
Importance Of Biology: Biology, the natural science dedicated to understanding life and living organisms, underpins advancements and innovations in an incredible array of areas that impact human civilization. As a fundamental science exploring the mechanisms, processes, interactions, and overarching complexity of living systems, biology provides an informational foundation for groundbreaking discoveries that shape our everyday lives.
This article dives deeper into 25 key reasons that showcase the sizable real-world impact of biological research on nearly every facet of the human endeavor. The multifaceted applications derived from the throughput of biological understanding spotlight biology as arguably humanity’s most vital science going forward.
From feeding the world to curing disease, conserving nature, and harnessing cutting-edge tech, the future powered by biological insight looks brighter than ever on our blue planet, teeming with life waiting to be explored.
Table of Contents
- Importance of Biology
- 1. Understanding the Fundamentals of Life
- 2. Unraveling Evolutionary Mysteries
- 3. Advancing Human Health: Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
- Types of Doctors
- 4. Gene and Cell Therapies: The Frontier of Treatment
- 5. Agricultural Innovations: Improving Yields and Nutrition
- 6. Sustainable Farming and Bioengineering
- 7. Conservation: Species and Ecosystem Preservation
- 8. Habitat Restoration and Environmental Management
- 9. Climate Change: Biological Insights and Solutions
- 10. Biotechnology: Synthesis and Innovation
- 11. Human Anatomy and Physiology
- 12. Career Development Across Various Fields
- 13. Solving Global Problems: Food Security and Pollution
- 14. Basic Living Concepts and Lifestyle Applications
- 15. Fundamental Questions: Origins and Existence
- 16. Scientific Investigations and Exploration
- 17. Advanced Medical Research: Regenerative and Personalized Medicine
- 18. Neurobiology and Cognitive Sciences
- 19. Botany and New Food Source Exploration
- 20. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- 21. Marine Biology and Ocean Ecosystems
- 22. Mental Health and Biological Psychology
- 23. Ethics, Education, and Biological Literacy
- 24. Microbiome Research and Human Health
- 25. Biosecurity and Disease Prevention
- Conclusion
Importance of Biology
1. Understanding the Fundamentals of Life
Biology provides an unparalleled window into life’s origins, diversity, workings, genetics, and evolution. By studying the basic building blocks that constitute life–like cells, DNA, proteins, organs, and tissues — scientists uncover secrets of how living organisms grow, develop, adapt and interact with the environment.
Fundamental biological discovery reveals life’s operational blueprints through areas like:
- Molecular Biology: Studying cellular molecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins underpinning life.
- Microbiology: Understanding microscopic organisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi.
- Physiology: Analyzing functions and mechanisms of organs, organ systems.
- Anatomy: Investigating physical structures of organisms.
As researchers connect the dots between chemistry, physics, and biology, new paradigms like molecular evolution emerge by integrating different disciplines.
Groundbreaking work across the 20th and 21st centuries in untangling DNA’s double helical structure, the Central Dogma of molecular biology, evolutionary trees, the genetic code, bioelectricityWhat is bioelectricity?Bioelectricity refers to the electrical energy produced and used by living organisms, crucial for processes like nerve signal transmission and muscle contraction., epigenetics, CRISPRWhat is CRISPR?CRISPR, which stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, is a cutting-edge genetic editing tool enabling precise alterations to DNA in living organisms. gene editing, and countless other elemental concepts form the very foundation for trailblazing advances in medicine, biotechnology, neuroscience, agriculture and more.
By revealing biology’s instruction manual — from biomolecules to entire ecosystems — fundamental research lays the conceptual groundwork for applications furthering human innovation and bolstering the quality of life. Ongoing biological discovery constantly rewrites the playbook for what’s possible in leveraging life’s inner workings for good.
Suggested Reading:
10 Levels of Biological Organization
2. Unraveling Evolutionary Mysteries

Charles Darwin’s landmark ideas on evolution via natural selection utterly transformed humanity’s understanding of where we came from and how life diversified over eons. Evolutionary biology research reconstructing the Tree of Life continues to illuminate life’s interconnectedness while revealing the drivers of biodiversity and adaptation over geological ages.
Powerful insights unlocked by evolutionary biology include:
- Evolutionary relationships between organisms based on morphological, anatomical, genetic, and fossil data.
- Elucidating adaptation and convergence in organism traits shaped by ecology.
- Genomic studies comparing key model organisms to retrace evolutionary steps.
- Tracing evolutionary origins of crucial physiological developments like the eye, brain, and cardiovascular system over hundreds of millions of years.
- Reconstructing extinct species phenotypes using new techniques in paleogenomics.
Ongoing work in evolutionary development sheds light on alterations in developmental pathways establishing diversity in body plans between different phyla. Long-term evolution experiments directly demonstrate evolution in action, tracking generational microevolution in bacteria, fruit flies, and more.
Studying evolution gives researchers tools to forecast viral or cancer cell mutation rates, design smarter conservation initiatives to protect biodiversity, bioengineer novel microbes, domesticate improved livestock breeds, combat antibiotic resistance through genomic epidemiology, and make custom designer enzymes using directed protein evolution.
Altogether, biology’s billion-year backlog of evolutionary knowledge presents a goldmine of nature’s ingenious solutions waiting to be studied and emulated.
Suggested Reading:
Woolly Mammoth Clone Project: Can It Be Resurrected?
3. Advancing Human Health: Medicine and Pharmaceuticals

