Respiratory System Fun Facts: The air we breathe, rich in oxygen, is filtered and taken up by the respiratory system. The respiratory system comprises several organs and structures, including the nasal cavity, windpipe, bronchial system, the lungs, and alveoli. The alveoli then branch into capillaries that help distribute oxygen to the blood system that carries it to the organs and organ systems.
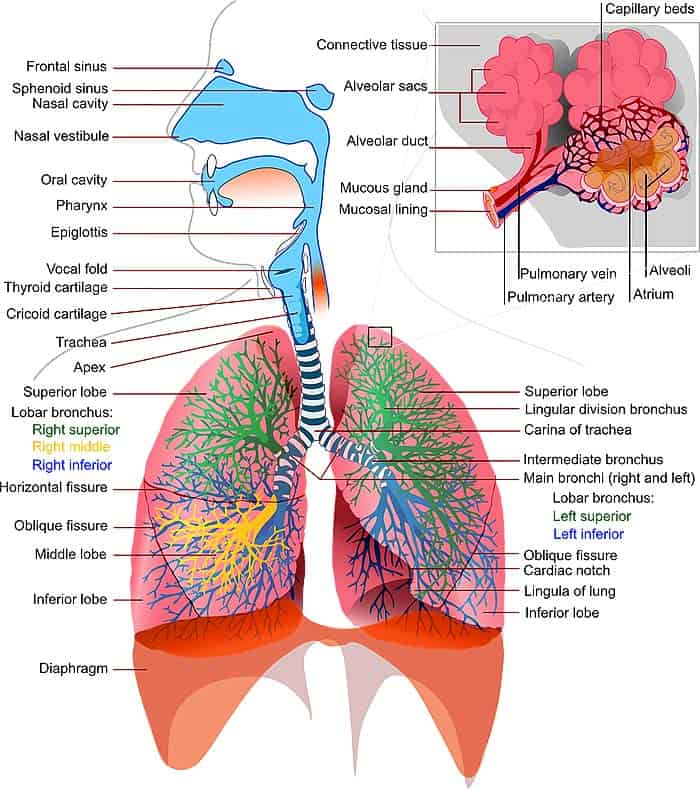
At the organ or tissue level, carbon dioxide (CO2) is released into the bloodstream, which is then taken back to the lungs via the heart to be released into the external environment with the help of the bronchial system and the windpipe. This process, at the surface, is known as breathing; and that including the internal network is known as respiration.
The respiratory and the circulatory system are interconnected. The circulatory system is of two types – systemic and pulmonary; where the latter involves the process of breathing and the function of the respiratory system.
25 Respiratory System Fun Facts
1) Vibrissae help to filter the air
 Tiny hairs present in the nostrils help filter the air we breathe.
Tiny hairs present in the nostrils help filter the air we breathe.
- Tiny hairs that are found in the nostrils help prevent the entry of pathogens like bacteria into the respiratory tract.
- These hairs are also called Vibrissae, and their density decides the efficiency of the filtering mechanism.
- Studies indicate that the density of vibrissae in the nostril can affect the likelihood of developing asthma. This behavior is due to the decreased filter efficiency that helps filter out allergens that cause asthma when vibrissae density is low.
![]()
2) Women and Men have different respiratory rates
 During embryonic development, male and female fetuses diverge significantly regarding respiratory tract development.
During embryonic development, male and female fetuses diverge significantly regarding respiratory tract development.
- Metrics such as respiratory volumes and breathing rate also differ between the sexes.
- Apart from this, children also have different breathing rates than adults. In general, children have a higher breathing rate than their adult counterparts.
![]()
3) Alveoli are connectors between the lung and the blood vessels
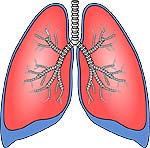 Alveoli are tiny saccules in the lung that aid in respiration and gaseous exchange between the lungs and the blood vessels.
Alveoli are tiny saccules in the lung that aid in respiration and gaseous exchange between the lungs and the blood vessels.
- Alveoli are structures present inside the lungs that serve as the functional unit of the respiratory system.
- They have a large surface area that, in total, spans to 525 square feet for both lungs. This length equates to the size of a tennis court!
- The surface area of the alveolar surface decides the diffusing capacity of the lung that governs the respiratory process.
