A sports medicine physician is a medical doctor who diagnoses explicitly and treats injuries and conditions related to sports activities. These specialists often work with sports teams, dance companies, or specialized schools.
In this page, explore what is sports medicine, different types of sports doctors, what do sports physicians do, different types of sports injuries, how to become a sports medicine doctor, and the average salary for sports doctors in the United States.
Table of Contents
- What is Sports Medicine?
- Types of Sport Medicine Specialists
- What is A Sports Medicine Physician?
- What Do Sports Medicine Physicians Do?
- What are the Sports Injury Treatment Options?
- What are Sports injuries?
- How to Become a Sports Medicine Physician?
- What is a sports medicine specialist salary?
- Additional Resources
- Key References
What is Sports Medicine?

Sports medicine specializes in helping people improve their athletic performance, recover from injury, and prevent future injuries. Sports medicine is one of the fast-growing and high-demanding health care specialty. Sports medicine physicians help not only athletes but also all types of people in physically demanding jobs such as construction workers.
![]()
Types of Sport Medicine Specialists
Within sports medicine, there are three major categories of specialists, namely:

- Physical therapists: Physios help injured people in sports to quickly rehabilitate and recover from injuries by performing physical therapy such as adjustments and massage treatments.
- Certified athletic trainers: These sports medicine specialists provide rehab exercise routines to help patients recover strength. Additionally, they work with the patients on conditioning programs to avoid future injury.
- Nutritionists: The last category of doctors within Sports medicine are nutritionists. They help athletes with required weight loss or weight gain. Also, they provide dietary advice to help people improve their physical functioning.
![]()
What is A Sports Medicine Physician?

A sports medicine physician has specialized training in both the treatment and prevention of illness and injury. They are ideally suited to provide complete medical care for athletes, sports teams, dance teams, or active people who are looking to manage a healthy lifestyle.
Sports medicine physicians specialize wholly in non-surgical treatment options and serve as team physicians at the youth level, NCAA, NFL, MLB, NBA, WNBA, MLS, and NHL, as well as with Olympic teams.
![]()
What Do Sports Medicine Physicians Do?

Sports medicine doctors have specialized training for physical injuries during sports. They are as follows:
- To restore function to injured people so they can get moving again as quickly as possible.
- To help the athletes in preventing illness and injuries.
- Although sports medicine doctors do work with professional sports teams, they also treat children and teens involved in sports. They also work and assist with personal fitness centers such as gyms.
![]()
What are the Sports Injury Treatment Options?
Sports medicine doctors provide non-surgical treatments, which include medications and rehabilitation.

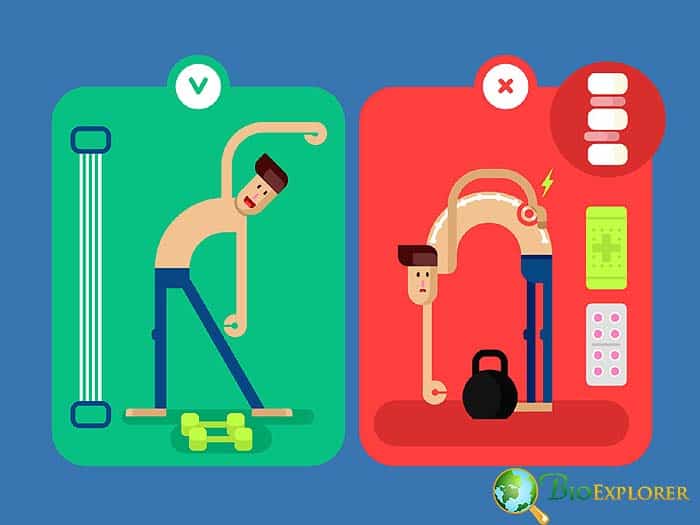
- Medications: Sports doctors prescribe medications for pain/inflammation management for most kinds of injuries. The medications include Acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) such as ibuprofen or naproxen to fight inflammation as well as pain.
- Rehabilitation: Once the pain and inflammation are subsided, the next treatment options are returning to exercise to regain strength. They start with gentle range-of-motion exercises, and then gradually increase to weight-bearing resistance activities.
![]()
What are Sports injuries?

All sports injuries feel identical, but there are subtle differences between them. Here is a glossary of some common sports injuries:
- Sprains: Injuries to ligaments, the fibrous connective tissues that connect one bone to another.
- Strains: Injuries to muscles or tendons, the fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones (Muscle pulls).
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of a tendon, often caused by overuse or poor body mechanics.
- Fasciitis: Inflammation of the layer of fibrous tissue that covers many muscles and tendons. Overuse is usually a cause.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the small, fluid-like sacs that cushion joints, muscles, or bones like miniature shock absorbers.
- Arthritis and Synovitis: Inflammation of a joint (arthritis) or the membrane that surrounds it (synovitis). Pain and swelling are common symptoms.
- Dislocations: Often, very painful and disabling, dislocations occur when bones slip out of their proper alignment in a joint.
- Fractures: A disruption in the continuity and integrity of a bone. This disruption includes broken bones and hairline fractures, which will require medical treatment.
- Contusions: Bleeding into tissues caused by direct trauma.
- Muscle cramps and spasms: Improperly supported and intense muscle contractions, which is very painful. This injury occurs very often in all kinds of sports.
- Lacerations and Abrasions: Cuts and scrapes; small ones can be managed with soap and water and Band-Aids, but larger ones may require special dressings or sutures.
![]()
How to Become a Sports Medicine Physician?

In order to become a sports medicine specialist, one should:
- Graduate from high school with a high GPA.
- Complete the 4-years Bachelor of Science degree from an approved pre-med program.
- Pass the Medical School Admissions Test (MCAT).
- Complete the required training at a medical school or osteopathic school (4 years).
- Pass the three stages of the United States Medical Licensing Exam (USMLE).
- If you study at an osteopathic school, you would need to pass the United States Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination (COMLEX-USA).
- Obtain a degree in medicine or osteopathic medicine (M. D. or D. O.).
- Join a 3-5-year residency in:
- Internal medicine.
- Family medicine.
- Orthopedic medicine and rehabilitation (4 years).
- Emergency medicine.
- Orthopedic surgery (5 years).
- Get board certified by the American Board of internal medicine / American Board of Pediatrics.
- Complete a 1-year fellowship in sports medicine.
- Get board certification (certificate of added qualification ).
- Orthopedic surgeons need to be certified in sports medicine from the American Board of Orthopedic Surgery.
How To Become A Physiatrist?
![]()
What is a sports medicine specialist salary?
The average salary range for a sports medicine specialist in the USA is between $59,000 and $245,000.
![]()
Additional Resources
![]()
Cite This Page
Key References
- “What Is Sports Medicine?” – University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.
- “What is a Sports Medicine Specialist?” – American Medical Society for Sports Medicine. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.
- “Treating sports injuries – Harvard Health”. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.
- “Primary Sports Medicine Fellowship” – HSS – Hospital for Special Surgery. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.
- “Home | ABIM.org”. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.
- “The American Board of Pediatrics | Certifying excellence in pediatrics for a healthier tomorrow”. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.
- “Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellowship | ortho.duke.edu”. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.
- “Sports Medicine | ABFM | American Board of Family Medicine”. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.
- “Orthopaedic Sports Medicine | ABOS”. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.
- “Physician / Doctor, Sports Medicine Salary | PayScale”. Accessed December 31, 2019. Link.

















