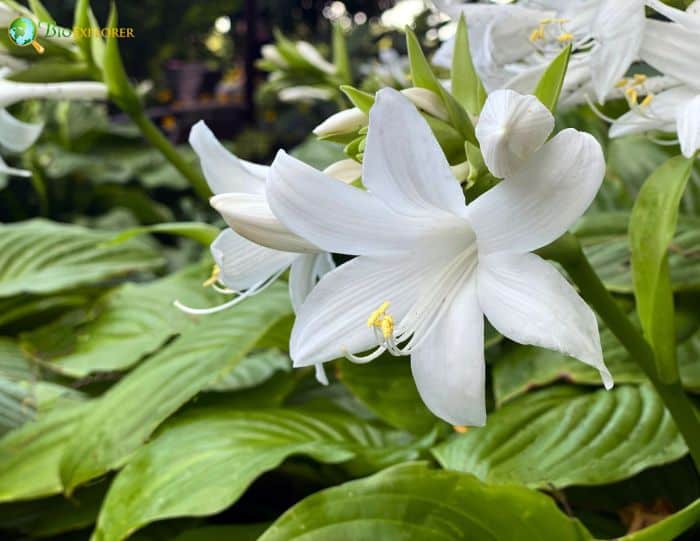
August Lily

The August Lily, scientifically known as Hosta plantaginea, is a beloved perennial plant prized for its lush foliage and fragrant white flowers. Native to southeast and south-central China, this species has captured the hearts of gardeners and horticulturists worldwide.
Its ability to thrive in shaded areas and its stunning floral display make it a versatile addition to any garden. Beyond its ornamental value, the August Lily holds significance in traditional medicine and modern scientific research.
This article delves into the various aspects of this remarkable flowering plant, from its characteristics and growing needs to its ecological benefits and scientific studies.
Jump to:
Key Takeaways
- Hosta plantaginea, also known as August Lily, is a fragrant, ornamental plant native to China.
- This plant features broad, glossy leaves and large, white, fragrant flowers.
- August Lily thrives in shaded areas with well-drained soil and moderate water needs.
- It has notable medicinal properties, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits.
- August Lily plays a vital role in garden ecosystems, providing habitat and food for pollinators.
- Scientific studies have explored its phytochemical composition, pharmacological potential, and environmental benefits.
- Fun facts about August Lily highlight its unique traits and historical significance.
What is August Lily (Hosta plantaginea)?
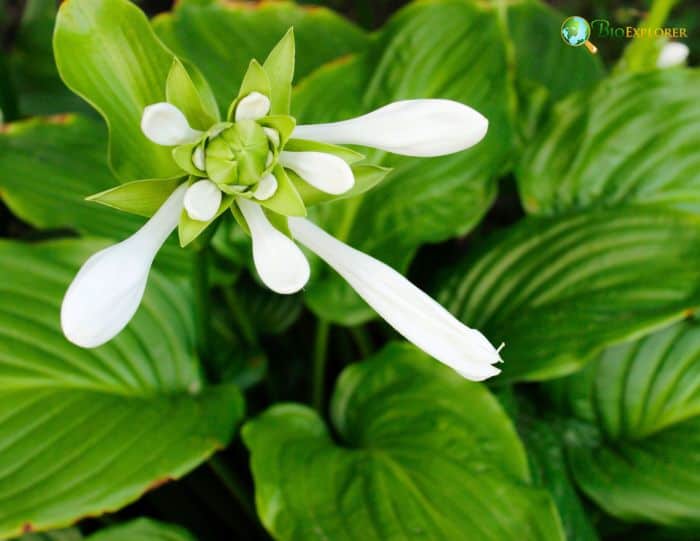

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plantae | Asparagales | Asparagaceae | Hosta | Hosta plantaginea |
- Plant Type: Perennial
- Common Names: August Lily, Fragrant Plantain Lily, Gibōshi, Banana Lilies.
- Flower Dimensions: 6 to 7 inches (15 to 18 cm) long.
- Flowering Season: Late Summer to Early Fall.
- Flower Colors: White
August Lily (Hosta plantaginea) belongs to the family Asparagaceae and is a perennial plant native to southeast and south-central China. It has also become naturalized in various parts of the world, including the United States and Europe.
