
The year 2017 has seen ground-breaking advancements in the field of genetics. Genetics is the biological study of genes, genetic variation, mutations, and heredity in living organisms. In this article, we will explore top 12 genetics news in 2017.
Table of Contents
- Top Genetics News In 2017
- CRISPR-CAS9 Gene Editing Technique
- Scientists Find Genes That Cause Alzheimer’s
- Research on DNA’s Base-Pairing Rules
- Study Shows Dodder Plant Can Silence Gene Expression in Crops
- Scientists Find Protein Responsible For Schizophrenia
- Research Finds Alcohol Damages DNA In Stem Cells
- New Treatment Strategy For X-Chromosome Related Disorders
- Gene Swapping To Control Mosquito-Borne Diseases
- Creative Solution To Solve World’s Food Shortage Challenge
- Breakthrough Study of Protein (Slient Code)
- Researchers Discover PRPS1 Gene’s Role in Hear Loss in Young Boys
- Interesting Genetic Variants Discovery of Skin Color Diversity
Top Genetics News In 2017
CRISPR-CAS9 Gene Editing Technique
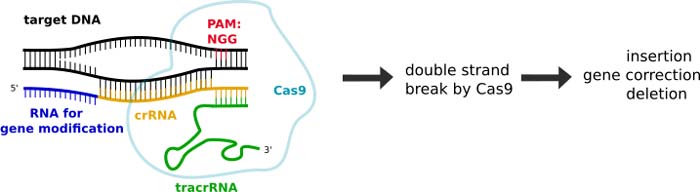
The year 2017’s biggest breakthrough was undoubtedly the development of the CRISPR-CAS9 gene editing technique. This technique allows genetic material to be edited (added, removed or altered) at particular locations in the genome, providing faster, cheaper, accurate and better results than any other technique used before.
![]()
Scientists Find Genes That Cause Alzheimer’s

Scientists at the Boston University school of medicine have identified new genes involved in the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Three genes, SRRM4, MTUS1, and GRIN2B are known to cause structural and functional changes leading to building up of AD proteins found elevated in the CSF of AD patients.
![]()
Research on DNA’s Base-Pairing Rules
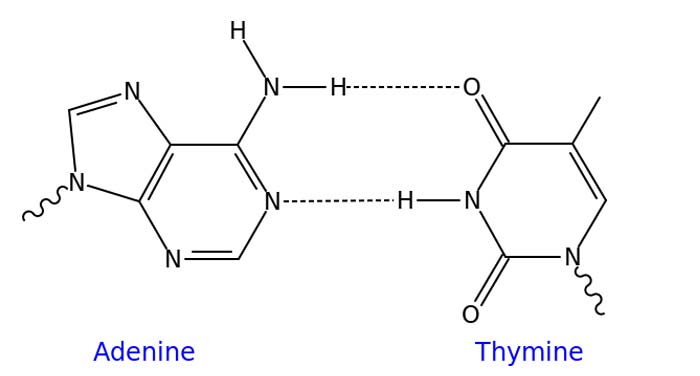
Researchers at the Arizona state university have elucidated DNA’s base-pairing rules further. Complementary base pairing rules suggest that G pairs with C and A pairs with C, thereby providing an organism with a specific G-C and A-T content. This content varies widely over species, and this study showed that natural selection favors higher G-C contents. Most mutations are found to occur in DNA’s G-C regions.
![]()
Study Shows Dodder Plant Can Silence Gene Expression in Crops
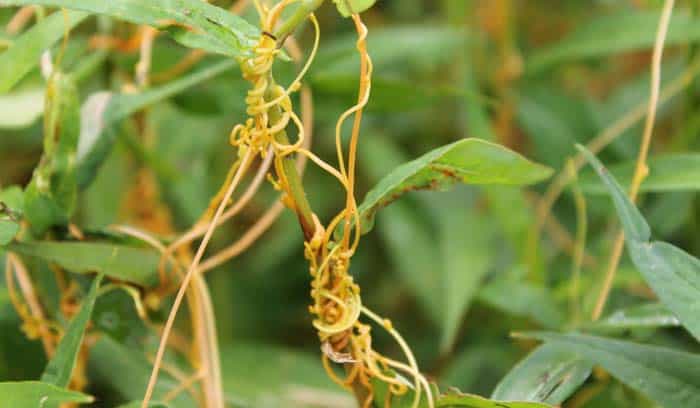

A recent study shed new light on the behavior of the parasitic plant, Dodder. This plant Is known to cause major damage to crops by attaching to its host and deriving water and nutrients from it. The findings from this study suggest that Dodder can silence gene expression in the host plant, leading to cross-species gene regulation.
![]()
Scientists Find Protein Responsible For Schizophrenia

Scientists at John Hopkins identified mutations in a protein linked with Schizophrenia. This protein attacks receptors at junctions between neurons. The findings of this study showed a successful reversal of certain schizophrenia symptoms in mice by targeting this protein.
![]()
Research Finds Alcohol Damages DNA In Stem Cells

A recent study published in nature, conducted by Cancer Research UK has further elucidated how alcohol damages DNA in stem cells, increasing the risk of seven types cancer. The study also explains how the cells attempt to defend themselves from DNA damage.
![]()
New Treatment Strategy For X-Chromosome Related Disorders
Researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital have discovered a new strategy for treating X-chromosome linked disorders. The technique was used to reactivate the inactivated portion of the X-chromosome thereby increasing the expression of a healthy protein to treat Rett syndrome.
![]()
Gene Swapping To Control Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Scientists at the University of California studied genetic changes that equip the Anopheles mosquito with pesticide resistance. Pesticide target sites in mosquito DNA were found to be mutated, thus conferring insecticide resistance. The ability to swap genes further enhances the mosquito’s insecticide resistance.
![]()
Creative Solution To Solve World’s Food Shortage Challenge

A recent study conducted at the Donald Danforth Plant Center has aimed to solve the world’s food shortage challenge. The study identifies certain mechanisms that are responsible for developmental traits of cereal grains. By studying and employing this mechanism, scientists may be able to enhance the yield of cereal grains.
![]()
Breakthrough Study of Protein (Slient Code)
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania discovered the reason why proteins with nearly the same amino acid code can perform separate, and distinct functions. The answer lies, not in the amino acid code but the nucleotide code of the DNA that coded the protein – also called “silent code. ” Researchers found that difference in the nucleotide code causes the differing density of ribosomes to be assembled for each protein translation.
![]()
Researchers Discover PRPS1 Gene’s Role in Hear Loss in Young Boys

A team of researchers at the University of Miami that the development of the middle ear is governed by expression of the PRPS1 gene. This gene is associated with a progressive hearing loss in males aged between 5 and 15.
![]()
Interesting Genetic Variants Discovery of Skin Color Diversity

Scientists have discovered the genetic variants underlying skin color diversity in the African population. This piece of research studies the evolution of these genes, leading to the finding that the genetic variants that contribute to skin color diversity have traveled from all over the world.
![]()

















