
What Do Gorillas Eat?: Did you know gorillas are the biggest living primates on earth? Although IUCN declared all species of gorillas as critically-endangered, they live mostly in tropical forests in Africa. They live on land rather than in trees, unlike rainforest monkeys. By nature, gorillas are omnivorous.
According to biological DNA analysis, it is determined that about 99% of gorillas’ DNA (gene makeup) is identical to humans. So we can confidently say that gorillas are our closest living relatives, followed by chimpanzees, orangutans, and bonobos. Humans are sometimes called “the fifth great ape“.
Since these mammals occupy the forest floor layer of the tropical or subtropical rainforests, what do gorillas eat? Are gorillas herbivores? What is the gorilla diet? Do gorillas ever eat meat? Do gorillas hunt other animals? What are the sub-species of gorillas and their eating patterns? Most importantly, do gorillas attack and eat humans?
On this page, let’s explore the answers to all these gorilla diet questions with images. Also, we will explore the gorilla food chain diagrams and silverback gorilla foods. Without much further ado, let’s investigate what gorillas eat now!
Table of Contents
What Do Gorillas Eat?
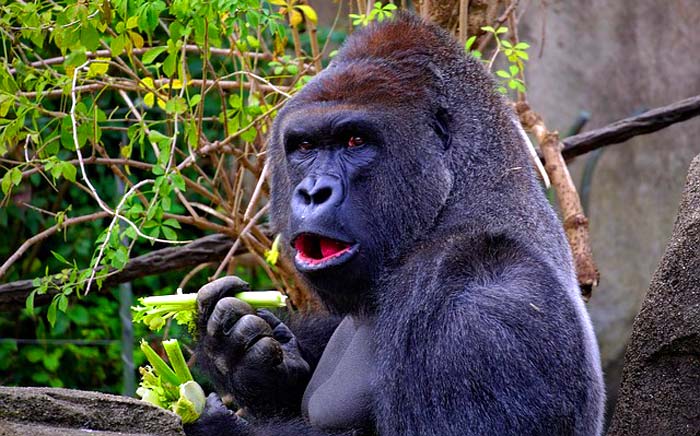

The term “Gorilla” refers to a genus of animals including many different species. By nature, gorillas are omnivorous, meaning that they eat both plants and animals. There are mainly two types of gorillas, namely western gorilla and eastern gorilla, which we will explore more on their sub-species later in the article.
- Gorillas’ diet directly depends on their habitat and the time of the year.
- Gorillas primarily eat green leaves, juicy fruits, seeds, tree barks, stems, pith (soft inner stem), and bamboo shoots of about 200 such plant species.
- Occansionally gorillas consume small animals too in food scarce such as rodents, snails, weaver ants, caterpillars, termites, and lizards.
- Gorillas tend to favor plants of ginger and arrowroot families.
- Gorillas’ favorite plants are Galium, thistles, nettles, and celery.
- The average lifespan of a gorilla is about 37 years.
![]()
Gorilla Food Chain Diagram
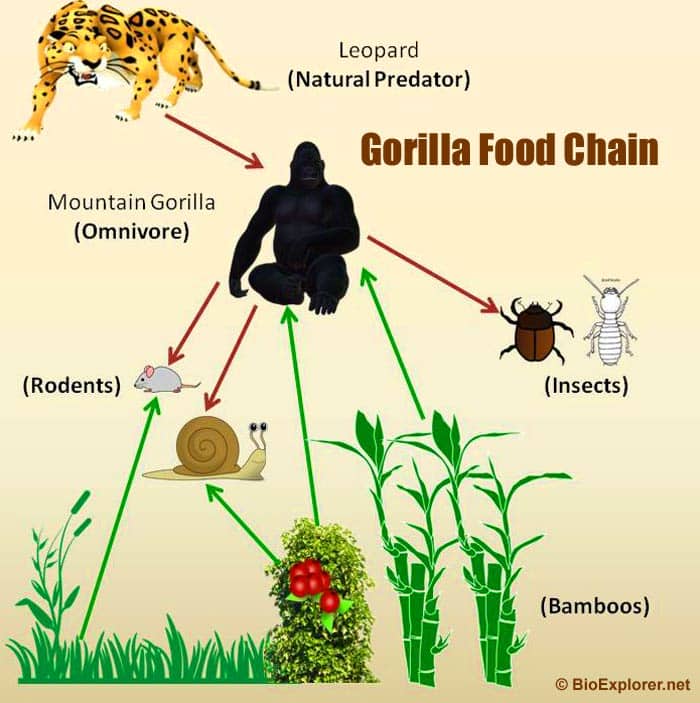
In the ecological pyramid, gorillas come under the secondary consumer bracket. Their natural direct predator is leopard in the wild however due to deforestation and loss of habitats, their next immediate threats are humans from illegal poaching and hunting.
![]()
How Much Do Gorillas Eat?
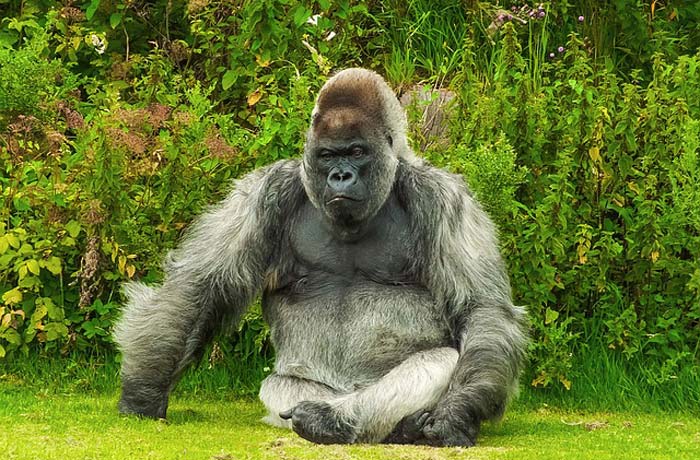

