
The human body is made up of trillions of cells that are the foundation for different tissue and organ systems. When an injury or damage is incurred, new cells are generated from unspecialized precursor cells.
These precursor cells are known as stem cells, and they are known to have potent regenerative capabilities. Stem cells are the basis for worldwide research in the field of therapeutics and are widely viewed as an effective treatment regime for some different diseases.
We will explore some of the stem cell research pros and cons within the scope of this article. Let’s begin.
Table of Contents
- What is Stem Cell Therapy?
- Pros/Advantages of Stem Cell Research:
- 1. Stem Cells In Therapeutics & Regenerative Medicine:
- 2. Stem Cell Research Detects Birth Defects Early:
- 3. Stem Cell Research Opens Up New Avenues In Cell Biology:
- 4. Transplant Rejection Minimized Using Stem Cells:
- 5. Stem Cell Research Enables Generation of Body Organs:
- 6. Embryonic Stem Cell Research Utilizes Miscarried Embryos:
- 7. Stem cell research Helps For Better Drug Testing:
- 8. Certain Stem Cells can be converted into Pluripotent Stem Cells:
- 9. Stem Cells Can Reduce the incidence of Pregnancy Loss:
- 10. Stem cells Grow & Replicate In Bulk:
- 7 Cons/Disadvantages of Stem Cell Research:
- 1. Long-Term Effects of Stem Cell Therapy Are Unknown:
- 2. Harvest of Embryonic Stem Cells Is A Long-Debated Issue:
- 3. Adult Stem Cells Can Specialize Only Into Specific Lineages:
- 4. Stem Cell Research May Not Provide Solutions To All Ailments:
- 5. Embryonic Stem Cell Transplants Mostly Rejected:
- 6. Stem Cell Research is Expensive & Requires Funding:
- 7. Stem Cell Therapy Has Side Effects:
- References
What is Stem Cell Therapy?
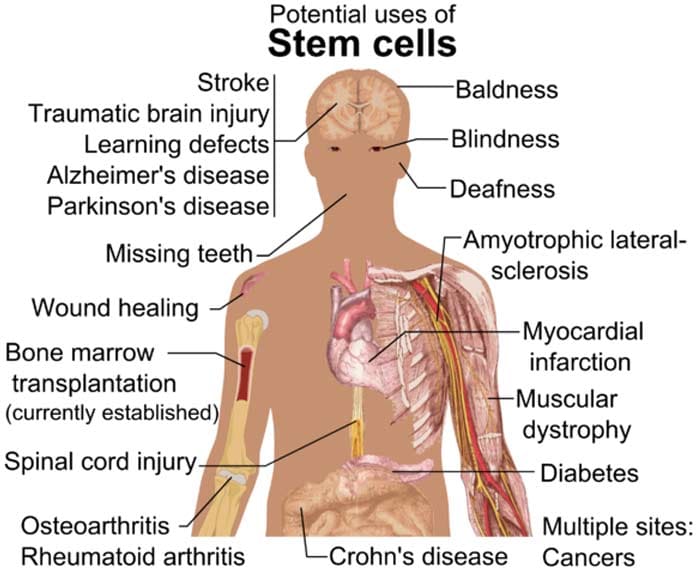
Stem cell therapy involves isolating stem cells from their respective niche and using them to treat a disorder, area of injury or damaged tissue.
- The ability of stem cells to renew themselves and generate new cells can aid in the treatment of neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, diabetes, or in the regeneration of bone and cardiac tissues, as well as in bone and spinal cord injuries.
- There are different types of stem cells and based on the types, a plethora of therapeutic applications exist for stem cells.
- However, the use of stem cell therapy entails specific advantages, disadvantages and ethical concerns.
![]()
Pros/Advantages of Stem Cell Research:
1. Stem Cells In Therapeutics & Regenerative Medicine:
The immense regenerative and specialization potential of stem cells makes them valuable for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, injuries or damages to tissues, and diseases such as diabetes.
- In a disease such as diabetes, the pancreatic cells are destroyed by the immune cells, thereby reducing the production of insulin for the body.
- Stem cells can be engineered to be transformed into pancreatic cells that can produce insulin. These cells can then be transplanted into the patient’s body that will help cure the effects of diabetes.
- Stem cell treatments are also used in spinal cord injuries and are actively being researched upon for artificial limb generation.
![]()
2. Stem Cell Research Detects Birth Defects Early:
 Embryonic stem cells are found in the blastocyst, in the embryonic stages of development.
Embryonic stem cells are found in the blastocyst, in the embryonic stages of development.
- Research into stem cell development can help researchers understand problems that arise during these stages that lead to birth defects, and other problems that occur during pregnancy.
- For instance, researchers may be able to study closely the development of the embryo and changes that can lead to the occurrence of physical and genetic defects in the fetus. Detecting these defects at an early stage is crucial for prospective treatment and care.
![]()
3. Stem Cell Research Opens Up New Avenues In Cell Biology:
Stem cell research can help scientists understand and investigate cellular growth and development.
- The field of stem cells is in itself a separate field that encompasses its principles, modes of research and techniques. Over time, it has proven to be one of the most widely researched upon, and popular fields in science.
- It provides insight into cell biology, by helping scientists understand the genetic mechanisms of the cell that control cell specialization and cellular markers that define each stage of the cell cycle.
- It enables scientists to study closely, the mechanism of cellular regeneration and the changes associated with the transformation of one cell type to another. Using this information, scientists have successfully been able to replicate the transformation process in vitro.
![]()
4. Transplant Rejection Minimized Using Stem Cells:
- Stem cells are genetically and physiologically the cells of the patient’s own body, thus reducing the risk of rejection when these cells are transplanted for therapeutic purposes. This is true only for adult stem cells that are extracted from the patient’s tissue.
- Adult stem cells have the capability of transforming into a cell type of their lineage. For example, the Hematopoietic stem cell can transform into any blood cell type.
![]()
5. Stem Cell Research Enables Generation of Body Organs:
Stem cells can be used to grow organs or limbs in patients with loss of limb or loss of function of an organ.
- Since stem cells have the endless capacity to replicate and transform into specialized cells, isolating bone stem cells, can help regenerate and grow bone cells in vitro by providing them with the required factors and growth factor.
- This is true for other tissues as well such as pancreatic tissue, and retinal cells of the eye.
![]()
6. Embryonic Stem Cell Research Utilizes Miscarried Embryos:

Embryonic stem cells have immense potential in therapy, as they can regenerate into any cell type of the body.
- Embryos are scientifically thought not to have a life. However, there are many debates related to this topic. Embryonic stem cells are isolated from the blastocyst stage of the embryo.
- Individuals who have experienced pregnancy loss at this stage, sometimes donate the embryos for research purposes.
![]()
7. Stem cell research Helps For Better Drug Testing:
The use of stem cells in therapeutics can minimize the need for animal testing. With stem cells, a colony of cells can be grown that mimic a disease and act as a model for drug testing and treatment (E.g., cancer cells).
![]()
8. Certain Stem Cells can be converted into Pluripotent Stem Cells:
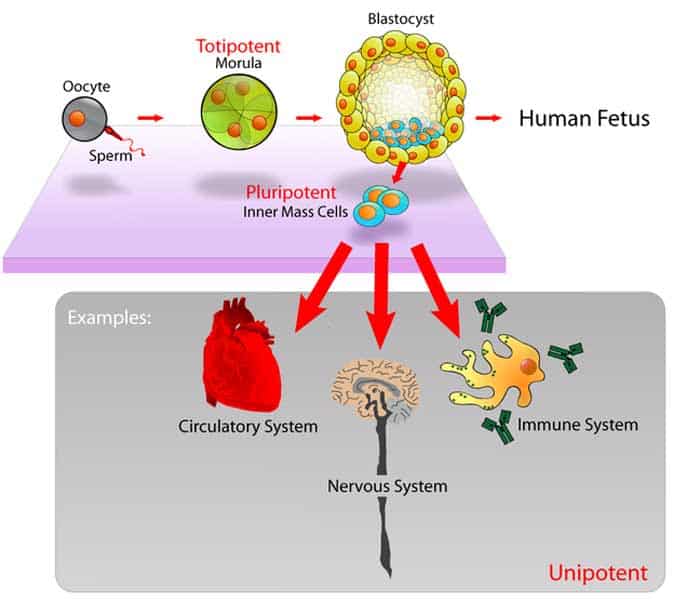
Although adult stem cells only retain the capacity to specialize in a specific cell type, they are reprogrammable into pluripotent stem cells.
![]()
9. Stem Cells Can Reduce the incidence of Pregnancy Loss:

Some pregnancies end in miscarriage mostly because of a defect or a fault at the embryonic stage of development.
- A look into embryonic growth and how stem cells function can provide insight into how they can be used to prevent pregnancy loss in the early trimester.
- Scientists may be able to pinpoint the genetic defects and underlying causes that lead to pregnancy loss in the early trimester by studying isolated embryos that have miscarried and the properties of embryonic stem cells within.
![]()
10. Stem cells Grow & Replicate In Bulk:
Embryonic stem cells have large regenerative capacities and can be maintained as cell lines for research and treatment purposes.
- The regenerative capacity of the embryonic stem cells makes it very easy to propagate and culture different kinds of cell lines for research and testing purposes.
![]()
7 Cons/Disadvantages of Stem Cell Research:
1. Long-Term Effects of Stem Cell Therapy Are Unknown:

With any new technology, the long-term effects may be unknown or hard to decipher. Similarly, the effects of stem-cell therapy on treatment of diseases or transplants may be untested in the long run and treatments in clinical trials should be well planned and studied before administering it on patients as a medical product.
![]()
2. Harvest of Embryonic Stem Cells Is A Long-Debated Issue:

Embryonic stem cells, albeit highly potential, are the center of much debate and discussion. This is because embryonic stem cells are harvested from the blastocyst stage of the embryos that are either miscarried or aborted.
- To some groups, embryos are the equivalent of human beings and using embryos for this purpose is unethical, as embryos are considered to have life from the time of conception and should not be used for research or testing purposes.
![]()
3. Adult Stem Cells Can Specialize Only Into Specific Lineages:

Adult stem cells have limited specialization properties.
- They can specialize only in cells of their respective lineage and as such cannot be cultured to produce any cells in the body.
- Moreover, harvesting volumes of adult stem cells are usually low. For example, adult stem cells isolated from pancreatic tissue retain the ability to specialize in the alpha and beta type of pancreatic cells that produce glucagon and insulin respectively.
![]()
4. Stem Cell Research May Not Provide Solutions To All Ailments:

Stem cell therapy may not apply to genetic disorders which are more complicated.
- Genetic conditions have their root at the gene level, as such, other types of treatments need to be developed to target genetic disorders.
- Stem cells may provide the answer to symptomatic treatment of such disorders but may not cure it at its root.
![]()
5. Embryonic Stem Cell Transplants Mostly Rejected:
Embryonic stem cells are harvested from blastocysts or embryos. Therefore, they are not a patient’s body cells and may be rejected on transplantation. This differs from adult stem cells which do not pose a risk of rejection as they are a patient’s cells.
![]()
6. Stem Cell Research is Expensive & Requires Funding:

It is known that stem cell researchers rely heavily on external funding and the procedures are likely an expensive affair. Still, many scientists and researchers believe that the potential benefits outweigh the cost incurred.
![]()
7. Stem Cell Therapy Has Side Effects:

Stem cell transplants in the treatment of cancer may have certain side effects such as nausea, vomiting, etc. Like all treatments, stem cell treatment also has its side effects.
![]()
Stem cell research today is of prime importance and extremely beneficial. With the rates at which diseases are progressing, it is vital today, to efficiently be able to employ stem cell therapy into total practice and reap the benefits it offers in the field of therapeutics.
Further research in this field, can help decipher how to control side effects, and what long-term effects these therapies may render.
By large, stem cells can revolutionize the field of medicine and therapeutics and provide a solution to some different ailments that are widespread today.
![]()
Cite This Page
References
- “Pros and Cons of Stem Cell Therapy”. Accessed April 12, 2018. Link.
- “What is Stem Cell Therapy? | ReeLabs”. Accessed April 12, 2018. Link.
- “Stem Cell Research – Advantages and Disadvantages – Advantages and disadvantages table in GCSE Biology”. Accessed April 12, 2018. Link.
- “14 Key Pros and Cons of Embryonic Stem Cell Research | Green Garage”. Accessed April 12, 2018. Link.
- “19 Advantages and Disadvantages of Stem Cell Research | Vittana.org”. Accessed April 12, 2018. Link.















[…] bioexplorer.net […]