. This is how you gain a lot of learning.
- Start by looking for internships or fieldwork near the sea or ocean.
- Work done here can add to your knowledge.
- Learn about fish, plants, and seaweed in saltwater places.
- The stuff you learn from internships helps you do better later as a marine biologist.
- Even experts do these kinds of work to keep learning new things.
- This learning is used to help keep our oceans safe and full of life.
- Meeting people through your work leads to good connections in your job field.
- These people can then help you find more work later on.
- The joy of this work lets you protect sea life now and in the future.
![]()
Career opportunities in academia, research institutions, and government agencies
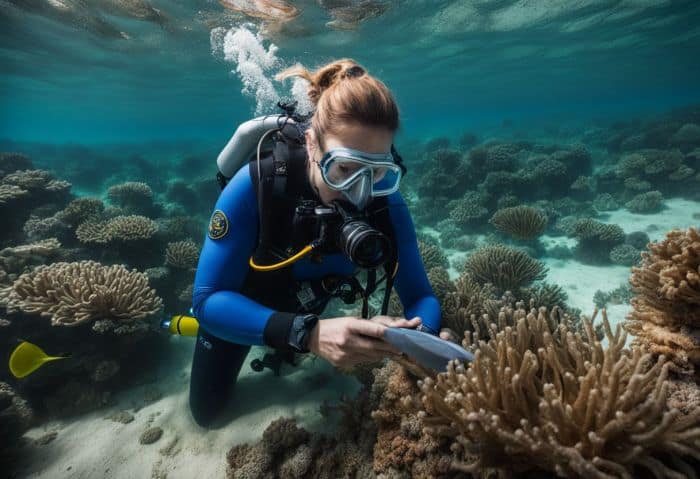

A marine biologist’s job opens many doors. You might work for a school, research place, or the government.
- Working in a school is one chance for you. You can teach others about the sea.
- Another choice is working at a research place. Here, you dig into facts and find new things about sea life.
- The government has jobs too! They need help deciding how to look after our seas and sea life.
- Some marine biologists work in private groups. They do tests and make new ways to learn about the sea.
- Other marine biologists serve in groups that keep fish safe.
- And some work with the army! They use what they know to aid in defense work.
- A few work as tool helpers or sea plant growers also!
- Many choose to be protectors of the sea as guides for keeping our waters clean.
![]()
Frequently Asked Questions
What is marine biology?
Marine biology delves into the intricate study of marine organisms, from tiny microorganisms to majestic whales and their interactions within marine ecosystems.
It seeks to understand how these creatures adapt to saltwater habitats, exploring cellular structures, migration behaviors, and photosynthesis.
Marine biology offers a holistic view of life beneath the ocean’s surface, bridging various scientific disciplines such as astronomy, ecology, and geology. It’s a captivating journey into biochemistry and biological oceanography, all contributing to the broader understanding of Earth’s rich biodiversity.
What do marine biologists do?
Marine biologists delve into the depths of oceans to study and understand marine life, encompassing everything from individual species to entire ecosystems. Their expertise ranges from marine mammal biology to ecology, aiding in analyzing intricate undersea interactions.
Collaborating with other scientists, they offer specialized insights into marine ecosystems. Their knowledge is crucial for sustainable conservation efforts and mitigating human impacts on these vital habitats.
How can I start a career in marine biology?
To embark on a career in marine biology, certain steps need to be followed:
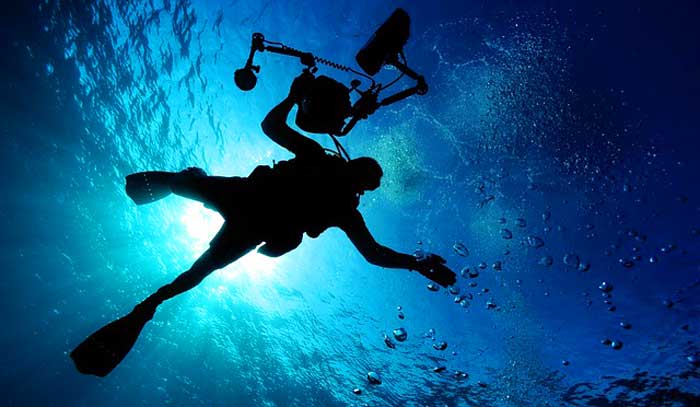

- Start by obtaining a bachelor’s degree in marine biology or a related field like aquatic or environmental science.
- Focus on core subjects such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology during undergraduate years, which are essential for this career path.
- Consider further education – a master’s degree is often favored within this profession.
- Gain exposure and experience in the field. This could be through internships, fieldwork, or research projects related to marine ecology, oceanography, or marine conservation.
- Seek job opportunities at various platforms such as research institutes, universities, government agencies, aquariums, and conservation organizations where marine biologists work.
- Stay updated with marine mammal research techniques and continuously learn about the intricacies of the marine ecosystem and animal behavior.
Where do Marine Biologists work?
Marine biologists explore marine ecosystems in diverse settings, from government agencies where they devise conservation strategies to aquariums that offer research labs on aquatic ecology and animal behavior.
While some venture into open oceans for field studies, others educate budding marine scientists in academic institutions. Additionally, wildlife rescue centers rely on their expertise for rehabilitating and reintroducing marine animals to their natural habitats.
What are some job duties of Marine Biologists?
Marine biologists delve deep into oceans, studying everything from vast ecosystems to minute organisms. They gather essential data, monitor sea creatures exposed to pollutants, and conduct experiments to understand aquatic behaviors.
Their responsibilities also encompass caring for injured marine life, collaborating with wildlife biologists, and reporting findings to influence policy-making.