Biomedical research and translational medicine depend intrinsically on foundational biology to make game-changing improvements in detecting, diagnosing, understanding, and treating different diseases.
Cutting-edge areas where biological knowledge drives better healthcare encompass:
- Molecular medicine: Harnessing genetics/omics data for personalized diagnostics and therapies.
- Pharmacogenomics: Tailoring medications per patient genetics, ensuring safety and efficacy.
- Regenerative medicine: Using stem cell and tissue engineering innovations to regrow damaged organs.
- Microbiome therapies: Tweaking resident gut bacteria composition to improve health.
- Gene therapy: Correcting root genetic causes of disease by editing mutated genes.
- Immunotherapy: Weaponizing the immune system against cancer and autoimmunity.
- Neuroprosthetics: Interfacing bionic limbs directly with the nervous system to restore motor control.
Additionally, essential drug development relies on biological and biochemical techniques like:
- High-throughput screening of compound libraries against target proteins, cells.
- Structural Biology determining therapeutic molecule binding modes.
- Bioinformatics modeling of drug interactions, adverse effects.
- Clinical trials assessing safety, efficacy per biology of disease.
Without sustained lab and clinical research probing life’s intricacies, the promise of scientific medicine collapses. Biopharmaceutical milestones like insulin therapy for diabetes, monoclonal antibodies fighting cancer, statins lowering cholesterol, and nucleic acid vaccines against viruses illustrate biology’s immense capacity to relieve suffering when translated through the drug discovery pipeline.
Suggested Reading:
Types of Doctors
4. Gene and Cell Therapies: The Frontier of Treatment
Beyond conventional drugs, revolutionary medical advances rely on directly leveraging cellular or genetic manipulations to cure disease. Cutting-edge gene and cell therapies build on foundational genetics and molecular biology to fix root biological causes of cancer, genetic conditions, and degenerative disease.
Gene therapy approaches correct disease-causing genetic defects by:
- Introducing functional genes via engineered viral vectors.
- Eliminating mutant sequences using programmable nucleases like CRISPR.
- Editing single mutated DNA bases using new base editor systems.
Cell therapy methods like those below reignite regenerative potential:
- Stem cell transplantation restores damaged tissue by differentiating into specialized cell types.
- T-cell engineering supercharges immune cells against pathogens and cancers.
- Tissue engineering employs biocompatible scaffolds facilitating organ regeneration.
Pioneering clinical milestones include:
- Gene therapies curing congenital blindness and spinal muscular atrophy.
- CAR T-cell immunotherapy driving leukemia remission.
- Bioengineered skin grafts healing severe burns and diabetic ulcers.
- Lab-grown organoids mimicking human organ microanatomy for drug testing.
Accelerating the adoption of such interventions promises a new era of personalized, biology-driven medicine — where root genetic culprits of disease are precisely edited at the molecular level while engineered cells are customized to each patient.
Suggested Reading:
Top 34 Gene Therapy Pros and Cons
5. Agricultural Innovations: Improving Yields and Nutrition
Feeding the world’s booming population sustainably depends increasingly on biological research intersecting plant and animal sciences. Improving agricultural productivity while conserving resources hinges on biology-powered farming advances encompassing:
Enhanced crop breeding via:
- Marker-assisted selection identifying gene variants boosting yields.
- Genome editing using CRISPR to accelerate crop improvements.
- Microbial bioprospecting finding plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria.
Optimized animal husbandry through:
- Probiotic supplements enhancing livestock digestive health.
- Manipulating rumen microbiomes for better feed digestion efficiency.
- Data-driven smart farming tracking cattle genetics and milk yields.
Food biofortification via:
- Metabolic Engineering Boosting Golden Rice Vitamin A Levels.
- Enriching tomato and potato antioxidant concentrations.
- Mining diverse seed varietals to uncover heartier, more nutritious strains.
Altogether, biotechnology and food science breakthroughs will enable more food production on less land with fewer inputs. Tailoring crops to regional climates and soils while creating resilient lineages will be key to nourishing the planet.
Suggested Reading:
6 Major Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Foods
6. Sustainable Farming and Bioengineering