The plant is known for its striking appearance and Sweet-scented flowers, which bloom in late summer, typically in August, hence the name “August Lily”.
In the wild, August Lily typically grows in the herb layer of mountain forests at altitudes below 2000 meters. It thrives in shaded or partially shaded areas with moist, well-drained soil. This adaptability to various environments has made it a popular choice for gardens around the world.
Besides “August Lily”, this plant is also known as “Fragrant Plantain Lily” or “Banana Lily” due to its large, plantain-like leaves and fragrant flowers. Other synonyms include Hosta japonica and Hosta grandiflora.
Characteristics of August Lily
The August Lily is renowned for its lush, attractive foliage and beautiful, fragrant flowers. Here, we delve into the specific features that make this plant a standout in any garden.
Leaf Structure and Coloration
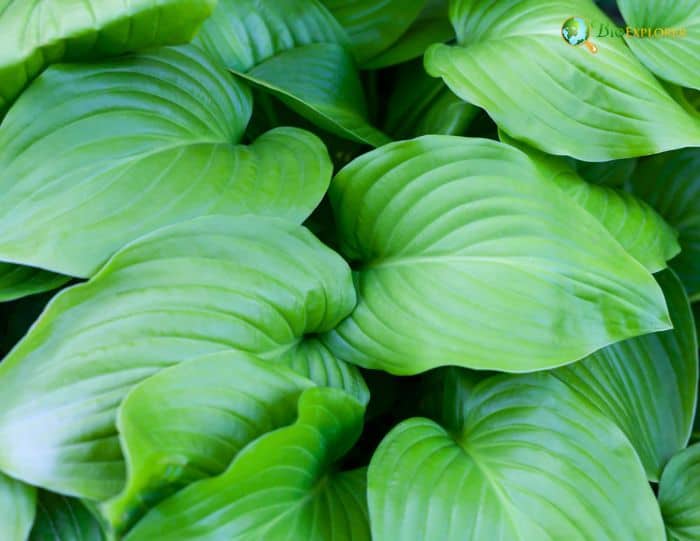

The leaves of the August Lily are green-colored, broad, ovate to heart-shaped, and can grow up to 12 inches long and 10 inches wide. They are typically bright green with a glossy surface, providing a lush, verdant backdrop in shaded garden areas. The prominent veins and smooth edges add to the plant’s aesthetic appeal.
Flower Characteristics and Fragrance
One of the most distinctive features of the August Lily is its large, pure white flowers, which can reach up to 6 inches in length. These trumpet-shaped blooms are not only visually striking but also emit a powerful, sweet fragrance, especially in the evening. This characteristic makes them a favorite for planting near patios and pathways where their scent can be fully appreciated.
Growth Habit and Size
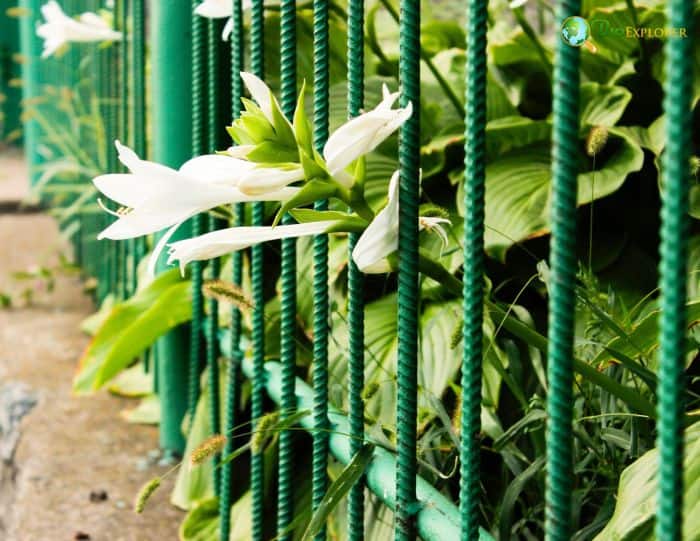

The August Lily has a clumping growth habit, with mature plants reaching up to 2 feet in height and spreading to about 3 feet wide. This size makes it an excellent choice for ground cover in shaded or partially shaded areas of the garden. The plant’s robust root system helps it establish quickly and spread moderately over time.