Beyond research, they champion ocean conservation through outreach programs and, as marine mammal biologists, play a pivotal role in species protection.
What types of animals could they study?
Marine biologists study diverse aquatic life, from crustaceans and fish to unique marine mammals like cetaceans and pinnipeds. These sea creatures, each with distinct lifestyles, provide endless exploration avenues.
While some experts specialize in specific groups like mammals or plankton, others delve into broader ecosystems like corals. The four primary taxonomic groups they study are cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, and fissipeds.
Through their research, they uncover captivating insights into the physiology, behavior, and psychology of life beneath the ocean’s surface[10].
What does an Aquatic Biologist do?
Aquatic biologists dive deep into the mysteries of marine life and ecosystems, exploring the physiology and behavior of underwater organisms. They uncover nature’s secrets, from dolphin migrations to underwater plant photosynthesis across oceans, seas, and coasts.
Beyond observing species, they analyze interactions between marine life and environmental factors like climate change, pollution, and human activities. Experiments and research continually enhance our understanding of the intricate web of life in aquatic habitats[11].
What is the salary of an average marine biologist?
In the US marine biologists have a competitive average annual salary of $66,877, translating to an hourly wage of roughly $34.04.
Experienced marine science or ecology specialists can earn up to $59.94 per hour. The Bureau of Labor Statistics categorizes them with zoologists and wildlife biologists, reporting a 2022 average income of $72,610.
However, there’s a noticeable salary disparity among ethnic groups, with white marine biologists[13] earning the lowest average at approximately $54,584.
Is there a demand for marine biologists?
The US job market for marine biologists is promising yet competitive. The Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts a 5% growth in employment for wildlife biologists and zoologists, encompassing marine biologists, by 2020.
This growth is driven by the continuous demand for experts knowledgeable about marine ecosystems and conservation.
About 1,500 marine biology positions open annually, offering budding professionals opportunities to explore marine biodiversity and study unique behaviors in various aquatic environments[14].
What are the education requirements to become a marine biologist?
To venture into the captivating world of marine biology as a career, there are specific educational milestones one needs to achieve. Here’s what you should know:
- The journey begins with a Bachelor’s degree in marine science[15] or a similar area. Courses usually include biology, chemistry, physics, and math.
- Taking highly relevant subjects during undergraduate studies is advisable for future marine biologists. These involve diving deep into maths, physics, chemistry, and biology.
- A Ph. D. is necessary to excel in specialized areas like photobiology or deep-sea biology.
- Strong emphasis is placed on field research and applied skills in this industry.
- A solid general science and biology foundation remains beneficial throughout a marine biologist’s career.
- Earning at least a Master’s degree often shows potential for career growth for ambitious marine biologists.
- Some universities offer specialized courses in photobiology and deep-sea biology during the Bachelor’s program. Still, these are generally offered at the master level course.
- Besides the core subjects of study, other useful skills that can aid aspiring marine biologists include SCUBA certification, experience with laboratory research techniques, and statistical software proficiency.
What kind of jobs can marine biologists find?
Marine biologists have a wide array of job options available in diverse areas. Fieldwork, academic research, and laboratory studies allow scientists to be at the forefront of marine discoveries.
Some marine biologists may find fulfillment in consulting roles, advising organizations on ecological practices and strategies that support marine conservation.
Take ethical actions further by stepping into policy-making roles within government agencies or non-profit organizations. A career as an aquaculture farmer, aquarium, and museum worker opens avenues for comprehensive animal care. It can also carve paths towards teaching others as part of marine education programs.
Other exciting roles include becoming an animal behaviorist, aquatic botanist, chemical oceanographer, or coastal resources specialist dedicated to preserving wetlands and seashore habitats against pollution.
What is oceanography?
Oceanography delves into the intricate world of oceans, extending beyond marine biology to study marine life and the ocean’s physical properties, such as temperature and salinity.
This multidisciplinary field encompasses geology, chemistry, and meteorology, offering insights into Earth’s climate system. Through oceanographic research, we understand the interplay between marine systems and global weather, a pivotal knowledge area in climate change debates.
Thus, pursuing oceanography isn’t just about understanding the seas but making significant scientific contributions with broader global implications[16].
What is marine life?
Marine life encompasses many species inhabiting oceans and saltwater environments, ranging from minuscule plankton to immense blue whales, vibrant coral reefs, and mysterious deep-sea creatures.
Oceans covering over 70% of Earth’s surface house an impressive 236, 878 known species[17]. Beyond their ecological significance, marine life is crucial for human sustenance, providing seafood for global consumption and raw materials for industries.
Some marine organisms offer unique compounds pivotal for medical breakthroughs. Additionally, the allure of underwater wonders bolsters eco-tourism, emphasizing marine conservation and sustainable enjoyment of these natural treasures.
What are some common job titles in the field of marine biology?
Marine biology boasts a myriad of job titles, each tailored to specific areas of interest and expertise. Wildlife biologists observe creatures in their natural settings, while dive operations managers handle underwater exploration logistics[18].
Aquatic ecologists and fish biologists[19] specialize in understanding species behaviors. Roles like marine conservation coordinators and reef restoration project managers emphasize ecosystem preservation and addressing threats like pollution.
Marine research technicians analyze data from fieldwork in labs. The field even extends to genetic studies, with marine biotechnologists exploring genetic modifications. This vast career landscape in marine biology caters to passions centered on oceanic life.
Marine biologists do great work. They study the ocean and its life forms. This helps us understand our planet better. We should all thank them for their hard work learning about and saving our seas.
![]()