Alongside boosting agricultural output, innovations in sustainable farming enabled by biological and ecological insights remain imperative for long-term food security. Biology offers solutions reconciling future needs with environmental limits through:
Regenerative agriculture paradigms:
- No/low till methods maintaining soil biodiversity.
- Cover cropping and crop rotation to improve soil health.
- Integrated pest control, minimizing synthetic chemical usage.
Biological microbe-based amendments:
- Biofertilizers fixing nitrogen and increasing mineral availability.
- Biopesticides leveraging pathogens/microbes to control pests.
- Mycoherbicides utilizing fungi to defeat herbicide-resistant weeds.
Biomass-derived biofuels and bioproducts like:
- Cellulosic ethanol made from crop residues or grasses.
- Microbial oils converting algal lipids into renewable diesel.
- Bioplastics created using synthetic biology platforms.
Livestock microbiome tweaking for:
- Increased growth rates and meat/dairy yields.
- Enhanced ruminant digestion of grasses/fodder.
- Reduced enteric methane emissions from cattle.
Stewarded properly through evidence-based biological inputs, the global farm can transform into a robust regenerative ecosystem supporting abundant human civilization while nurturing rich biodiversity.
Suggested Reading:
Top 20 Biomass Energy Pros and Cons
7. Conservation: Species and Ecosystem Preservation

As Earth’s sixth mass extinction gathers steam, conservation biology leveraging diverse biological data plays a crucial role in preserving threatened species and vulnerable ecosystems. Key conservation methods informed by organismal biology include:
- Population monitoring: Tracking species demographics and geographic ranges to model extinction risk.
- Genetic rescue: Augmenting inbred populations with offspring from a wider gene pool.
- Assisted migration: Managed relocation of species to more hospitable habitats.
- De-extinction: Using genomic data synthetic biology to resurrect extinct species.
Conserving ecosystems hinges on maintaining vital ecological and evolutionary processes that sustain all inhabitants. Tactics like protected area management, habitat corridor construction, and ecosystem restoration require grounding in community ecology and the abiotic/biotic factors enabling resilience.
Emerging biome-scale conservation frameworks like rewilding boost landscapes’ carrying capacity for rich biodiversity based on inherent environmental features and historical species assemblages. Advanced simulation models also allow predictive analysis guiding evidence-based conservation actions under climate change.
Advancing conservation ultimately requires understanding the complex living networks, evolutionary capacities, and ecological interactions that permit species and environments to persist. Biology illuminates paths for orchestrating human activities around this biosphere, sustaining all life.
Suggested Reading:
40 Different Types of Birds
8. Habitat Restoration and Environmental Management

Beyond preserving existing ecosystems, applied environmental biology informs active habitat restoration initiatives seeking to heal and revitalize damaged or polluted areas. Key principles from community ecology, landscape architecture, ecotoxicology, and more guide approaches to rehabilitating struggling regions:
- Reforestation of degraded forestlands.
- Waterway revitalization removing invasive species/pollutants.
- Wetlands regeneration via hydrology restoration allows native plants to recover.
- Coral reef reconstruction through sexually reproduced nurseries.
Environmental planning relies on biological indices measuring ecosystem health plus stressor agent transport models balancing urban development with conservation. Additional solutions supplied by environmental biology include:
- Bioindicators like lichens assessing regional air pollution levels.
- Phytoremediation utilizing plants to absorb toxic waste.
- Biomimicry innovations inspired by nature’s efficient designs.
- Integrated landscape management fusion of diverse data layers to optimize land use.
Insights from various biological specialties equip science-supported regeneration of green spaces, nurturing native flora and fauna while sustaining clean air, water, and soil, supporting human communities.
Suggested Reading:
Top 15 Current Environmental Issues in the US
9. Climate Change: Biological Insights and Solutions

Climate change represents an existential threat to global ecosystems, making biological studies of its myriad impacts pivotal for mitigation and adaptation. Key climate domains where biology proves critical encompass:
- Ecological impact assessment: Documenting timing mismatches in predator-prey relationships, disruptions of sensitive niche habitats, shifting of species geographic ranges and migration calendars, coral bleaching, pest and pathogen outbreaks, and invasion of noxious weeds.
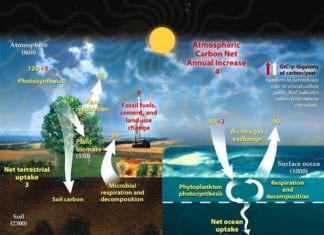
- Carbon sequestration: Investigating the carbon storage potential of marine ecosystems, soil biology, forest biomass, and geological formations to model natural climate solutions like coastal blue carbon habitats and afforestation.
- Renewable energy innovations: Using synthetic biology to engineer microbes generating biohydrogen and oils for the bioeconomy while studying extremophiles like thermophilic bacteria to guide enzyme design.
- Climate-adapted agriculture: Exploring the genetics behind heat/drought-resistant crop variants, livestock breeds better acclimated to warmer environments, and growth-enhancing microbiome shifts.
- Earth systems modeling: Building computational simulations integrating biogeochemical cycles, ecological processes, and feedback dynamics to forecast climate change downstream effects.
Though climate change stems from physics and chemistry, its ultimate ramifications manifest across Earth’s interconnected ecosystems and organisms — the remit of biological sciences.
Suggested Reading:
Carbon Cycle Steps: Overview & Importance in Biosphere
10. Biotechnology: Synthesis and Innovation