![]()
4) The respiratory system is made of Bronchial tree
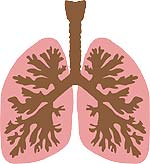 The respiratory system is made up of a structure known as the bronchial tree.
The respiratory system is made up of a structure known as the bronchial tree.
- The respiratory system begins with the nose, opens into the nasal cavity, and through the trachea that opens into the bronchus.
- The bronchus further divides into the left and right bronchi and finally into the bronchioles.
- The bronchioles open into the alveoli, which are the basic structural unit of respiration and facilitate gaseous exchange between the lungs and blood vessels.
![]()
5) Epiglottis covers the opening into the trachea
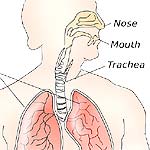 The epiglottis (the flap of tissue) covers the opening into the trachea.
The epiglottis (the flap of tissue) covers the opening into the trachea.
- When breathing, it remains open to let air enter the trachea.
- The trachea remains covered by the epiglottis when swallowing food.
- This arrangement prevents food from entering the trachea and prevents choking.
![]()
6) Rib muscles are critical for breathing
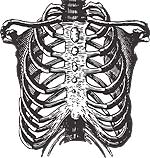 Muscles present in between the ribs aid in respiration.
Muscles present in between the ribs aid in respiration.
- The muscles present in between the ribs, such as the intercostal muscles, aid in the movement of the chest cavity and the breathing process.
- The muscles contract and relax, leading to the expansion and contraction of the chest cavity, thereby changing the internal air pressure and aiding in the breathing process.
![]()
7) The lungs differ in size and structure
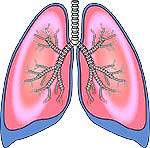 The right lung is divided into 3 lobes, and the left lung is divided into 2 lobes.
The right lung is divided into 3 lobes, and the left lung is divided into 2 lobes.
- Each of the lungs is covered by a thin membrane called the pleura that separates the lungs from the chest cavity.
- The lungs are spongy and elastic. They can expand and contract in size during the process of breathing.
![]()
8) The breathing is a 2-step process
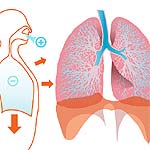 The act of breathing involves two steps: inhalation and exhalation.
The act of breathing involves two steps: inhalation and exhalation.
- Inhalation involves the intake of air through the nasal cavity into the lungs by expanding the chest volume with the help of rib muscles.
- Exhalation involves the removal of air from the lungs to the exterior by contraction of the chest cavity by the action of the rib muscles.
![]()
9) The diaphragm is a thin muscular structure beneath the lungs
 The diaphragm is present beneath the lungs and separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
The diaphragm is present beneath the lungs and separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
- This anatomical arrangement increases the chest cavity and reduces the air pressure, thereby inhaling the air into the lungs from the external environment.
- It is pulled down by the action of the rib muscles during expansion or inhalation.
- The rib muscles pull it upward into the chest cavity during contraction or exhalation. This decreases the chest volume and increases the pressure, thereby expelling air from the lungs.
![]()
10) Diaphragm and rib muscles contract and relax 16 times/minute
 The diaphragm and rib muscles are constantly contracting and relaxing.
The diaphragm and rib muscles are constantly contracting and relaxing.
- The rib muscles and the diaphragm relax and contract about 16 times per minute.
- The frequent contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and the rib muscles control the expansion and contraction of the chest cavity, which helps in breathing.
![]()
11) Lung function is measured by different metrics and air volumes
 Metrics such as required air volume, residual volume, and tidal volume measures the amount of air entering and leaving the lungs under certain circumstances.
Metrics such as required air volume, residual volume, and tidal volume measures the amount of air entering and leaving the lungs under certain circumstances.
- The airflow rate measures the efficiency of airflow through the lungs.
- The diffusion efficiency measures the rate at which oxygen diffuses into the blood through the alveoli and is also a measure of alveolar function.
![]()
12) Every time we breathe in 7 ml of air/kg body weight
 Each breath taken causes the inhalation of around 7 ml of air per kg body weight.
Each breath taken causes the inhalation of around 7 ml of air per kg body weight.
- The amount of inhaled air depends on the body weight of the individual breathing.
- Thereby, the respiratory rate of children is much faster than an adult’s.
- The respiratory rate of athletes also differs from non-athletes.
