Fun Facts About The Nervous System: The human body is made up of a system that enables us to access our five senses and interpret information according to what we see, smell, taste, hear or touch.
Imagine not being able to interpret information that is gathered by our eyes or our sense of touch.
We would be incomplete without our senses, and thus incomplete without the vital system that governs them, known as the nervous system.
The nervous system is a complicated web of nerve fibers and cells that run to and from the brain and spinal cord throughout the body. It innervates every organ in the body and carries messages to the brain to be interpreted.
Top 38 Fun Facts About The Nervous System
The nervous system is a wonder in itself, a complicated system without which other systems would not function fully. Here are 38 fun facts about the nervous system:
There are 2 main parts in the nervous system.
- There are two parts to the nervous system namely the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- The peripheral nervous system is further comprised of two subdivisions, namely the somatic and the autonomic nervous system.
![]()
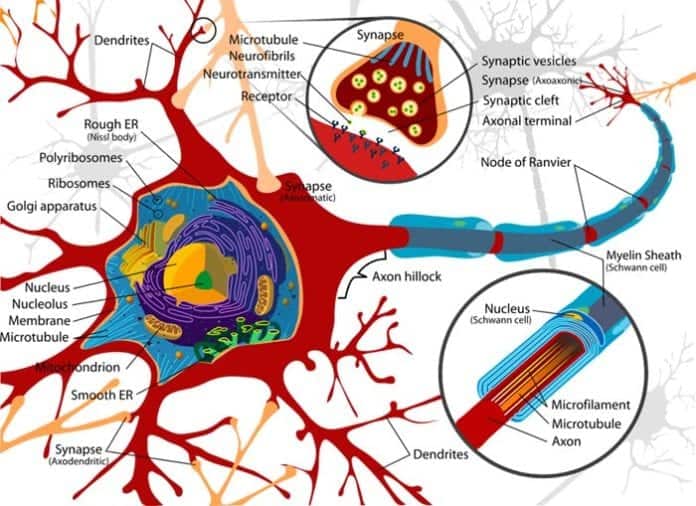
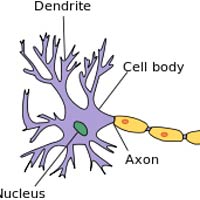
Neurons, Axons & Dendrites are the basic building blocks in the nervous system.
- The basic functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron.
- There are billions of neurons in the nervous system, most of them in the brain.
- The neuron consists of long cables-like extensions that protrude out of its body termed axons and short, thick extensions termed dendrites.
- Together, axons and dendrites act as cables to carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord.
- Billions of these neurons work in conjunction with the brain to provide information about the surroundings to the human body.
![]()
The brain requires and utilizes more energy than any other organ in the body.
- The brain uses more than 20% of the body’s total energy production.
- Most of this energy is channeled through the brain towards transmitting electrical impulses whether we are awake or asleep.
- It is a well-known fact that the brain works tirelessly, even during sleep.
![]()
The brain’s structure is not static; it changes with acquiring new knowledge.

- The structure and density of an infant’s brain vary significantly with an adolescent or an adult.
- This is due to the learning process, which contributes towards developing new neuronal connections in the brain.
- The more we learn, the more electrical connections are generated in our brains.
- These connections help establish memory, and the more they are reinforced, the stronger the memory. As they say practice makes perfect!
![]()
Info in the nervous system can travel as fast as 268 miles per hour (431 kph)!
- The alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord transmit the signals at the super speed of 268 mph – the fastest transmission in the human body.
- Neural receptors in the skin, which miss the speed-boosting insulating layer called a myelin sheath, are with the slowest transmission speed of 1 mph!
![]()
Reflexes that are involuntary are not interpreted and processed by the brain.

- Certain reflexes are involuntary, which means they are automatic and do not require the intervention of a thinking process (Example: when you touch something hot and pull your hand back away immediately).
- This reflex is controlled by reflex arcs, and the brain is not involved in this pathway.
![]()
Neuronal cells do not divide.
- Neuronal cells do not undergo the process of mitosis or cell division; hence they do not have growth or repair capacity.
- Nerve damage is usually irreversible and can result in loss of function.
- Today, researchers are exploring the potential of neuronal stem cells or pluripotent stem cells in neuronal repair and regeneration.
![]()
As the brain ages, it loses neurons but can form new connections between remaining neurons.

