
How Do Viruses Reproduce? Viruses are not considered living organisms – but still, they are everywhere. These unique intracellular parasites have managed to reproduce using other cells.
There are multiple types of viruses, and each type has a slightly different way to make copies of themselves using proteins and ribosomes inside the cells.
Let us look closely at how they manage to do this.
Table of Contents
- Are Viruses Living Things?
- Can viruses reproduce on their own?
- What do viruses need to reproduce?
- Do viruses have DNA?
- What is the genetic material of a virus?
- How Do Viruses Reproduce?
- Do all viruses reproduce the same way or it differs between viruses?
- How do viruses cause diseases?
- Lysogenic Cycle Stages
- Key References
Are Viruses Living Things?
As you may know, there is an ongoing debate about whether one should list viruses among living things. Here are the reasons for the confusion:
- Viruses are much smaller than bacteria. According to research, viruses range in size from 20 to 400 nm (10-9 meters), while average bacteria range from 0.5 to 5 micrometers in size. To see them, we need powerful microscopes.
- Viruses have a straightforward structure. A single virus called a virion is composed of a viral genome and an envelope made of proteins to protect it called a capsid. Some viruses can have additional features and look more complex, for example, like a bacteriophage shown below:
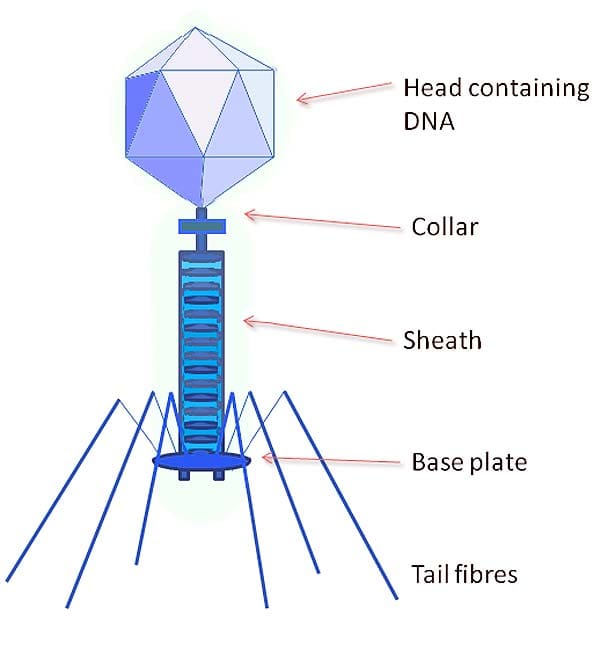
Bacteriophage Structure (Source: Wikimedia)
So, we can see that viruses are small – but so are bacteria. Viruses also contain substances found in living organisms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and sometimes even lipids. The main difference between a living and non-living entity is whether it can reproduce.
![]()
Can viruses reproduce on their own?
If we look closely at viral capsids, we would see that they usually contain some proteins that can assist in copying their genome material. However, this is not enough.
- They still do not have complex structures of the cell, such as membrane or ribosomes, i.e. they are acellular.
- So, viruses use cells to make viral proteins and viral genomes instead.
- Even the most complex viruses cannot achieve self-reproduction.
![]()
What do viruses need to reproduce?
Why is it so crucial that viruses are acellular? It is crucial precisely because cells have everything; they need to produce their own molecules:
- Cells have enzymes that specialize in the production of nucleic acids;
- Cells have ribosomes that assist in protein synthesis;
- Cells have other vital proteins that provide energy to make synthesis possible.
Viruses lack all that. That is why they need to use a cell of their choice to do the work for them.
![]()
Do viruses have DNA?
We have already mentioned that all viruses have genomes. Genomes are essential for a virus and are hidden within the protein capsid.
- What is interesting about those genomes is the fact that they are much more varied than our own.
- Some viruses do have DNA – but unlike own cells, some viruses have only one strand of DNA instead of two inside the capsid.
![]()
What is the genetic material of a virus?
Besides DNA, viruses can also have RNA-based genomes. There are several types of viruses – and each has a different nucleic acid that serves as its genetic material:
- Single strand DNA viruses
- Double strand DNA viruses
- Single strand RNA viruses
- Double strand RNA viruses
Whether the viral genome is composed either of RNA or DNA, they still contain very few genes. However, those few genes still make the virus able to hijack cells for its own purpose. This process has several stages, and some stages are different between various virus types.
![]()
How Do Viruses Reproduce?
Viruses go through a process called the viral replication cycle which has several stages:
- Attachment stage
- Penetration stage
- Uncoating stage
- Replication stage
- Assembly stage
- Virion release stage
![]()
Do all viruses reproduce the same way or it differs between viruses?
Most viruses go through the same stages of replication. However, depending on the type of genetic material they have, or types of proteins their capsid contains, they may replicate in a slightly different way.
The main differences can be noticed at the stage of penetration and replication stage, which we would see later.
I. Attachment stage
First of all, a virus finds the cell it needs and attaches to its cellular wall or plasma membrane (depending on the type of cell).
- Usually, each virus species can attach to only one type of cell: a bacterial cell, a cell of a protist, a fungus, a plant, or an animal.
- Viruses are extremely specific. They usually infect only certain cell types (for instance, HIV infects only one type of immune cells), or particular species (for example, tobacco mosaic virus, the first virus to be discovered, infects only tobacco plants).