Beyond insights into fundamental biology, direct applications leveraging biological systems as platforms for innovative designs and green technology constitute another vast domain unlocking immense potential. Top biotechnology areas fueled by biological knowledge include:
- Synthetic Biology: Designing and constructing novel biomolecular components, circuits, and pathways for programmable purposes.
- Industrial Biotechnology: Harnessing microbial metabolism for efficient chemical manufacturing with reduced waste.
- Agricultural Biotechnology: Genetic engineering of designer crops and livestock using CRISPR and other biotechnologies.
- Environmental Biotechnology: Employing microbes and biosystems for renewable energy, bioremediation, and biomaterials.
- Biosensors and Diagnostics: Integration of biology with nanotechnology and computing for point-of-care analytic devices.
- Biomanufacturing -Scaled-up precision fermentation platforms brewing pharmaceuticals, textiles, and nutraceuticals.
Additionally, burgeoning fields like digital biology, which create biological-electronic interfaces and intelligent sensor-actuator closed-loop systems, continue pushing the envelope ever further.
Fundamentally, biotechnology success depends wholly on humanity’s collective biological knowledge bank. Continued exploration of natural wonders and mysteries thus begets ever-expanding practical innovation.
11. Human Anatomy and Physiology
Understanding the structures and functions of the human body stands as a cornerstone of biology with immense medical relevance. Anatomical mapping of human organ systems, tissues, and cellular architecture provides an informational scaffold for physiology research unraveling operational mechanisms powering life.
Core insights unlocked by human biology span:
- Elucidating the endocrine system’s glandular secretion of regulatory hormones.
- Documenting the cardio-respiratory system‘s delivery of oxygen and nutrients supporting cellular metabolism.
- Characterizing the nephron’s filtration of blood to remove waste while maintaining electrolyte balance.
- Modeling neurotransmission underlying neural communication throughout the nervous system.
- Describing musculoskeletal leverage of skeletal structure through coordinated muscle contraction during body movement.
Additionally, the study of embryology traces human morphological development from fertilized ovum to fetus and birth. Evolutionary remnants in human anatomy, like the recurrent laryngeal nerve route around the heart, reflect shared common descent.
Altogether, the foundational mapping of human biology constitutes a cornerstone supporting modern medicine — helping decipher disease etiologies when homeostasis goes awry while informing surgical interventions. Ongoing work continues, revealing elegant examples of nested complexity at localized scales from biomolecules to the coordinated whole.
Suggested Reading:
14 Best Anatomy and Physiology Books
12. Career Development Across Various Fields

Beyond direct research, foundational literacy in biological concepts, terminology, and techniques prepares students for diverse career pathways in healthcare, tech, environment, policy, education, and more by honing critical thinking and technical skills.
Common biology-related roles include:
- Doctors: Physicians, dentists, pharmacists, nurses, physical therapists.
- Scientists: Biologists, biotechnologists, biochemists, epidemiologists, ecologists.
- Engineers: Biomedical, genetic, agricultural/environmental.
- Technicians: Lab technicians, dental hygienists, physician assistants.
- Business: Pharmaceutical sales, biotech venture capital, science publishing.
- Law: Intellectual property, healthcare regulations.
- Policy: Science advisors, conservation officers, public health officials.
- Education: Teachers, university lecturers, museum curators.
Hands-on biological training develops competency in data analysis, modeling, laboratory methods, bioethics considerations, and communicating science — assets transferrable beyond bench research. Understanding biology also fosters an appreciation of environmental interdependence and empathy for all life.
In essence, biology coursework opens professional avenues and cultivates an informed, compassionate worldview benefiting any career path.
Suggested Reading:
Biology Boomtowns: 10 Best US Cities for Job Opportunities
13. Solving Global Problems: Food Security and Pollution

As humanity’s most pressing issues stem directly or indirectly from biological systems, scientific insights offer paths to mitigate interlinked challenges like food insecurity, environmental decline, disease emergence, and climate instability.
- For example, biofortified vitamin-enriched crops and CRISPR gene edits conferring resistance to pests, pathogens, and drought can enhance nutrition and resilience in the food system. Optimizing photosynthetic efficiency promises higher-yielding plant varieties needing less land.
- Pollution abatement successes highlight phytoremediation using sunflowers to absorb toxic heavy metals, mycoremediation leveraging fungi-eating oil spills, and biodegrading plastic with enzyme tweaks. Additional biotechnology solutions range from algal biofuel production to microbial electrosynthesis of commodity chemicals.
- Drug-resistant infection cure rates can be improved by understanding evolutionary dynamics and targeting non-coding regulatory elements or virulence factors. Surveillance of zoonotic disease reservoirs also allows preemptive vaccine development.
- While biological exploitation underlies sustainability crises, its principled application conversely enables redemption through revelatory systems analysis, technological innovation, and ecological restoration guided by nature’s wisdom.
Suggested Reading:
Types of Flowers
14. Basic Living Concepts and Lifestyle Applications
Insight into core life principles directly informs healthy diet, exercise, and wellness choices. For instance, appreciating digestion mechanics, nutritional biochemistry, and microbiome activities encourages more informed dietary decisions, boosting energy, immunity, and longevity.
Likewise, grasping the basics of human metabolism, muscle physiology, and the endocrine system’s response to workouts enables safer, more efficient exercise regimens supporting weight loss or athletic goals.
Regarding mind-body connections, psychoneuroimmunologyWhat is psychoneuroimmunology?Psychoneuroimmunology is the study of how psychological processes, the nervous system, and the immune system interact and affect each other. traces signaling between the immune system, nervous system, and external environment — revealing stress-reduction techniques that potentially prevent inflammation-linked disorders.
Botanical reagents from willow bark to yeast fermentation have fueled traditional medicines for millennia. Pharmaceutical prospecting continues harnessing phylogenetic knowledge of overlooked biomes like rainforest ecosystems harboring rich biodiversity with therapeutic potential.
Overall, lifestyle fields from nutrition to herbalism to mindfulness are grounded fundamentally in illuminating healthy biological function. This everyday biological literacy empowers individuals to pursue flourishing through evidence-based self-care regimens that are fine-tuned to individual needs.
Suggested Reading:
Top 25 Endocrine System Fun Facts
15. Fundamental Questions: Origins and Existence