- By age 20, we begin to lose neurons to aging.
- By age 75, nearly 1/10 of the neurons die out from your original neuron count.
- However, it does not mean you would lose 10% of your intelligence.
- With the remaining neurons, they form new connections to make up for the lost neurons.
![]()
The brain is wrinkled!
- Our brains have that wrinkly, walnut shape because the white matter constrains the fast maturity of the brain’s external or outer brain (the gray matter).
- Scientists found the specific pattern of the ridges and crevices of the brain’s convoluted surface, which are called gyri and sulci.
![]()
Electrical impulses are actually chemicals.
- Current electricity is transmitted from one point to another due to the flow of electrons.
- Similarly, electrical impulses that flow through neurons and nerve cells are conducted by the flow of tiny chemical.
![]()
Potassium and sodium ions are indispensable to the functioning of the nervous system.
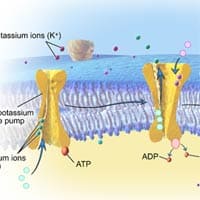
- Neurons transmit information (electrical pulses) electrochemically.
- Chemicals in the body are electrically charged when they have an electrical charge; they are called ions.
- The critical ions in the nervous system are sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+), calcium (Ca++) and chloride (Cl-).
![]()
As we grow, our brain shrinks!
- Inside the womb, neurons grow at the rate of 250,000 neurons a minute in the brain of a child.
- A newborn’s brain grows over three times its size in the first year of growth.
- In adults, a gram of the brain’s weight is lost yearly.
![]()
The nervous system cannot efficiently repair itself.
- Unlike the bones heal themselves, the nervous system has limited regenerative or repair potential.
- Scientists are now looking at stem cells in the nervous system to uncover their potential in neuronal repair and regrowth.
![]()
The hypothalamus helps in regulating body temperature!
- The hypothalamus is a small part of the brain that regulates body temperature.
- When the body gets too cold, signals are sent to the brain, which helps warm and maintain body temperature. Refer to homeostasis for more details.
![]()
The human brain weighs about 3 lbs (1.4 kg or 1336 grams).

- After 8000 autopsies of healthy adult male and female patients, the average brain weight is 1336 grams for a male and 1198 grams for a female.
- As we age, brain weight decreases by 2.7 grams in males, and by 2.2 grams in females per year.
![]()
The composition of the brain varies between the sexes.
- Male brains have more gray matter content, whereas female brains have white matter content.
- The gray matter consists of whole neuronal cells, while white matter contains neuronal connections.
- Men have about 6.5 times the mass of gray matter compared to overall intelligence than women.
- Women have almost 10 times the amount of white matter related to intelligence than men.
- Gray matter denotes information processing centers in the brain.
- White matter signifies the connections between the processing centers.
![]()
A cross-connecting optic nerves enable us to see images in the retina!

- The optic nerve carries information from the eyes to the brain for interpretation.
- However, the right optic nerve crosses over the left and transmits a signal to the left side of the brain, while the left optic nerve transmits signals to the right side.
- Together, these signals enable the brain to interpret the image formed at the retina.
![]()
Glial cells aid the neurons in signal transmission and maintenance.
- Glial cells are support cells that help create myelin, a substance that coats the neurons and the nerve fibers.
- Myelin helps insulate the fibers, preventing leakage of electrical impulses and protecting the nerve fibers. It helps in the efficient and fast transmission of signals.
![]()
Mirror neurons enable us to mimic actions of others!

- Scientists have found a group of neuronal cells in primates that help enable them to mimic the action of other animals.
- These neurons are called mirror neurons.
- Mirror neurons are responsible for laughter & yawning being contagious!
![]()
Neurons have different functions.
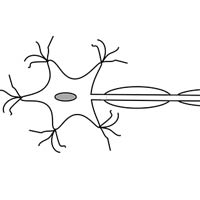
- Neurons have different types and morphologies and perform different functions.
- Neurons that gather information from immediate surroundings and stimuli are receptor neurons.
- Those that carry signals to the nervous system are called sensory neurons, and those that bring signals or information back to the effector organ are termed motor neurons.
![]()
The autonomous nervous system has two important functions.

- The autonomous nervous system has an interesting feature. It is activated under emergencies and stress conditions and transmits signals to either “fight” or “flight” (run away).
- It is also activated in normal conditions such as rest and digestion.
![]()
The Sciatic nerve is the largest and longest nerve in the body.
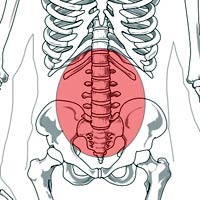
- The sciatic nerve runs from the spine to the toe and is a continuous length of fibers.
- In certain individuals and pregnancy, this nerve can be pinched, either due to the weight of the baby carried in the womb or due to a spinal disc problem that pinches the nerve;
- This can cause pain from the lower back to the toe. The condition is called sciatica.
![]()
There are 43 pairs of nerves in the peripheral nervous system.

- In total there are 43 pairs of nerves in the peripheral nervous system.
- Out of the 43 pairs of nerves, 12 pairs are connected directly with the brain, and 31 pairs are connected to the spinal cord.
![]()
Nerve endings act as receptors.
- Receptor neurons are located in the nerve endings, which acquire a signal from the environment.
- For example, the nerve endings in the tips of the fingers can signal an individual to pull back their hand upon touching a hot object.
- In milliseconds, information is processed to perform the required action.
![]()
Stress weakens the brain’s activity to process memories.

