 Microbiology is the study of the structure, bodily functions and physiological processes of microorganisms. It deals with the structural diversity and classification of microorganisms and covers the whole range of microbial life. The study of microbiology expands its scope to both prokaryotic (no true nucleus and no membrane-bound organelles) and eukaryotic (have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles) organisms[1]. The history of microbiology starts from the 16th century, even before the invention of the microscope.
Microbiology is the study of the structure, bodily functions and physiological processes of microorganisms. It deals with the structural diversity and classification of microorganisms and covers the whole range of microbial life. The study of microbiology expands its scope to both prokaryotic (no true nucleus and no membrane-bound organelles) and eukaryotic (have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles) organisms[1]. The history of microbiology starts from the 16th century, even before the invention of the microscope.
The word microbiology comes from the Greek words micro, which means “small or minute”, and logos, which means “study of”. Hence, broadly, microbiology is the scientific study of microorganisms. Microbiology has numerous sub-fields, and these include phycology (algae), virology (virus), mycology (fungi), bacteriology (bacteria), protozoology (protozoans), and medical microbiology (pathogenic microorganisms)[2].
History of Microbiology
Top 11 Microbiology News In 2017
Top 15 Latest Microbiology & Virology Discoveries in 2018
Latest Discoveries In Microbiology 2019
Top 10 Microbiology News of 2020
Top 15 Microbiology News of 2021
Top 15 Microbiology News of 2022
References
[1] – Microbiology in 20th Century. 2011. Link (accessed July 21, 2016).
[2] – Introduction to Microbiology. 2016. Link (accessed July 21, 2016).
[3] – Microbiology, American Society For. Significant Events in Microbiology 1861-1999. 2006. Link (accessed july 21, 2016).
[4] – Rhoads, Dan. History of Cell Biology. 2007. Link (accessed July 22, 2016).
[5] – genbacteriology. Bacterial Growth. 2015. Link (accessed July 22, 2016).
[6] – Utah.edu. PCR. 2016. Link (accessed July 22, 2016).
- Bisceglia, N. Cell Biology. 2016. www.nature.com/scitable/topic/cell-biology-13906536 (accessed July 22, 2016).
- Innes, Centre John. Microscopy. 2016. https://www.jic.ac.uk/microscopy/intro_EM.html (accessed July 22, 2016).
- Mikell, Meredith. Understanding Cell Biology: History & Theories. 2003. http://study.com/academy/lesson/understanding-cell-biology-history-theories.html (accessed July 22, 2016).
- Pasteur, L. “”Animalcules infusoires vivant sans gaz oxygene libre et determinant des fermentations.”.” Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci., 1861: 344-347.
- Pray, L. “Discovery of DNA Structure and Function: Watson and Crick.” Nature Education, 2009: 100-101

























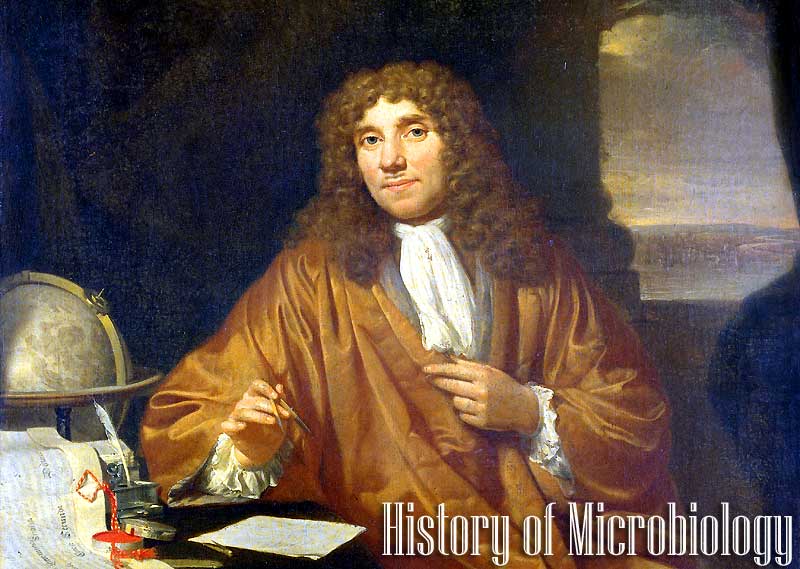
Microbiology essentially began with the development of the microscope. Although others may have seen microbes before him, it was Antony Van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch draper whose hobby was lens grinding and making microscopes, who was the first to provide proper documentation of his observations. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek is considered a father of microbiology as he observed and experimented with microscopic organisms in 1676, using simple microscopes of his own design. Scientific microbiology developed in the 19th century through the work of Louis Pasteur and in medical microbiology Robert Koch.