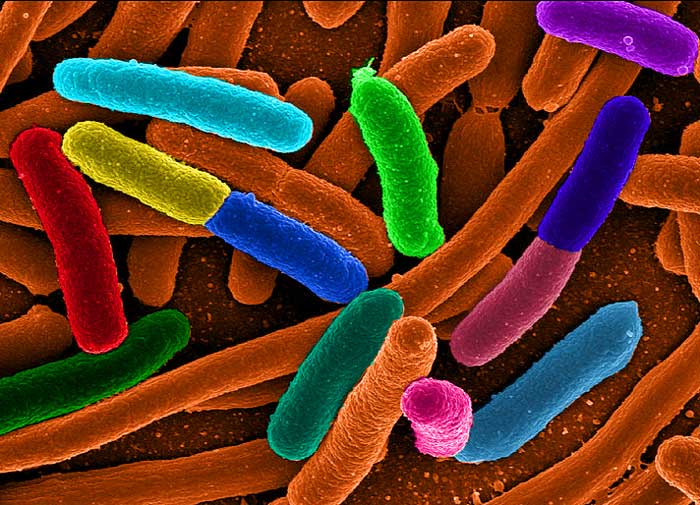
E-Coli or Escherichia is a strain of bacteria commonly found in the guts or lower intestines of warm blooded organisms, also known as endotherms. Though E-coli have earned the reputation of a lethal pathogen often hidden in eatables, it might be worth mentioning that the bacteria have many more befitting aspects to it.
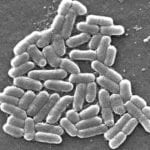 Several strands of E-coli are present in the digestive tracts of organisms and most of them are harmless. On the contrary, some of these bacteria like the O157:H7 are highly contagious, leading to the occurrence of deadly and malicious disorders like anemia, diarrhea or an absolute kidney failure.
Several strands of E-coli are present in the digestive tracts of organisms and most of them are harmless. On the contrary, some of these bacteria like the O157:H7 are highly contagious, leading to the occurrence of deadly and malicious disorders like anemia, diarrhea or an absolute kidney failure.
The pathogenic bacteria of Escherichia coli, first discovered by Theodor Escherichia, the famous German bacteriologist, and pediatrician in 1885 have been assigned a class and family, Gammaproteobacteria and Enterobacteriaceae respectively.
They are anaerobic in nature and rod-shaped in structure, approximately 2.0 micrometers in length and 0.25-1.0- micrometer in diameter. Studies show that E-coli colonize with hydrogen-consuming bacteria like methanogens in anaerobic conditions using mixed-acid fermentation. As byproducts, E-coli releases ethanol, lactate, acetate, succinate, and carbon-dioxide. It has been observed that temperatures ranging from 37 degrees Celsius to 49 degrees Celsius are ideal for the growth and multiplication of E-coli bacterium.
E-coli is highly contagious in some cases. For example, if you happen to gulp down food or drink water that has been infected by feces, chances of getting afflicted with serious discomfort in the abdominal tract is quite obvious. Sometimes proteins like animal meat, if not cooked properly at a minimum temperature of 71°, continue to carry bacteria that if left unchecked can poison the meat completely.
Dairy products, especially raw milk are a chief source of E-coli. Are you curious to know how? Well, bacteria can easily be transmitted from a cow’s udders to its milk. Hence dairy farms progress with a technologically advanced method of pasteurization before selling milk or other dairy items.
You should know that organic eatables like fruits and vegetables if left peeled and exposed for a very long time eventually becomes infected with bacteria. Therefore, it is imperative for people to learn about regular hygiene conditions and ways to maintain higher standards of sanitation in order to stay free from diseases caused by E-coli.
![]()
Completing the E. coli proteome.
A database containing information on E. coli genes which have been characterised since the completion of the genome sequence. Link
EcoCyc: Encyclopedia of E. coli Genes and Metabolism
EcoCyc is a bioinformatics database that describes the genome and the biochemical machinery of E. coli. The long-term goal of the project is to describe the molecular catalog of the E. coli cell, as well as the functions of each of its molecular parts, to facilitate a system-level understanding of E. coli. Link
The E. coli Genome Center
The UW Genome Project is a genome research center originally established to complete the sequence of the Escherichia coli K-12 genome. Building upon that foundation, we continue to maintain and update that annotated sequence and are currently working on the functional characterization of E. coli K-12 genes and their regulation. Link
The E. coli index
Resource for E. coli and general microbiologists alike. Link