Philosophical quandaries about life’s meaning, origins, and fundamental nature represent knowledge gaps where biological sciences strive to shed light. Research programs exploring such open-ended lines of inquiry encompass:
- Abiogenesis: Seeking clues to unravel life’s genesis on Earth through seminal experiments like Miller-Urey’sWhat is Miller-Urey's experiment?The Miller-Urey experiment, conducted in the 1950s, was a groundbreaking study that simulated early Earth's conditions to demonstrate the potential formation of organic compounds, essential for life, from simpler inorganic substances. 1950s simulated primordial soup sparking amino acid synthesis. Ongoing work investigates geological/hydrothermal reactions begetting complex organics while assessing biosignatures distinguishing biotic from abiotic origins.
- Astrobiology: Questing for extraterrestrial life and biosignatures beyond Earth by investigating extreme habitats showing life’s resilience; identifying potentially habitable exoplanets; searching for organic indicators in samples from Mars’s icy moons like Europa.
- Artificial Life: Attempting digital simulations of evolutionary dynamics through avatars in virtual worlds. Programming reproducing synthetics like cyberplasm further blurs definitions of life by creating autonomous living technology.
- Consciousness Studies: Probing neurobiological substrates of awareness and phenomenal experience within integrated information theory frameworks using tools ranging from EEGWhat is EEG?EEG, or Electroencephalography, is a non-invasive medical test that records electrical activity in the brain using small electrodes attached to the scalp. to neural network models to philosophical discourse on qualia.
Though concrete answers remain scarce, the compelling quest itself builds foundations of knowledge inhabited by future generations.
Suggested Reading:
History of Biology
16. Scientific Investigations and Exploration