Life Cycle and Growth Requirements
Understanding the life cycle and optimal growing conditions of the August Lily is crucial for successful cultivation.
Soil Preferences and pH Requirements
August Lily prefers well-drained, fertile soil with a neutral to slightly acidic pH, typically between 6.0 and 7.0. Adding organic matter such as compost can enhance soil fertility and improve drainage, creating ideal conditions for the plant.
Light and Water Needs
While the August Lily thrives in shaded environments, it can tolerate some morning sun. However, too much direct sunlight can scorch the leaves. It requires moderate watering; the soil should remain consistently moist but not waterlogged. Mulching around the base of the plant helps retain soil moisture and keeps the roots cool.
Optimal Growing Conditions (Temperature, Humidity)
August Lily is hardy in USDA zones 3 to 9, meaning it can withstand a wide range of temperatures, from cold winters to warm summers. It prefers moderate humidity levels and benefits from a stable environment without extreme fluctuations.
Hosta Plantaginea Variations and Cultivars
There are several cultivars of Hosta plantaginea, each with unique traits that can add variety and interest to gardens.
- Hosta plantaginea ‘Aphrodite’: Known for its double white flowers that are even more fragrant than the species.
- Hosta plantaginea ‘Grandiflora’: Features larger leaves and flowers, making it a dramatic addition to any garden.
Each cultivar may vary in leaf size, coloration, and flower form, allowing gardeners to select varieties that best suit their aesthetic preferences and garden conditions.
Benefits and Uses of August Lily
August Lily, is widely appreciated for its ornamental value. Its lush foliage and fragrant flowers make it a versatile plant in various garden settings.
Landscaping Applications

The August Lily is perfect for shaded garden areas, under trees, or along borders. Its broad, glossy leaves provide a lush ground cover, while its tall, fragrant flowers create a striking vertical accent. This plant is often used in:
- Shaded Gardens: To brighten dark corners with its light-reflective leaves.
- Borders and Edges: As a soft, green edge for pathways and garden beds.
- Containers: For patios and balconies, where its fragrance can be enjoyed up close.
In garden design, August Lily can be paired with other shade-loving plants like ferns, astilbes, and hellebores. Its white flowers provide a contrast to darker foliage plants, adding depth and interest. Consider creating a fragrance garden by combining August Lily with other aromatic plants such as lavender and jasmine.
Medicinal Properties
The August Lily has been used in traditional Chinese medicine and continues to be the subject of modern scientific research due to its numerous medicinal properties.
In traditional Chinese medicine, August Lily is known for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. It has been used to treat conditions such as sore throat, inflammation, and fever.
Modern research has identified several active compounds in August Lily, including:
- Flavonoids: Known for their antioxidant properties, these compounds help protect cells from damage.
- Steroidal Glycosides: These have shown potential in reducing inflammation.
- Indole Alkaloids: Studied for their ability to inhibit steroid 5α-reductase activity, which is important in treating conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Case Study: A study titled “Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of Megastigmane Glycosides from Hosta plantaginea” demonstrated that compounds isolated from the plant’s flowers exhibit significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. These findings support the traditional use of the plant in treating inflammatory diseases.
Modern Research and Potential Health Benefits
Recent studies have explored the pharmacological potential of August Lily, revealing its effectiveness in:
- Reducing inflammation: By inhibiting pathways such as NF-κB signalingWhat is NF-κB signaling?NF-κB signaling is a pathway in cells that controls the expression of genes involved in immune response, inflammation, and cell survival. When activated, it helps the body respond to stress, infection, and injury by promoting inflammation and protecting cells from damage..
- Antioxidant activities: By neutralizing free radicals, thus protecting against oxidative stress-related diseases.
- Potential anti-cancer properties: Some compounds have shown promise in preliminary studies for their anti-tumor effects.
Ecological Benefits
Beyond its beauty and medicinal uses, the August Lily plays a significant role in garden ecosystems.
August Lily provides essential cover and habitat for various small animals and insects. Its large leaves offer shelter for ground-dwelling creatures, while its flowers attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies.
