
Ever heard of a tomato that is resistant to rotting? How about a corn resistant to pests? Here are the disadvantages of genetically modified foods and why you should care.
In the continuing battle for hunger, food production has gotten more technologically improved through the years. Hence the production of food that is said to be “Genetically Modified,” like the ones previously mentioned.
Recombinant DNA technology or genetic engineering, the process behind the production of these, is seen as a potential tool for enhancing food quality and crop yield in the field of food and agriculture.
Table of Contents
But What Does Being Genetically Modified Mean?

Being genetically modified means that a “Gene of Interest” from one organism is extracted and inserted into the target organisms’ genes.
For example, if researchers want to make a particular organism produce a nutrient that it naturally isn’t capable of producing, they will look for another organism that can produce that specific nutrient.
The “Gene of Interest” may come from bacteria, insects, and animals with a specific target trait. Hence, genetically modified (GM) organisms are also called as “transgenic” because they involve such transfer of genes.
The primary objectives of genetically modifying food products are to increase yield and increase resistance to a pest in animals and plants. Although some genetically modified foods have already been approved and passed to be safe as their traditional counterparts, their continued production is still controversial.
Did you know that despite their seemingly wonderful characteristics, it is believed that several disadvantages may result from genetic engineering?
This is because the mere process of recombinant DNA technology is already prone to a mutation that can lead to unpredictable changes in the DNA and their proteins produced. The following are just some of these harmful effects.
Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Foods To Humans
Allergic reaction
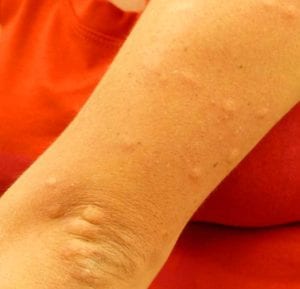
In humans, the number one most common side effect of consuming GM foods is allergic reaction. This allergic reaction happens when a certain protein/allergen present in the GM crop enters the body and stimulates an immune response.
As alluded to earlier, genetically modified foods are created by inserting foreign genes into an organism. This process is considered to have adverse effects on humans because these inserted genes may carry specific allergens that trigger such an immune response.
In addition, there is also the fear that new allergies could happen because of the mixing of genes from two organisms. And because some inserted genes come from bacteria and viruses, the possibility of transmitting disease is also being feared.
Production of toxins

GM food may also increase its production of toxins at levels already harmful to humans. Such may result from toxins produced when there is damage in the “Gene of Interest” during the insertion process.
Another reason is when the inserted gene is not generally accepted by the recipient organism because it interferes with its metabolic pathway. Thus, by eating such foods with toxins, the possibility of ingesting the toxin and being harmed by it may happen.
Reduced nutritional value

Ironically, some genetically modified foods have been reported to be void of nutritional value. As genetic engineering tends to focus more on increasing their production, prolonging their lifespan, and deterring pests, the nutritional value of some crops is sometimes compromised.
In fact, in a study published in the journal Food Chemistry, it has been found out that organic soybeans are far higher in nutritional components like healthy sugar, proteins, selenium, and zinc, as compared to genetically modified soybeans.
This finding also suggested that by making a plant more resistant to pests, the antioxidant phytochemicals are reduced. Hence, by genetically modifying foods, quantity is compromised over quality.
Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Foods On The Environment
Release of toxins to soil

As you can see, the disadvantages of GM crops are much larger than simply harming our health. Regarding its environmental effects, toxicity is a huge issue concerning GM crops. One particular example is the Bt Corn (Bacillus Thuringensis Corn), which is widely known for its pest controlling ability.
Bacillus thuringensis is a soil bacterium that has a gene that produces certain protein toxins that effectively destroy pests and insects, like larval caterpillars. This gene is then inserted into the corn to make it more resistant to pests.
While such characteristic helps control pests, this may result in releasing the said toxin into the soil. Too many toxins in the soil can prevent the growth of bacteria essential for plant growth. As a result, the soil becomes void of all necessary nutrients.
Resistance of pests to toxins