The scientific method pioneered natural philosophers’ transition into modern scientists by formalizing evidence-based testing of falsifiable hypotheses. Biology has embraced and extended various knowledge-discovery techniques like:
- Fieldwork expeditions document unfamiliar flora and fauna, survey ecosystems, and sample environmental DNA from niches like deep-sea hydrothermal vents to Arctic tundra. Findings expand biodiversity logs and inform conservation priorities.
- Microscopy advances enabling magnified study of cells, intracellular structures, infectious agents, and tissues with rising clarity to nanometer scales. CryoelectronWhat is Cryoelectron?Cryoelectron microscopy is a scientific technique that involves freezing biomolecules in mid-movement and visualizing them at atomic resolution, useful for studying the structures of cellular components. imaging achieves near-atomic visualization of ephemeral protein complexes and dynamic processes.
- Omics proliferation fusing biochemistry, genetics, and computational power to globally profile biological system components spanning genomicsWhat is genomics?Genomics is the study of genomes, the complete set of DNA in an organism, encompassing its structure, function, evolution, and mapping., epigenomicsWhat is epigenomics?Epigenomics is the comprehensive study of epigenetic modifications on the genetic material of a cell, which affect gene expression without altering the DNA sequence., transcriptomicsWhat is transcriptomics?Transcriptomics is the study of the transcriptome, the complete set of RNA transcripts produced by the genome, under specific circumstances or in a specific cell., proteomicsWhat is proteomics?Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteomes, the entire set of proteins produced or modified by an organism, to understand their structures and functions., metabolomicsWhat is metabolomics?Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule intermediates and products of metabolism in a biological system., and metagenomicsWhat is metagenomics?Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples, allowing for the analysis of communities of organisms without needing to isolate and culture individual species..
- Model organisms like bacteria e.coli, nematode C. elegans, fruit fly Drosophila, and lab mouse Mus musculus serve as experimental testbeds, offering convenience, speed, and analytical power for hypothesis testing within biomedical research.
Altogether, the objective practice of probing life’s mysteries systematically constructs an ever-clearer picture of our living planet while propelling technology transformation.
Suggested Reading:
25 Mind-Blowing Biology Breakthroughs That Shaped Our World!
17. Advanced Medical Research: Regenerative and Personalized Medicine
The avant-garde of healthcare involves leveraging genomic insights, synthetic biology tools, and stem cell science to customize curative interventions to each patient’s unique biology. Known as precision or personalized medicine, this emerging paradigm promises superior outcomes by targeting the molecular underpinnings of disease.
Key innovations include:
- Cell atlases mapping the hundreds of specialized human cell types and associated genetic markers enabling targeted therapy.
- Organoid modeling using stem cells to grow miniaturized organ proxies for pathogenic and pharmacologic testing.
- Gene editing corrects disease-causing mutations, disables viral entry proteins, and supercharges T-cell potency.
- DNA nanotechnology allows ultra-precise delivery of chemotherapeutics masked as viruses invading tumors.
- Bioelectronic medicine uses nerve stimulation to tweak organ function, control inflammation, and regulate the microbiome.
Additionally, integrated diagnostics now provide comprehensive multi-omics profiling — encompassing genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and more to inform personalized treatment.
Together with regenerative medicine breakthroughs in tissue engineering and biofabrication of organs, the future healthcare ecosystem will harness exponential technological growth rooted fundamentally in ever-expanding biological knowledge.
Suggested Reading:
How Are Viruses Different From Bacteria?
18. Neurobiology and Cognitive Sciences
Fundamental insights unlocked by studying the nervous system and cognition run the gamut from synaptic signaling pathways underlying memory formation to emerging frameworks explaining consciousness.
Cutting-edge neuroscience research directions include:
- Whole-brain neural activity mapping in model organisms like fruit flies and zebrafish to clarify connections between clustered neuron firing and behaviors.
- Optogenetics ingeniously uses light-responsive opsins to precisely activate or silence target brain circuitry.
- Computational neuroscience modeling brain regions and systems-level function using statistics, machine learning, and AI to test theories.
- Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) enable paralyzed patients to control prosthetic limbs with just thoughts.
- Psychedelic-assisted therapy leveraging substances like psilocybin to treat psychiatric diseases, including addiction, depression, and PTSD. .
Teasing apart the staggering biological complexity behind psychology, emotion, personality, intelligence, decision-making, and other quintessential human qualities remains an unfinished grand challenge calling generations of brain scientists to come. The cerebral summit presents perhaps biology’s ultimate unconquered peak.
19. Botany and New Food Source Exploration

Beyond staple cereal crops and produce offerings at the grocery store lies a neglected cornucopia of obscure, underutilized plants containing untapped human nutritional and medicinal value.
Researchers are cataloging and assessing properties of little-known species like:
- Moringa trees with antioxidant and amino acid-rich leaves.
- Andean lupin beans packed with vegetarian protein.
- Sacha inchi jungle vines bearing omega-3-rich seeds.
- Sky fruit trees yielding antioxidant-loaded berry-vegetables.
- Lemongrass herb containing antimicrobial citral compounds.
Explorations also continue in extreme ecosystems hosting improbably hardy flora, like succulents growing in Saharan deserts and mosses embedded within Antarctic sea ice.
Structural characterization of exotic phytochemicals further informs nutritional supplementation and drug development. For instance, dragmacidins from tropical tree species show potent anti-cancer cell line activity.
Altogether, bioprospecting flourishing niches of Earth’s plant biodiversity offers sustainable paths to enhance global nutrition while unearthing potent medicines synthesized naturally through evolutionary time.
Suggested Reading:
History of Botany
20. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology

The exponential rise of biological data from high-throughput DNA sequencing, molecular dynamics simulations, proteomic mass spectrometry, and other sources demands cutting-edge computational analysis. Bioinformatics bridges biology, computer science, mathematics, and statistics to unravel complex phenomena.
Notable techniques include:
- Machine learning algorithms predict protein structures, clinical outcomes, evolutionary relationships, and more based on multivariate biomolecular data.
- Molecular modeling estimating drug candidate binding affinities and optimizing chemical structures for potency.
- Systems biology dynamically simulates complex gene regulatory, protein interaction, cell signaling, and metabolic networks using supercomputers.
- Synthetic biology programming novel genetic circuits, biosynthetic pathways, and whole genome assemblies using principles from electrical engineering.
- Precision medicine leveraging AI alongside genomics and multi-omics profiling to enable personalized diagnostics/treatment.
Looking forward, ubiquitous sensors and exponential data growth will accelerate biotechnology advances through increasingly sophisticated analytics, automation, and designed learning systems.
21. Marine Biology and Ocean Ecosystems