The fragrant flowers of the August Lily are particularly attractive to nocturnal pollinators like moths. By planting August Lily, gardeners can support local pollinator populations and enhance the biodiversity of their gardens.
Scientific Research on August Lily

Phytochemical Studies
Research into the phytochemical composition of Hosta plantaginea has revealed a wealth of active compounds that contribute to its medicinal properties.
Several studies have identified key phytochemicals in August Lily, including:
- Flavonoids: These compounds have potent antioxidant properties. Research published in the article “Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of Megastigmane Glycosides from Hosta plantaginea” highlighted the presence of new megastigmane glycosides with significant health benefits.
- Steroidal Glycosides: Identified as hostaplantagineosidesWhat is hostaplantagineosides?Hostaplantagineosides are natural compounds found in the August Lily (Hosta plantaginea). They have shown potential in reducing inflammation and providing antioxidant benefits. These compounds are currently being studied for their health-promoting properties. A, B, C, and D, these compounds are known for their anti-inflammatory effects. The study “New Steroidal Glycosides from Hosta plantaginea” provided detailed structural elucidation of these glycosides.
- Indole Alkaloids: A new indole alkaloid and eight known derivatives were isolated and shown to inhibit steroid 5α-reductaseWhat is steroid 5α-reductase?Steroid 5α-reductase is an enzyme that changes testosterone into a stronger hormone called DHT. It's involved in male traits and conditions like baldness and prostate enlargement. activity, as discussed in “Indole Alkaloids from Hosta plantaginea and Inhibition of Steroid 5α-Reductase Activities In Vitro. “.
Researchers have employed various methods to extract and analyze these compounds:
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Used to separate, identify, and quantify the chemical components.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: For structural elucidation of isolated compounds.
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): Provides detailed molecular weight and structure information.
Pharmacological Research
August Lily’s pharmacological potential has been extensively studied, revealing its therapeutic applications.
Studies have confirmed the significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of compounds extracted from August Lily:
- “Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of Megastigmane Glycosides from Hosta plantaginea”: This research demonstrated that the isolated glycosides have notable COX-1What is COX-1?COX-1, or cyclooxygenase-1, is an enzyme that helps produce prostaglandins. These chemicals protect the stomach lining, support kidney function, and aid blood clotting. and COX-2What is COX-2?COX-2, or cyclooxygenase-2, is an enzyme that produces prostaglandins involved in inflammation and pain. Unlike COX-1, it is usually activated during injury or infection to help the body respond to damage. inhibitory effects, indicating their potential as anti-inflammatory agents.
- “Hostaflavone A from Hosta plantaginea Blocked NF-κB/iNOS/COX-2/MAPKs/Akt Signaling Pathways”: This study showed that Hostaflavone A effectively inhibits multiple inflammatory pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages.
The identified compounds in August Lily hold promise for various medical applications:
- Anti-inflammatory Agents: Potential use in treating conditions such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Antioxidants: Protecting against oxidative stress-related conditions, including cardiovascular diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Anticancer Properties: Preliminary studies suggest some compounds may inhibit tumor growth, offering a potential pathway for cancer treatment.
Environmental Studies
Research has also explored the environmental benefits and interactions of August Lily, particularly its role in phytoremediation.
A study on heavy metal accumulation in bioretention plants revealed that Hosta plantaginea can effectively remove lead (Pb) from contaminated environments. This capability makes it a valuable plant for:
- Soil Remediation: Improving soil health by extracting heavy metals.
- Water Filtration: Used in constructed wetlands to clean polluted water.
August Lily contributes to the overall health of garden ecosystems:
- Soil Stabilization: Its robust root system helps prevent soil erosion.
- Improving Soil Quality: The organic matter from decaying leaves enriches the soil.
- Biodiversity Support: Providing habitat and food sources for a variety of insects and small animals.
Case Study: Fusarium Leaf Rot on August Lily
In 2022, a study titled “First Report of Fusarium ipomoeae Causing Leaf Rot on Hosta plantaginea in China” documented an outbreak of Fusarium leaf rot in Chongqing City. The study detailed the symptoms, isolation of the pathogen, and molecular identification methods. This case study underscores the importance of ongoing research and disease management strategies for maintaining healthy August Lily populations.
