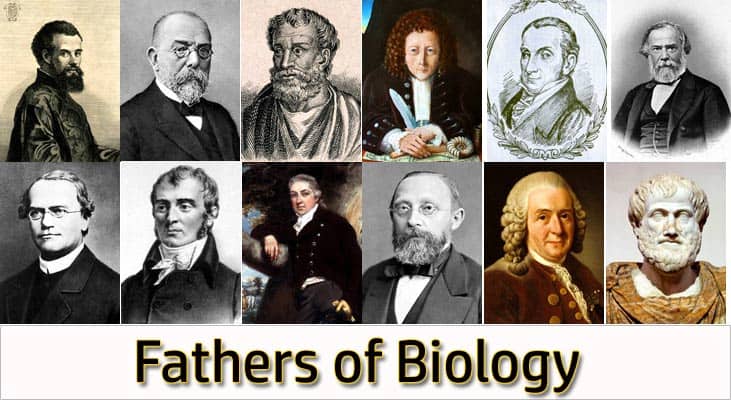
Uncovering the Fathers of Biology: The Geniuses Who Unveiled Life’s Secrets
In this post are the names of the so-called “Fathers of Biology” and the scientific contributions they’ve made that will all be remembered forever.

Biology, the study of life, is not limited to a single topic but actually involves several aspects like structure and function, behavior, name, applications, etc.
Since its advent as a scientific discipline, many scientists have contributed to its advancement and development, voluntarily or by serendipity. With that, names of significant discoverers come to mind, along with their great contributions to specific fields of biology.
On this page, we have explored the names of the founding scientists or the so-called “Fathers” in the field of biology and the corresponding scientific contributions they’ve made that will be remembered forever.
The father of biology is Aristotle. Here are the fathers of biology in various sub-disciplines of biology.
Jump to:
- Fathers of Biology
- Father of Anatomy | Herophilus
- Father of Bacteriology | Robert Koch
- Father of Botany | Theophrastus
- Father of Cytology | Robert Hooke
- Father of Ecology | G. Evelyn Hutchinson
- Father of Embryology | Kaspar Friedrich Wolff
- Father of Endocrinology | Charles-Edouard Brown-Séquard
- Father of Genetics | Gregor Johann Mendel
- Father of Histology | Marie Francois Xavier Bichat
- Father of Immunology | Edward Jenner
- Father of Mycology | Pier Antonio Micheli
- Father of Paleontology | George Cuvier
- Father of Pathology | Rudolf Virchow
- Father of Plant Physiology | Stephen Hales
- Father of Taxonomy | Carolus Linnaeus
- Father of Virology | Wendell Meredith Stanley
- Father of Zoology | Aristotle
- Jump to comments
Fathers of Biology
Father of Anatomy | Herophilus
![]()
 Born in the Greek town of Chalcedon, Herophilus was a physician who taught at the Hippocrates medical school. Herophilus was the first ever person to perform human dissection and because of his outstanding anatomic discoveries, Herophilus was regarded as the “Father of Anatomy“.
Born in the Greek town of Chalcedon, Herophilus was a physician who taught at the Hippocrates medical school. Herophilus was the first ever person to perform human dissection and because of his outstanding anatomic discoveries, Herophilus was regarded as the “Father of Anatomy“.
- On the other hand, Andreas Vesalius is regarded as the “Father of Modern Human Anatomy“, regardless of all the prohibitions about the dissection of humans during his time (16th century A.D.).
- The development of the field of anatomy became stagnant for centuries as it took more than 1800 years before human dissection was allowed again since Herophilus’ time. Refer to the history of anatomy for more details.
![]()
Father of Bacteriology | Robert Koch
![]()
 Robert Koch was notable for his discovery of the bacterium Bacillus anthracisin 1876. Such had launched the new scientific field of bacteriology. Refer to History of Microbiology for further details.
Robert Koch was notable for his discovery of the bacterium Bacillus anthracisin 1876. Such had launched the new scientific field of bacteriology. Refer to History of Microbiology for further details.
- His discoveries about microscopic techniques and different pathogenic bacteria like the Bacillus anthracis, Staphylococcus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Vibrio cholera, etc. ensued the “golden age” of scientific discovery.
- In honor of his phenomenal discoveries, Koch was called the “Father of Bacteriology“.
![]()
Father of Botany | Theophrastus
![]()
 Known for his exemplary published books on botany (i.e. “On the history of plants” and “On the Causes of Plants“), the Greek philosopher Theophrastus is often called as the “Father of Botany“.
Known for his exemplary published books on botany (i.e. “On the history of plants” and “On the Causes of Plants“), the Greek philosopher Theophrastus is often called as the “Father of Botany“.
- Theophrastus generally focused on integrating botany into agriculture and was the first person to study plant growth and analyze plant structure.