Earth’s oceans, covering over 70% of the planet’s surface, host monumental diversity-supporting key global cycles, climate regulation, and human sustenance. Investigating marine biology thus offers bountiful research directions:
- Documenting life inhabiting extreme lightless hydrothermal vent, subglacial, and seabed ecosystems.
- Tracing evolutionary adaptation in marine species to inform genetic engineering innovations.
- Conservational genomics preserving endangered whales, sea turtles, and coral species.
- Microbiome tweaking to improve aquaculture and fish hatchery yields.
- Exploring anti-cancer and antimicrobial properties of sponge, algae, and ascidian compounds.
- Engineering photosynthetic ocean-farmed algae as biofuel sources.
- Studying Psychological benefits of “blue environments” on mental health.
- Modeling shifting ocean currents, oxygen levels, and acidification from climate change.
Additionally, seafloor sediment contains unique paleoenvironmental records spanning millennia — unlocking evidence of prehistoric mass extinctions, climate shifts, and their impacts on marine species distribution and biodiversity.
Marine scholarship offers humanity boundless frontiers brimming with planetary life support systems, pharmaceutical promise, evolutionary wisdom, and more drowned treasures awaiting discoverers sailing science’s uncharted waters.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Best Marine Biology Colleges
22. Mental Health and Biological Psychology
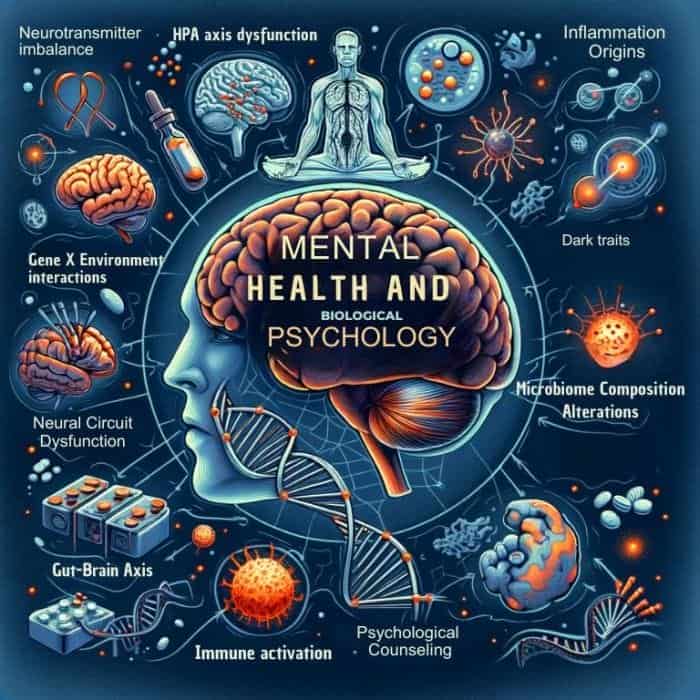
The biology underlying mental well-being and common psychiatric conditions like anxiety, mood disorders, and addiction is being unraveled through brain imaging studies, genomic analysis, and psychopharmacology.
Key developments showcasing biology’s role include:
- Neurotransmitter Imbalance: Depression implicated in serotonin deficiency; ADHD linked with dopamine dysfunction.
- HPA Axis Dysfunction: Chronic stress disrupting hypothalamic-pituitary regulation of cortisol.
- Inflammation Origins: Immune activation and cytokineWhat is cytokine?Cytokines are proteins released by cells that act as signaling molecules to regulate immunity, inflammation, and blood cell production. release sparking lowered neurogenesis.
- Gut-brain Axis: Microbiome composition alterations driving anxiety and other disorders.
- Gene X Environment Interactions: Stress or trauma generating epigenetic changes increasing disease risk.
- Neural Circuit Dysfunction: Oversensitive amygdala alarm response manifesting as PTSD.
- Dark Traits: Psychopathy and narcissism tied to underactive empathy circuitry.
Integrative approaches blending psychological counseling with prescription psychoactive medications that modulate specific biological pathways demonstrate clinical success. Nonetheless, much remains undiscovered at the murky intersection of body, brain, and mind.
Suggested Reading:
How To Become A Sleep Doctor?
23. Ethics, Education, and Biological Literacy