- Stress is the primary leading factor that alters the brain’s architecture in a developing child.
- However, not all stress is the same.
- There is a specific kind of stress called “Toxic Stress,” which weakens brain activities and can disturb normal development.
- Toxic stress usually happens when no parents or guardians are nearby to buffer a child’s response to reoccurring adverse situations or experiences.
![]()
Research shows that being curious increases the number of connections between brain cells.

- Curiosity is a fundamental component of our cognition.
- Its biological role, mechanisms, and neural basis are inadequately understood.
- It is an essential motivator for learning, instrumental in decision-making, and crucial for healthy brain development.
![]()
EEG allows doctors to watch brain wave activity as it happens.

- The electroencephalogram (EEG) represents the electrical activity happening at the brain’s surface.
- This waveform pattern allows doctors to understand the brain patterns of varying frequency and amplitude measured in microvolts.
![]()
Headaches occur outside of the brain not inside!

- Almost all types of headaches occur in the nerves, blood vessels, and muscles that cover a person’s scalp and neck.
- Sometimes, the muscles or blood vessels bulge, pinch, or go through other changes that arouse the adjacent nerves or stress them.
- These nerves transmit pain messages to the brain, bringing out the headache.
![]()
No two brains are alike, even among identical twins!

- Identical twins have similar genes; however, they do not have identical brains because of the way the child goes through learning.
- The learning guides anatomical and physiological changes in the brain.
- As a result, they will end up having different social experiences, too.
- Hence twins will end up having different brains.
- It should be noted that every individual in the world has a somewhat different brain than any other person due to various social and environmental experiences.
![]()
The connections between neurons in the brain create a network that resembles a Spider web!

- The total number of neurons in the human brain is around the same ballpark as the number of constellations in the observable cosmos.
- The entire connection between the neurons in the human body resembles a spider web!
![]()
![]()
It would take more than 3,000 years to count all neurons in your brain!
- Your brain holds about 100 billion neurons.
- Counting them all would take you over 3,000 years.
- During dreaming, talking, laughing, thinking, seeing, or moving, tiny chemical and electrical pulses fly between these neurons along billions of neuron pathways.
![]()
It is a myth that humans use only 10% of their brain!

- Though nobody knows the exact fraction, scientists believe we use most or all of our brains.
- The 10% myth has unquestionably prompted many people to attempt greater creativity and productivity in their lives – hardly a bad thing!
![]()
The human brain is about 85% water!
- The brain is about 85% water.
- Water makes up more than 2/3 of the body weight.
- Also, the brain is 60% fat. It’s built on fat, although it runs on glucose.
![]()
The transmission rate of the axon in a neuronal cell is about 2,500 per second!

- The axon, which is the elongated cable-like protrusion from the neuronal cell responsible for transmitting signals, can transmit a large 2,500 signals per second.
- The transmitted signal path is directed by chemical messengers, which allow it to switch to different parts of the neuronal circuit.
![]()
In reality, brain control is the opposite of what is typically thought.
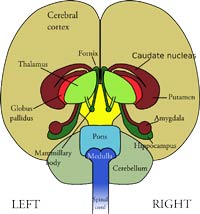
- The left part of the brain controls the right side of the body, and the right part controls the left side.
- It was also previously believed that in dominantly left-brained people, the left brain is more active and dominant than the right; they tend to be more creative and artistic.
- In dominantly right-brained, the right brain is more dominant and active than the left and tends to be more rational and logical.
- However, scientific research has proved that it is not all that simple!
![]()
The average length of the spinal cord measures to about 19 inches, but holds more than 10 million neurons!
- The spinal cord works together with a brain as well as independently.
- Some reflexes are handled by the spinal cord alone, and it contains more than 10 million neurons.
- The bunch of nerves that arise from the spinal cord are known as spinal nerves.
![]()
Only a small part of the brain is active.
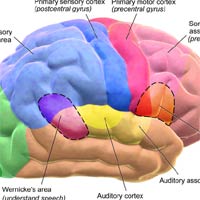
- There are over 100 billion cells in the brain. On the contrary, an octopus’s brain has only about 300 million neurons.
- However, only 4% of these cells are active and involved in electrical impulse generation and transmission.
- The rest of the cells are dormant or resting.
![]()
There are more cells in the human brain than human beings on the planet.
- The number of nerve cells or neurons in the human brain is over 100 billion.
- However, the current world population (as per April 2019 survey) stands at 7.7 billion individuals.
![]()
Without the proper functioning of the nervous system, all other systems would not be able to function optimally. The nervous system is indispensable to the human body and allows us to interact with the world.




















[…] The nervous system has less regenerative ability than most systems of the body, as these cells do not divide and reproduce. Scientists are currently examining stem cells to uncover their potential for repair and regrowth. […]