- In order to attach to the cell, a virus usually has specific substances on its surface that can be recognized by the unique proteins called receptors on the surface of the cell.
- More complex viruses, like the one shown above, also have individual fibers that attach to the plasma membrane of the cell firmly.
![]()
II. Penetration stage
Once a part of the virus is recognized by the receptor of the cell, the virus can use this receptor to enter the cell.
- The part that is recognized is like an “ID card” that allows the passage inside. Usually, a virus enters the cell through the process called endocytosis.
- During endocytosis, the cell surrounds the viral particle with a piece of its own membrane, makes a “traveling bubble” called vesicle and the virus travels in this bubble inside.
Some viruses do not use the transport of the cell to enter – they can make a hole in the membrane and inject their genomes through it directly.
![]()
III. Uncoating stage
After the virus has sneaked into the cell, it needs to release its genome. The capsid falls apart, some of its proteins get destroyed, and the “naked” genome appears in the cytoplasm. Then the genome can take several ways to replicate depending on its type.
![]()
IV. Replication stage
At this stage, the virus uses the proteins of the cell to replicate its genome. This particular stage is different in different types of viruses:
Single strand DNA viruses: the strand of viral DNA goes to the nucleus because DNA replication proteins are located there. The nuclear proteins make the second strand of viral DNA, and an intermediate double strand viral DNA is formed. It is used for two purposes:
- to produce RNA needed for viral proteins synthesis;
- to produce new single strand DNA genomes for new viruses;
Double strand DNA viruses: The double strand viral DNA also goes to the nucleus after uncoating. There, the nuclear protein can make new viral DNAs, as well as RNA “messages” for viral proteins.
As far as the RNA viruses go, they undergo a different process-they replicate in the cytoplasm:
- Single strand RNA viruses: The viral genome replicates in the cytoplasm. Also, the viral RNA can be directly used for the production of the new viral proteins.
- Double strand RNA viruses: The double-stranded RNA genome of the virus is used both for production of single RNA strands needed for protein synthesis, as well as for production of new complete RNA genomes made of two strands.
- RNA retroviruses: This is a unique group of viruses. While they have a genome made from the single strand of RNA, they reproduce quite differently:
- A special enzyme called RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, or revertase, uses this single strand to make a strand of DNA.
- Based on this new strand of DNA, a second strand is formed.
- The double strand viral DNA enters the nucleus and inserts itself into the genome of the host.
- The viral DNA can replicate together with the host DNA when the cell divides.
- The viral DNA region is used for making proteins and new viral genomes.
![]()
V. Assembly stage
All the newly made genomes and viral proteins are assembled into viral particles.
![]()
VI. Virion release stage
When there are too many viral particles inside the cell, they are ready for release. There are two ways the virions can exit the cell:
- Through lysis: Lysis means the destruction of the host cell. As the viruses exit, they destroy the plasma membrane and the cell itself.
- Through budding: Budding is less harmful to the cell than lysis. During budding, the virus uses the same mechanism of cellular transport it has used when entering: it makes the cell wrap a part of its membrane around the viral particle and exits the cell in this vesicle. This process is advantageous to the virus, too: it takes the pieces of the membrane with it, and they serve as an “ID card” for entering the new cell.
After the viruses exit, they move to another cell, enter it and start the cycle again. This cycle of virus reproduction is often called the lytic cycle.
![]()
How do viruses cause diseases?
The viruses that reproduce through a lytic cycle can cause diseases. There are several reasons why:
- Viruses subvert all the processes in the cell. An infected cell focuses its all resources on the production of new viruses and stops doing anything else. When multiple viruses infect multiple cells, the whole function of the tissue or an organ can get switched off;
- Viruses use different strategies to evade the immune system. That can lead to the development of new bacterial infections.
- Viruses kill host cells. This means two things:
- Tissue or an organ can stop working due to their cells dying;
- The immune system reacts to the destruction, causing inflammation and fever (for instance, when we have influenza).
Not all viruses cause infections right away. Some viruses do not pass through lytic but through the lysogenic cycle.
![]()
Lysogenic Cycle Stages
- The virus attaches to the cell and enters it.
- The virus goes through uncoating.
- Viral DNA enters the nucleus and inserts itself inside the genome.
- The viral DNA lies dormant inside the cell, and replicates with each cellular division.
- The virus can exit the host genome under certain conditions – such as stress, changes in nutrition, and changes in temperature. Then it can enter the lytic cycle, form viral particles, and kill the host cell.
![]()
Viruses that lie dormant usually do not cause diseases, but as they insert themselves into the host DNA randomly, they may disrupt the normal function of the cell genome and cause mutations. As such, they also may be contributing to the transformation of healthy cells into cancer cells.
As you can see, viruses have a variety of ways to reproduce despite being relatively simple in structure. Because viruses are intracellular parasites, viral infections are tough to treat.
The most effective way to counteract viral infections is vaccination. Unfortunately, not all common viral infections are preventable with the help of it.
![]()


















[…] We’ve found that viruses are everywhere, in us, around us, all over. We even learned they evolve when they inject their DNA or RNA into the host cell be it a bacteria or a mammal cell the host cell automatically copies their DNA or RNA and the […]