Fungi are mostly multicellular, heterotrophic, complex organisms that belong to the eukaryotic kingdom. They break down and utilize complex organic substances for their nutritional requirements. They are distinguished from plants and animal due to the feature of having specialized cell walls with a material called chitin.
Table of Contents
Other features that further distinguish them from other living cells include their mode of reproduction and uptake of nutrients. Thousands of fungal species contribute to it being one of the most widely distributed organisms.
How Do Fungi Reproduce?

Most fungi are holomorphs and can reproduce both sexually and asexually depending on environmental conditions.
- Sexual reproduction allows fungi to form more genetic variants and lineages and can enhance survival through genetic change and adaptation in unstable or unfriendly environments.
- Both asexual and sexual reproduction and vegetative reproduction are carried out in different ways.
![]()
How Do Eukaryotes Reproduce?

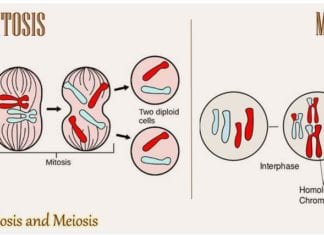
Although the basic concept of reproduction in all eukaryotes involves the fusion of gametes of two mating types in sexual reproduction (followed by meiosis), and production of identical progeny in asexual reproduction (also called mitosis), the reproductive methods in fungi occurs with the help of specialized structures called spores, as opposed to pollen and seed in eukaryotes like plants, and sperm and egg in animals.
![]()
Why Is Fungi Reproduction Special?

Fungi are of high medicinal, nutritional and environmental significance. Some are employed in various industrial functions, such as yeast in bread-making and as model organisms in scientific research. Most fungi comprise a network of threads called hyphae. This structure is called a mycelium. The mycelium can extend into surfaces as the fungus grows and reproduces.
Fungal spores are a unique feature of fungal reproduction and differ in type across various fungal species.
Fungi typically have three modes of reproduction. Some forms of fungi reproduce asexually and are known as anamorphs. Those that reproduce sexually are known as teleomorphs, and fungi that exhibit both types of reproduction methods are known as holomorphs.
A closer look at these modes can provide insight into how fungi reproduce and what structures are involved.
![]()
Vegetative Reproduction
Fragmentation: The mycelium of the fungus fragments into small pieces, and each piece develops into a new separate mycelium. This type of reproduction is seen in molds.
![]()
Fission: This mode of reproduction is more common in unicellular fungi like unicellular yeast. The parent cell elongates and cleaves itself into two identical daughter cells. The cell division begins from the nucleus of the cell, extends into the cytoplasm and then the cell membrane thus forming two daughter cells that thrive independently.
![]()
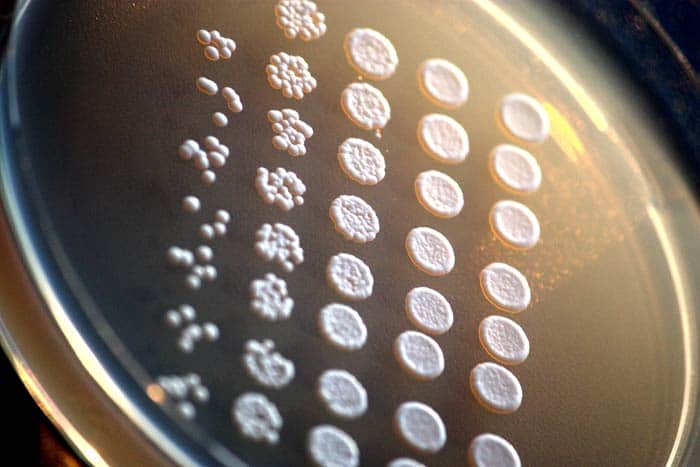
Budding: Budding is relatively common in yeast, scientifically known as, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The budding process starts with cell division occurring at one particular site in the parent fungus. This eventually leads to an outgrowth or bud formation at that site. The bud remains attached to the parent structure until maturity, following which it falls off as a newly developed independent organism. Genetically, the new organism is identical to the parent (clone).
Oidia: In some fungi, the parent body, or hyphae, breaks up into smaller cells called oidia, each of which develops into a separate mycelium or fungal body.
![]()
Special Types of Vegetative Reproduction
A few special reproductive processes occur under favorable conditions. They are categorized under vegetative reproduction – Chlamydospores, Rhizomorphs, and Sclerotia.