In addition to that, the long-term effects of GMOs are not certain. Scientists fear that excessive production of genetically modified foods with toxin-producing properties will be rendered ineffective over time. This is because the pests that these toxins used to deter might eventually develop resistance towards them.
Disruption of biodiversity

The production of GM foods imposes high risks to the disruption of biodiversity. This is because the “better” traits produced from engineering genes can favor one organism. Furthermore, the introduction of genetically modified organisms can eventually disrupt the natural process of gene flow.
So what does this mean? Disrupted gene flow can also lead to these genetically modified crops becoming weeds because they breed so rapidly and out-compete other crops.
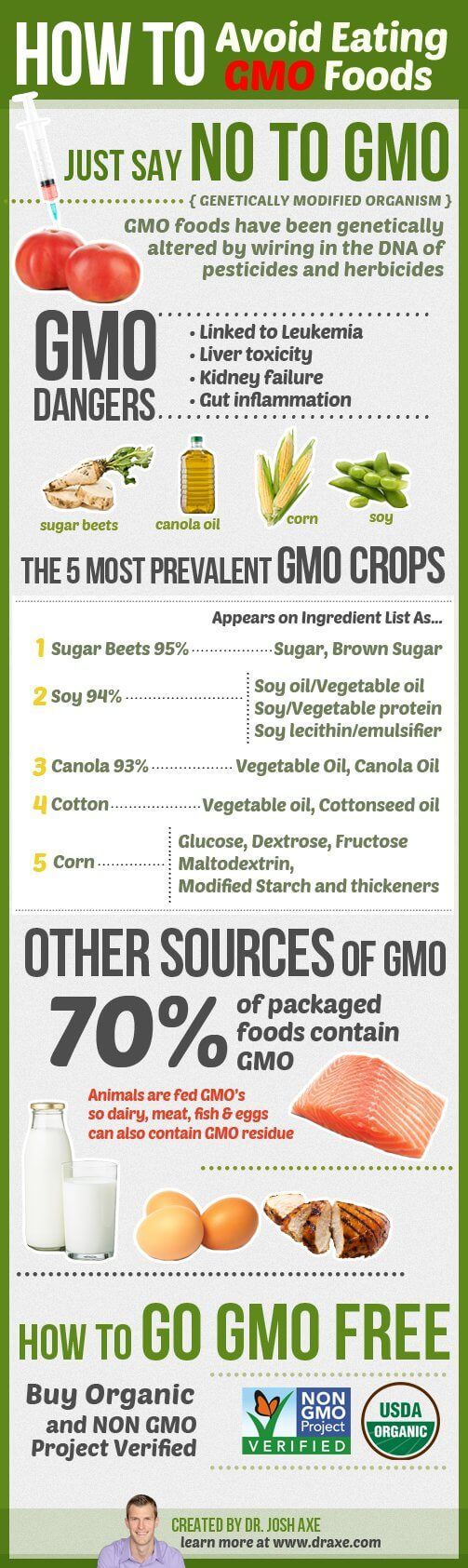
How to avoid GMO foods?
Social and Ethical Concerns
In addition to health and environmental issues, the production of GM crops and animals has become the center of social and ethical debates. And at present, it is still challenging to decipher their long-term effects, hence, leaving consumers the fear for safety.
Arguably, every food carries along with its associated health benefits and risks. Upon knowing all the mentioned disadvantages of genetically modified foods and crops not only to human health but also in the environment, the decision is all up to you.
But are you still willing to take the risk?























[…] Toxins can refer to a few things. The word can apply to environmental toxins like pesticides, chemical fertilizers in food, preservatives or additives in food, or genetically engineered foods. […]
[…] 6 Major Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Foods | Biology Explorer. (2018, October 30). Retrieved from https://www.bioexplorer.net/disadvantages-of-genetically-modified-foods.html/ […]
this is anti-gmo propaganda