According to THE B&RD organization, the average adult male gorilla (weighs about 200 kg or 400 lbs) eats about 30 kilograms of vegetation every day whereas the female gorilla consumes about 18 kgs of plants. Unlike humans, gorillas have strong chewing muscles and a healthy set of teeth (including long pointed canines), which help them to digest these mass plant materials efficiently. Note that the male gorillas use canines mostly in fights with another male.
![]()
Do Gorillas Drink Water?

According to SeaWorld Parks & Entertainment, Gorillas rarely drink water as they consume fleshy and juicy plant materials every day which is composed of 50% water contents anyway!
![]()
Do Gorillas Eat Meat?
As explained earlier, gorillas decide their food habits depending on their habitats. Besides plants, gorillas also eat small animals, mostly insects, rodents, termites, lizards, and snails.
Gorillas do not kill large animals. Overall in their food composition, it is estimated that gorillas’ diet includes 0.1% of animal matter, and the rest is all plants.
![]()
How Often Do Gorillas Eat?

Gorillas spend 50% of their day eating and foraging. These beasts look for food in the morning and the afternoon. Gorillas travel over 1100 meters a day looking for food!
![]()
Do Gorillas Eat Humans?
Like any other wild animals, gorillas are very shy and would stay away or avoid humans entirely if possible in the wild. However, if an intruder comes too close to the gorilla’s family, the leader silverback gorillas could react aggressively but only to drive them away. In general, gorillas never attack humans unless humans provoke them intentionally.
There are instances in history where gorillas attacked humans in conflicts due to their territory breaching, however, not to hunt humans for food.
In general, the gorilla will see you as harmless and would stay calm unless threatened with direct eye contact & rumors.
Here is a recent instance where gorilla named Harambe in Cincinnati Zoo caught the national attention. A three-year-old fell into the gorilla enclosure, and Harambe dragged the boy through the water to a safe place to protect the boy against the shouting mob.
Based on the past violent behavior of gorillas, the zookeeper shot Harambe rather than tranquilizing him to save the child.