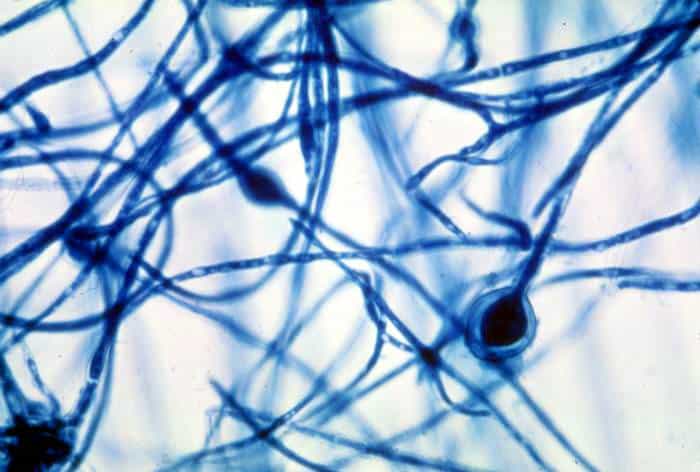
Chlamydospores: Chlamydospores are unicellular elongated fragments that function as a single body or can be found in chains. These cells developed a thick wall in unfavorable conditions and accumulated food and nutritional resources. When the conditions turn favorable, they germinate into new cells giving rise to mycelia. An example of a fungus employing this method of reproduction is Fusarium.
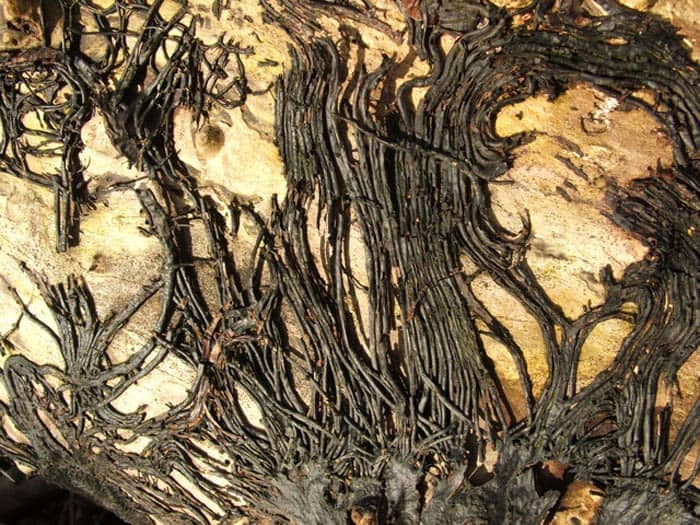

Rhizomorphs: Rhizomorphs are rope-like structures formed by hyphae entangled into one another. These remain dormant under unfavorable conditions and regrow into new mycelia under favorable conditions. Rhizomorphs are usually seen in fungi found in the soil.
Sclerotia: Sclerotia are structured similarly to rhizomorphs but are covered by a thick covering. They remain dormant and germinate under favorable conditions.
![]()
Asexual Reproduction
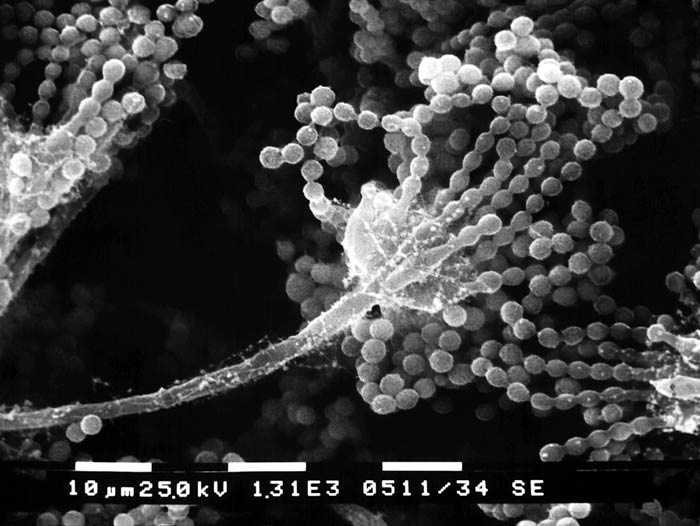
Reproduction by spore formation: Sporulation is a process of fungal reproduction where the haploid parent fungal cell produces haploid spores. These haploid spores mature and develop to become haploid individuals. Spores produced by fungi are disseminated by water or wind to different locations where they germinate under favorable conditions to produce hyphae and eventually individual fungi. Spores are formed due to mitosis in the parent plant and can differ in size, shape, and color based on the fungal species that produce them. They can be unicellular or multi-cellular.