Fun Facts about August Lily
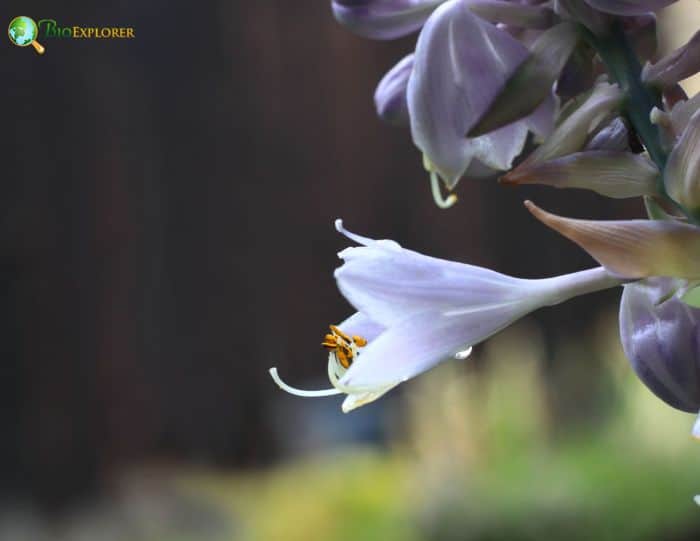

- Fragrant Flowers: The August Lily is the only species of Hosta known for its fragrant flowers. Its large, white blooms release a sweet scent, especially in the evening, making it a popular choice for nighttime gardens and walkways.
- Nighttime Blooming: Unlike many other plants, the flowers of August Lily often open in the late afternoon or early evening, and they remain open throughout the night, attracting nocturnal pollinators such as moths.
- Historical Use in Medicine: In traditional Chinese medicine, August Lily has been used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. It’s often employed in remedies to treat sore throats, fever, and inflammation.
- Versatile Growing Conditions: August Lily can thrive in a variety of soil types, though it prefers well-drained, fertile soil. It can grow in full shade to partial sun, demonstrating a remarkable ability to adapt to different garden environments.
- Easy Propagation: This plant is easy to propagate by division, making it simple for gardeners to expand their collections or share with friends. Division should be done in early spring or fall for best results.
- Scientific Interest: August Lily has been the subject of numerous scientific studies due to its unique compounds. Research has highlighted its potential in phytoremediation, helping to clean contaminated soils by accumulating heavy metals like lead.
- Variety of Cultivars: Several cultivars of Hosta plantaginea have been developed, each with unique features. For example, Hosta plantaginea ‘Aphrodite’ is known for its double white flowers, which are even more fragrant than the standard species.
- Long Blooming Season: While many plants have a short blooming period, the August Lily boasts a prolonged flowering season, typically from late summer into early fall, providing extended visual and olfactory enjoyment.
- Botanical Curiosity: The chloroplast genome of Hosta plantaginea has been sequenced, revealing fascinating details about its genetic makeup. This research helps scientists understand the evolutionary history and development of this beloved plant.
- Chameleon of the Garden: The blue hue of some August Lily leaves is actually an optical illusion! The leaves appear blue due to a waxy coating that covers them. As the wax melts away, the true green color of the leaves is revealed, making it seem like your garden plants have magically changed color over the season.
- Garden Time Travelers: Hostas, including the August Lily, have been globe-trotters long before it was cool. These plants originated in China, Korea, and Japan, and were introduced to the United States in the 1800s.
- Natural Snail and Slug Fighters: While many plants struggle with pests like snails and slugs, some hosta varieties have evolved a secret weapon to fend them off. Certain August Lily plants produce natural compounds that make their leaves less appetizing to these common garden pests.
Conclusion
The August Lily is more than just a beautiful garden plant. Its fragrant flowers, versatile growing conditions, and rich medicinal history make it a valuable addition to any garden. Whether you’re looking to enhance your garden’s aesthetic appeal or explore its potential health benefits, the August Lily offers a unique combination of beauty and utility.
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 4). August Lily. https://www.bioexplorer.net/plants/flowers/august-lily-hosta-plantaginea/