- Theophrastus’ discoveries and writings were extensive and detailed enough that it took more than 1800 years before any novel findings in the field were done.
![]()
Father of Cytology | Robert Hooke
![]()
 Known for his discovery of the first-ever compound microscope, Robert Hooke is often called the “Father of Cytology“. He used the such invention to view and observe the most minute and previously unknown structures called as the cells.
Known for his discovery of the first-ever compound microscope, Robert Hooke is often called the “Father of Cytology“. He used the such invention to view and observe the most minute and previously unknown structures called as the cells.
- He has written all his cell findings in the first-ever scientific publication bestseller, the Micrographia in 1665.
- Aside from his discoveries in biology, Hooke also has made several significant contributions to agriculture, physics, chemistry, and mechanical engineering.
![]()
Father of Ecology | G. Evelyn Hutchinson
![]()

The father of ecology is a UK born zoologist & Yale University professor, G. Evelyn Hutchinson.
- In 1957, he said an ecological niche was an “n-dimensional hypervolume.” According to this concept, the dimensions are the environmental factors that allow a species to survive.
- He proposed the idea that an organism's role in its niche could be how it feeds or how it reproduces. His work influenced other people to explain and explore the variety of resources used by one species and many other ecological questions.
![]()
Father of Embryology | Kaspar Friedrich Wolff
![]()
 The next biologist in this list is the German surgeon Kaspar Friedrich Wolff who is very famous for his scientific work Theoria generationis in 1759.
The next biologist in this list is the German surgeon Kaspar Friedrich Wolff who is very famous for his scientific work Theoria generationis in 1759.
- Wolff discoveries center on the idea that plant and animal cells that make up the embryo usually start as unspecialized but will later develop into specific cells that eventually form the tissues and organs.
- Before his discoveries, it was believed that adult living organisms are just exact copies of their offspring, only bigger. But the works of Wolff have proven them wrong. His discoveries have then paved the way for him to be considered as the “Father of Embryology“.
![]()
Father of Endocrinology | Charles-Edouard Brown-Séquard
![]()
 Many physicians and medical specialist regarding the controversial physician Charles-Edouard Brown-Séquard to be the “Father of Endocrinology“. In the year 1856, Brown-Sequard reported that the removal of adrenal glands could be detrimental to animals, and to address this problem, he began injecting extracts from other animals’ adrenal extracts to them.
Many physicians and medical specialist regarding the controversial physician Charles-Edouard Brown-Séquard to be the “Father of Endocrinology“. In the year 1856, Brown-Sequard reported that the removal of adrenal glands could be detrimental to animals, and to address this problem, he began injecting extracts from other animals’ adrenal extracts to them.
- However, one of his experiments, about the effects of injecting testicular extracts from animals into humans, made him appear ridiculous to some scientists.
- Even with Brown-Sequard’s findings, the field of endocrinology was initially regarded as “quackery” and not a serious scientific field, and it was only through the discovery of insulin in 1921 that this field became labeled as one.
![]()
Father of Genetics | Gregor Johann Mendel
![]()
 Famous for his work on pea plant Pisum sativum, the Austrian monk and scientist Gregor Johann Mendel is considered as the “Father of Genetics“.
Famous for his work on pea plant Pisum sativum, the Austrian monk and scientist Gregor Johann Mendel is considered as the “Father of Genetics“.
- Mendel proposed the three Laws of Inheritance: the Law of Segregation, the Law of Independent Assortment, and the law of Dominance.
- To propose these laws, Mendel had to grow over 10,000 pea plants, and it took him almost 8 years to finish them all. Unfortunately, during his time, Mendel’s work wasn’t appreciated much, and only after the rediscovery of his findings that the fundamentals of genetics were fully understood.
![]()
Father of Histology | Marie Francois Xavier Bichat
![]()
 A French anatomist, Marie Francois Xavier Bichat is well-known as the “Father of Modern Histology“.
A French anatomist, Marie Francois Xavier Bichat is well-known as the “Father of Modern Histology“.
- Bichat studied the effects of different diseases on the organs by performing more than 600 human autopsies. Based on these, he concluded that the study of the diseases must be on the tissue level rather than the organ or the entire body.
![]()
Father of Immunology | Edward Jenner
![]()
 An English physician, Edward Jenner lived in a period when smallpox was one of the deadliest diseases. To address this problem, Jenner made the first-ever vaccine against smallpox by rubbing some cowpox pus into an incision on one of his patient’s arms. Later on, his vaccine worked, and his theory was proven. Refer to the complete history of immunology here.
An English physician, Edward Jenner lived in a period when smallpox was one of the deadliest diseases. To address this problem, Jenner made the first-ever vaccine against smallpox by rubbing some cowpox pus into an incision on one of his patient’s arms. Later on, his vaccine worked, and his theory was proven. Refer to the complete history of immunology here.