This situation sparked a lot of controversies as some believe that the zookeeper shouldn’t have killed Harambe while others think that the zookeeper made the right decision.
![]()
Do Gorillas Eat Soil?
Believe it or not, occasionally, gorillas consume mud, soil, or even ash (near volcanos) to regulate their digestion system and absorb any minerals missing in plants. Also, dirt helps them to neutralize the poisonous substances from plants they feed on. This process of eating soil or clay or ash is known as geophagy.
![]()
Does Gorilla Eat Other Gorillas?
The short answer is perhaps. In the recent PLOS journal 2010, there was a recording of finding other monkey and antelope meat in western lowland Gorillas’ fecal samples. Cannibalism is quite common in Chimpanzees than gorillas. Adult chimpanzees can snatch the infant chimpanzees from their mothers and eat their fleshes.
However, there was no documented evidence of eating other adult chimpanzees.
![]()
Gorilla Diet By Sub-Species
The genus ‘Gorilla’ includes two species, western gorilla and eastern gorilla. Each of these species contains two sub-species.
- Western gorilla has western lowland gorilla and cross-river gorilla sub-species.
- Eastern gorilla has eastern lowland gorilla and mountain gorilla sub-species.
- The diet of each sub-species is very identical, as they all live in the same African continent.
![]()
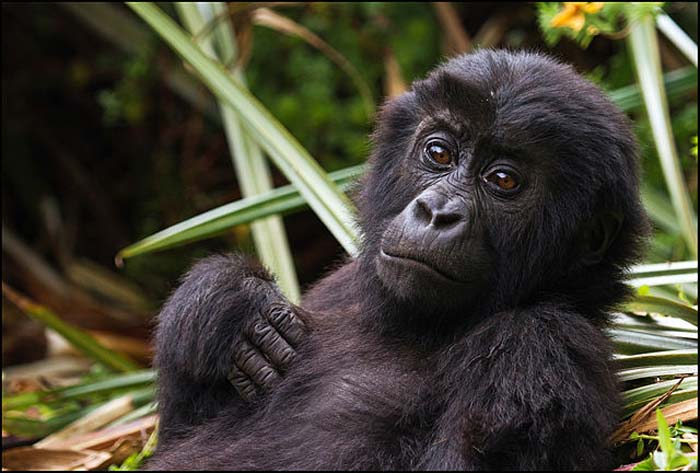
Diet of Eastern Lowland Gorilla (G. beringei)

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Hominidae | Gorilla | G. beringei |
- As gorillas generally have opposable thumbs, it makes life easier for eastern lowland gorillas to peel fruits and bamboo shoots. The eastern lowland gorillas are also known as Grauer’s gorillas.
- Eastern lowland gorillas are primarily herbivorous but sometimes eat animals, so they are classified as omnivores. Being omnivorous, they tend to travel long distances for their food.
- Majority of the eastern lowland gorilla diet includes green leaves, nuts, and wild berries from about 100 species of plants daily.
- Occasionally, eastern lowland gorilla eats small animals such as insects, lizards, rats, and other rodent families.
![]()
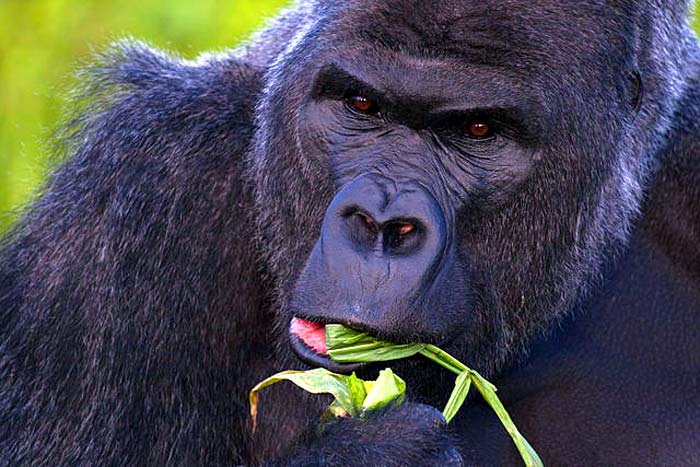
Diet of Western Lowland Gorilla (G. gorilla)