Based on the type and structure of spores, three types of spores are formed during asexual reproduction:
1. Sporangiospores: A structure called the sporangium that is formed on hyphae produces and stores spores. This structure is called the sporangiophore. Sporangiospores are categorized into motile and non-motile spores, most commonly seen in the Rhizopus species.
2. Zoospores: These spores are similar to the sporangiospores, but the structure bearing the sporangium is called the zoosporangium. Zoospores are typically known to be motile and are seen in aquatic fungi.
3. Conidiospores: Spores that can be unicellular or multicellular, usually motile, and are formed as separate cells. They are released from the tip of the hyphae or its side and can also be produced on the mycelium. Examples of conidiospore-forming fungi are Aspergillus and Penicillium.
![]()
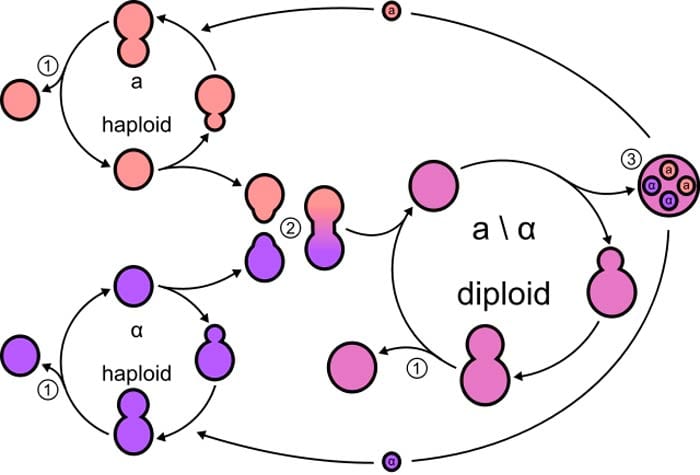
Sexual Reproduction
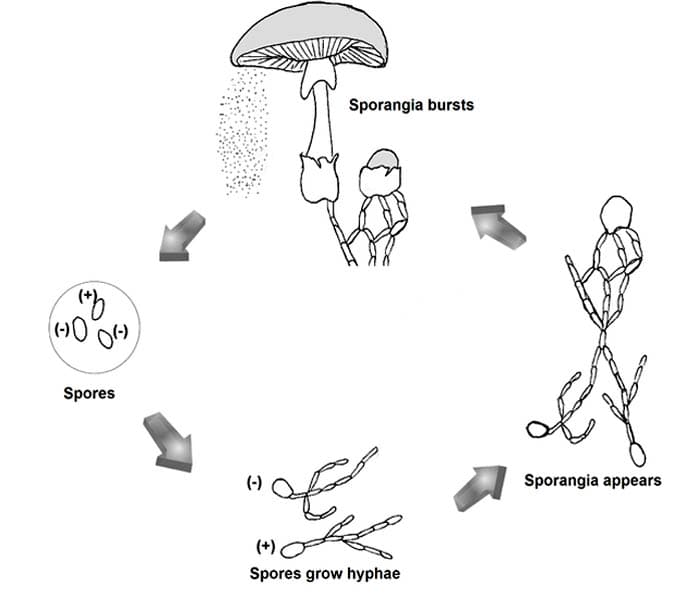
Sexual reproduction in fungi involves the fusion of two gametes or mating types and results in genetic variation in the offspring.
- Genetic variation equips the offspring with adaptations and features that allow for competition and survival in the natural environment.
- Two mating types are produced during sexual reproduction. The mating types need to be compatible with each other and be of opposite strains.
- The male mating type or gamete is called Antheridia, and the female mating type is called Ascogonia. Together these gametes are known as gametangia.
- Depending on the position of the mating type, sexual reproduction is classified as homothallic or heterothallic.
Homothallic reproduction occurs when both mating types are in the same mycelium, whereas homothallic reproduction occurs when both mating types are in separate mycelia.
The process of sexual reproduction has three phases: Plasmogamy, Karyogamy, and Meiosis:
1. Plasmogamy: This is the first phase of sexual reproduction, where both mating types of opposite strains fuse their cytoplasms without nuclear fusion. The resultant cell is called a dikaryon and consists of two nuclei – one of each mating type. The duration of this phase can sometimes be long.
2. Karyogamy: This phase involves the fusion of the nuclei of both mating types.
3. Meiosis: The process of cell division that eventually leads to the formation of 4 daughter cells.
Suggested Reading:
Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
![]()
Fungi are one of Earth’s most widely varied species. They differ not only in their nutritional requirements or habitats but also in the mode of reproduction. The variety of fungal spores produced and disseminated as a result of different reproductive methods leads to the generation of fungal species that have a significant impact on research, medicine, nutrition, ecology and the environment.
![]()