- Some say that Jenner’s discovery had saved more lives as compared to the study of any other scientist in history, earning him the prestigious title “Father of Immunology“.
- Interestingly, Louis Pasteur was traditionally regarded as the “Father of Immunology” because of his works like the Germ Theory of Disease.
![]()
Father of Mycology | Pier Antonio Micheli
![]()
 Mycology is the study of fungi and organisms alike. While its history is still unclear, many scientists acknowledge Pier Antonio Micheli’s role in developing the discipline.
Mycology is the study of fungi and organisms alike. While its history is still unclear, many scientists acknowledge Pier Antonio Micheli’s role in developing the discipline.
- Micheli pioneered using a microscope to study fungi; with that, he came up with detailed illustrations of different fungal species. Aside from that, he was also the first person to thoroughly study spores in fungi.
- Because of his contributions, Micheli is often called the “Father of Mycology“.
![]()
Father of Paleontology | George Cuvier
![]()
 During the 18th century, French naturalist George Cuvier single-handedly found the scientific discipline of paleontology. As a naturalist, Cuvier focused on various studies about the history and development of organisms. Check out the famous paleontologists here.
During the 18th century, French naturalist George Cuvier single-handedly found the scientific discipline of paleontology. As a naturalist, Cuvier focused on various studies about the history and development of organisms. Check out the famous paleontologists here.
- Aside from establishing the discipline, Cuvier also developed several methods for the study of organismal biology and discovered evidence that prove the extinction of species.
![]()
Father of Pathology | Rudolf Virchow
![]()
 Rudolf Virchow is considered as the “Father of Cellular Pathology” due to his scientific contribution that center on the idea that infectious diseases can be understood more when studied at the cellular level.
Rudolf Virchow is considered as the “Father of Cellular Pathology” due to his scientific contribution that center on the idea that infectious diseases can be understood more when studied at the cellular level.
- Unlike Bichat, who preferred to work on tissues, Virchow viewed cells highly, believing that each element inside is mutually independent.
- Virchow proposed his most famous dictum: “Omnis cellula e cellula” (All cells come from preexisting cells.) in 1855.
![]()
Father of Plant Physiology | Stephen Hales
![]()
 Aside from his machine inventions for ventilation, the English botanist Stephen Hales is most notable for being the pioneer in establishing plant physiology as a discipline.
Aside from his machine inventions for ventilation, the English botanist Stephen Hales is most notable for being the pioneer in establishing plant physiology as a discipline.
- Hales’ hypotheses served as the foundations for modern knowledge in plant physiology. Such were his thoughts on the process of transpiration and photosynthesis.
- In 1727, his most important works and discoveries were published in his book entitled Vegetable Staticks.
![]()
Father of Taxonomy | Carolus Linnaeus
![]()
 Often called the “Father of Taxonomy“, Carolus Linnaeus (also Carl von Linné) is famous for introducing his system of the description, identification, naming, and classification of living organisms, which is still used at present.
Often called the “Father of Taxonomy“, Carolus Linnaeus (also Carl von Linné) is famous for introducing his system of the description, identification, naming, and classification of living organisms, which is still used at present.
- In 1735, Linnaeus published his book entitled The Systema Naturae, which takes into account all of his detailed classification of living organisms.
![]()
Father of Virology | Wendell Meredith Stanley
![]()
 Because of his work on the crystallization of the Tobacco Mosaic virus (TMV), biologist Wendell Stanley is considered as the “Father of Virology“.
Because of his work on the crystallization of the Tobacco Mosaic virus (TMV), biologist Wendell Stanley is considered as the “Father of Virology“.
- For the same accomplishment, Stanley was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1946. Interestingly, this award was the first ever to be given to a virologist. (As such, Stanley can be considered to be a biochemist).
![]()
Father of Zoology | Aristotle
![]()
 Known to be one of the greatest Greek thinkers, Aristotle excelled not only on the field of philosophy but also in the natural sciences as well.
Known to be one of the greatest Greek thinkers, Aristotle excelled not only on the field of philosophy but also in the natural sciences as well.
- His approach and theories may appear to be quite primitive as compared to modern methods. Still, his discoveries helped in building the fundamental knowledge in zoology.
- Aristotle has written several works about the history, movement, growth, and parts of animals in general.
- Aside from being the “Father of Zoology“, Aristotle is also sometimes referred to as the “Father of Biology“.
![]()
What do you think would have happened if the aforementioned scientists never discovered anything?
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 28). Uncovering the Fathers of Biology: The Geniuses Who Unveiled Life’s Secrets. https://www.bioexplorer.net/fathers-of-biology.html/




Great People
I have learned a lot from these great biologists.