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Hominidae | Gorilla | G. gorilla |
- Western lowland gorillas are mainly herbivorous too. Fruits are the primary and essential food source of western lowland gorillas’ diet.
- According to Panda.org studies, over 100 fruit species are recorded in western lowland gorillas’ diets.
- When the fruits are not in the season, such as in drier months, western lowland gorillas enrich their diet with green leaves, pith, shoots, and tree barks.
- They also eat caterpillars, termites, and weaver ants to compensate for the food scarcity.
![]()
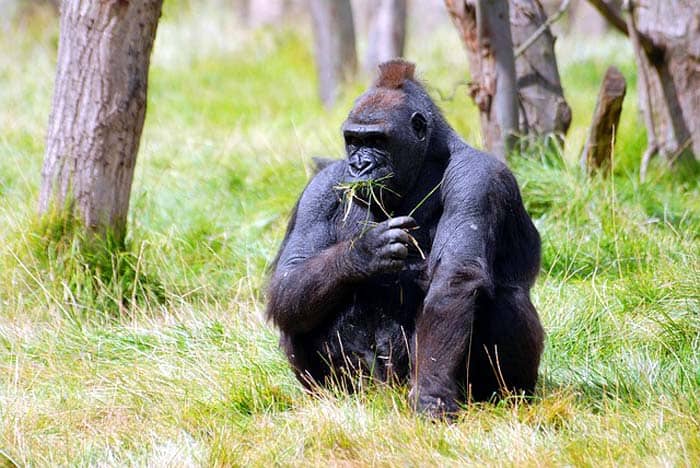
Diet of Mountain Gorilla (G. beringei)

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Hominidae | Gorilla | G. beringei |
As mountain gorillas in the thick forests of central and west Africa, they also eat roots, bamboo shoots, fruits such as berries, wild celery, tree barks, pulp, and occasionally insects and termites.
![]()
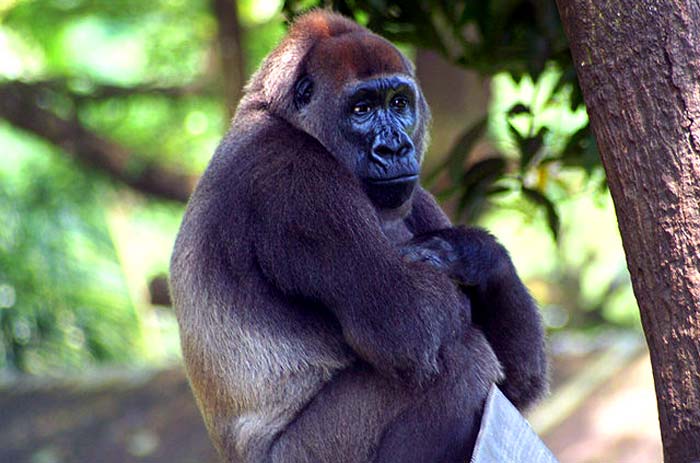
Cross River Gorilla (G. gorilla)

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Hominidae | Gorilla | G. gorilla |
- According to CrossRiverGorillas.org, Cross River Gorillas consume more liana (A Liana is a long tender stemmed, woody vine that is rooted in the soil at ground level and climbs up to the canopy) and tree barks around the year.
- Cross-river gorillas eat less fruit during periods of scarcity than Western Lowland Gorillas.
- When food is scarce, cross-river gorillas travel long distances to other sides of the forests in search of food. These primates sometimes get into human crops as well such as banana and plantain fields and cause conflicts.
![]()
Cite This Page
References
- “Gorilla gorilla ssp. gorilla (Western Lowland Gorilla)”. Accessed May 12, 2018. Link.
- “GORILLAS – Diet & Eating Habits”. Accessed May 12, 2018. Link.
- “Start – Berggorilla & Regenwald Direkthilfe e.V.”. Accessed May 12, 2018. Link.
- “Western lowland gorilla | WWF”. Accessed May 12, 2018. Link.
- “Cross River Gorilla Diet – Cross River Gorilla”. Accessed May 12, 2018. Link.
- “Vertebrate DNA in Fecal Samples from Bonobos and Gorillas: Evidence for Meat Consumption or Artefact?”. Accessed May 12, 2018. Link.

















[…] fully grown mountain gorilla partakes of more than 140 types of plants, shoots, stems and leaves, and can eat up to sixty pounds of […]