Studying biology and the history of science highlights ethical considerations when pursuing knowledge that affects lives through medicine, technology, and policy. Bioethics frameworks evolved steering codes of responsible conduct like informed consent, limited dual-use research, and fair access to treatments developed using public funding.
Science education centered on evidence-driven biological pedagogy also proves crucial for training new generations of diverse professionals and informed citizens who can leverage insights for societal betterment.
More broadly, fostering a wide public understanding of genomes, germs, brains, ecosystems, and other bio-based topics underpinning life improves everyday decision-making about:
- Personalized medicine exploring genetic disease risk counseling.
- Infectious disease mitigation via vaccines and behavioral modification.
- Neuro-nutrition strategically optimizing diets to nourish the mind and body.
- Wildlife conservation policy grounded in scientific population data.
- GMO legislation balancing anti-hunger benefits and ecological stewardship.
- Climate change attitudes calibrated to scientific consensus on anthropogenic global warming.
Fundamentally comprehending the science sustaining one’s health and surrounding environment signifies an underrated pillar of functional democracy.
Suggested Reading:
24. Microbiome Research and Human Health
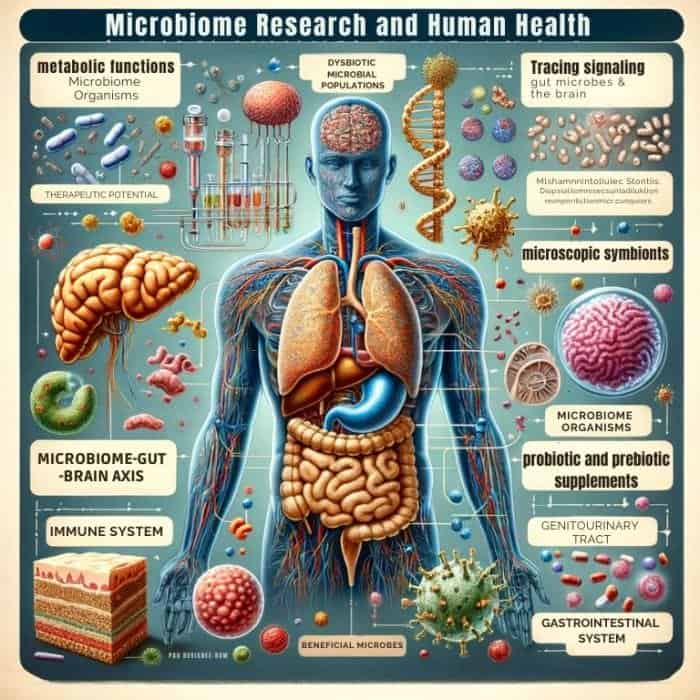
The microbiome encompassing trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi inhabiting the gastrointestinal system, respiratory passages, skin, and genitourinary tract influences human health. Deciphering microbiome contributions represents an exploding arena of biology with therapeutic potential.
Ongoing investigations focus on:
- Cataloging and modeling metabolic functions of microbiome organisms.
- Tracing signaling between gut microbes and the brain via the microbiome-gut-brain axis.
- Revealing roles of specific strains in training the immune system after birth.
- Associating dysbiotic microbial populations with disorders from autoimmunity to mental illness.
- Transplanting fecal matter containing beneficial microbes to treat intractable C. diff infections.
- Developing probiotic and prebiotic supplements that encourage favorable bacteria.
- Engineering synthetic microbiomes with enhanced genotypes better-promoting health.
As a key gatekeeper and metabolic organ, the microbiome offers medicine a pathway for correcting root dysfunction or imbalance from the inside out simply by adjusting populations of microscopic symbionts.
25. Biosecurity and Disease Prevention

Insights from epidemiology, microbiology, and public health biology inform infection control policies and biodefense, protecting human civilization from natural and artificial biohazards ranging from emergent pathogens to bioterrorism.
Strategic biosurveillance applications include:
- Global microbial genome databases for early detection of outbreak strains.
- Viral phylogenetic analysis revealing zoonotic spillover and mutation threats.
- Modeling prion, bacteria, and fungus infectious dynamics and transmission.
- Contact tracing harnessed against fast-spreading infections.
- Vaccine and therapeutic pipelines accelerated against known priority threats.
- Syndromic monitoring in clinics and hospitals identifying unusual morbidity.
- Screening global cargo supply chains for tampering or biowarfare agents.
Proactive investment in worldwide infectious disease intelligence, diagnostics development, medical countermeasures, and public health systems resilience pays perpetual dividends by upholding collective biosecurity. As COVID-19 demonstrated, robust preparedness represents society’s first defense should microscopic disasters strike.
Conclusion
The diverse biological domains highlighted across these 25 reasons underscore the monumental societal impact of advancing humanity’s understanding of life and living systems.
From foundational basic research probing the fundamental workings of cells, organisms, and ecosystems to translational applications revolutionizing medicine, agriculture, conservation, and technology – biological sciences empower breakthrough innovations that tangibly transform lives.
The ongoing investigation of genetics, physiology, evolution, symbioses, and more reveals emerging potentials limited only by curiosity and resources invested into the web of research constellations illuminated by biology’s central guiding light.
As a wellspring of possibility seeded by nature over billions of years, the living world offers an idea factory constrained solely by ethical imagination. Probing biology unlocks tomorrow’s solutions rooted in eons of evolutionary wisdom.
Through insight bridging the gulf between the mysteries of natural phenomenon and human innovation, biology allows its students to glimpse providential futures bettered by molecular manipulations, medical miracles, ecological enhancements and symbiotic synthesis with life’s genius.































It improves our understanding of diseases and their causes, prevention, and treatment
Thanks, it was really helpful.
It’s the key to the knowing of any other discipline to life
The life sciences are very close to us, and there is a lot of scientific knowledge to discover.
It’s all true, The importance of Biology helps us to know more about ourselves than how we know ourselves.
Good work
biology is really helpful?????
yes it is. especially in knowing the basic processes in the life of organisms especially humans and how to solve problems related to the environment and life as a whole
Biology help us to know the real nature of living things
Biology helps us to know the uniqueness of some creation.
That’s right