![]()
13) Fact: Respiration and Breathing are two different terms
- Respiration is the process that includes both pulmonary and systemic respiration. This process follows air inflow from the nasal cavity to the alveolar level, exchanging it into the blood that carries it to the heart and finally pumped to the rest of the organs.
- Breathing is the external process of inhalation and exhalation of air that involves the function of the diaphragm, lungs, and rib muscles.
![]()
14) The bronchi are lined with cilia
 Cilia are tiny like hair-like projections that are found inside the bronchial tubes.
Cilia are tiny like hair-like projections that are found inside the bronchial tubes.
- They move in wave-like forms that help move mucus through the respiratory tract toward the exterior, where it is coughed up.
- Mucus is a critical element of the respiratory system that is also present in the nostril.
- Mucus helps in preventing the entry of pathogens, allergens, dust, and other unwanted materials into the respiratory system.
![]()
15) Sinuses play a massive role in respiration
 Air spaces present in the head or skull called sinuses also play a role in respiration.
Air spaces present in the head or skull called sinuses also play a role in respiration.
- Sinuses are cavities or air spaces in the bones of the head connected to the nasal cavity by remote connections.
- They help in regulating the temperature and the humidity of the air we breathe in.
![]()
16) Adenoids are lymph tissue present in the throat
 At the top part of the throat, there is a pair of adenoids. They are overgrown lymph tissues.
At the top part of the throat, there is a pair of adenoids. They are overgrown lymph tissues.
- Lymph forms a part of the lymphatic system that aids in fighting infections and providing immunity.
- In some cases, the adenoids may be removed if they grow too large and interfere with breathing.
![]()
17) Lungs can float on water

- Due to the hollow structure of the lungs, they can float on water.
- They are essentially spongy and hollow in structure to be able to expand and contract to facilitate breathing.
![]()
18) 70% of the body’s waste is eliminated via breathing
 Did you know that 70% of the body’s waste is eliminated through breathing?
Did you know that 70% of the body’s waste is eliminated through breathing?
- Breathing is a process that helps eliminate carbon dioxide from the body and facilitates oxygen intake.
- At the end of cellular respiration, the cells contain a high amount of carbon dioxide, which is eliminated through the lungs in the process of breathing.
![]()
19) The left lung is smaller than the right
- The left lung is smaller than the right lung. The left lung is divided into 2 lobes, whereas the right lung is divided into 3. This difference is due to the heart’s position slightly towards the left.
![]()
20) The nose has tiny projections on its wall called turbinates.

- The nose is the foremost part of the respiratory system that helps filter the air that moves through it during inhalation.
- It contains tiny projections called turbinates that help to keep the air warm and bring it to body temperature.
![]()
21) Some air never leaves the lung
- The residual volume is the amount of air left inside the lungs during a complete exhalation.
- This volume is about 1200 ml and is a metric of lung function tests measuring lung efficiency.
![]()
22) Lung diseases can be caused by changes in lung’s anatomy
 Any change in the function and structure of the lung, such as its elasticity can lead to the development of diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis.
Any change in the function and structure of the lung, such as its elasticity can lead to the development of diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis.
- Other diseases, such as emphysema, caused by smoking, occur due to narrowing respiratory tubules and pathways.
- Pneumonia is an infection caused by a pathogen that leads to the loss of elasticity of the lungs and a decrease in the amount of air they can hold.
![]()
23) Lung cancer is caused by carcinogens from cigarettes
 Tobacco and smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer in the world.
Tobacco and smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer in the world.
- The carcinogens or cancer-causing agents present in tobacco and cigarette smoke damage the internal structure of the lungs, lead to blockages in the airways, and decrease the alveolar surface necessary for respiration.
- This leads to the development of cancer of the lung.
![]()
24) Respiratory diseases can be created by environmental pollutants.

- Environmental pollutants such as ozone and sulfur dioxide (SO2) can cause respiratory symptoms leading to the development of respiratory disease.
- A building material commonly known as asbestos is a harmful chemical that causes severe respiratory disorders.
![]()
25) Smoking affects other parts of the body
 The harmful effects of smoking are not limited to just the lungs.
The harmful effects of smoking are not limited to just the lungs.
- Harmful chemicals and carcinogens present in cigarette smoke hurt the tissues and organs of the body.
- This is because these chemicals are taken up in the blood and distributed to other tissues and organs.
![]()