Cellular Organization: Life exhibits a wide variety of levels of organization. For one, the cell is considered an entity’s smallest living functional unit and is always known as the basic unit of life. Despite their minute size, cells are still organized in a precise manner.
What is Cellular Organization?
By definition, cellular organization is the components that make up the cell and how they are arranged inside it. Each component, called an organelle, performs a specific function vital for the cell. This page will explore the basic functional components of the cell and cell shape and size. Let’s take a closer look.
![]()
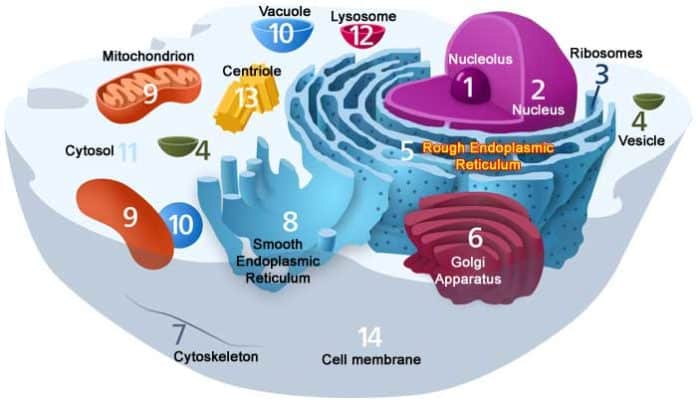
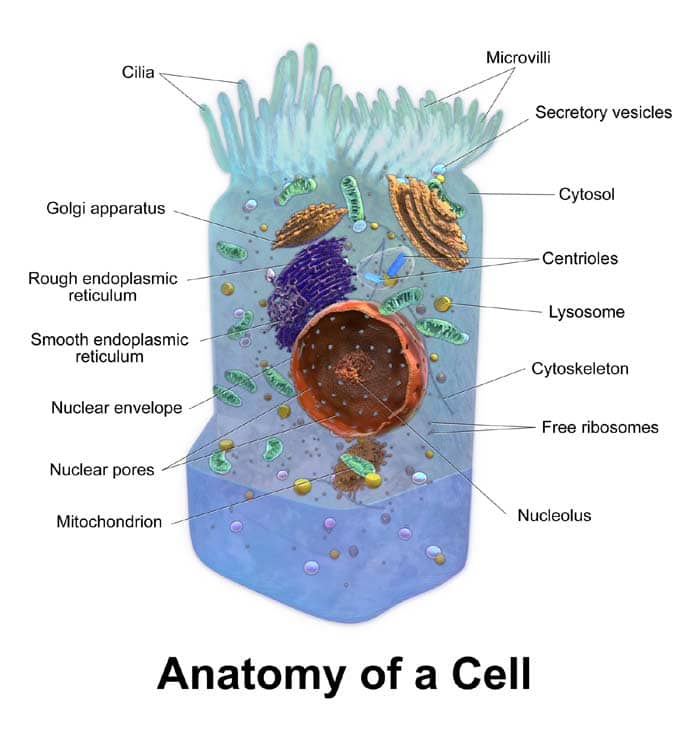
Functional Components Of The Cell
1. Nucleus
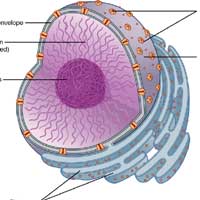 In eukaryotic organisms[1], the nucleus (plural: nuclei) is known to be the control center of the cell. It houses the cell’s genome (genetic material), where the processes such as DNA replication, transcription, and RNA processing occur.
In eukaryotic organisms[1], the nucleus (plural: nuclei) is known to be the control center of the cell. It houses the cell’s genome (genetic material), where the processes such as DNA replication, transcription, and RNA processing occur.
- The presence of a nucleus is the principal characteristic that distinguishes eukaryotes from prokaryotes. The latter only have a so-called nucleoid wherein the genetic material is embedded.
- In addition to that, the nucleus of eukaryotic organism is surrounded by a nuclear membrane that functions to separate the nucleus from the rest of the organelles in the cytosol.
![]()
2. Cell Membrane (also Plasma Membrane)
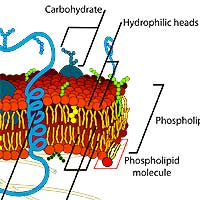 Like any other membranes, the cell membrane[2] is composed of a phospholipid bilayer (also described as the Fluid Mosaic Model) that creates a rigid barrier between the inside of the cell and its outside environment.
Like any other membranes, the cell membrane[2] is composed of a phospholipid bilayer (also described as the Fluid Mosaic Model) that creates a rigid barrier between the inside of the cell and its outside environment.
- As its name suggests, the phospholipid bilayer[3] is composed of two layers of phospholipids, with one layer having hydrophilic heads (water-loving; polar) in its outer side and hydrophobic tails (water-hating; nonpolar) interior side.
- The proteins found in the bilipid layer perform selective transport of molecules, recognition, and cells.
![]()
3. Cytoplasm
 By definition, the cytoplasm[4] is the fluid that fills the cell up and is surrounded by the cell membrane. The cytoplasm is mainly composed of salts and proteins dissolved in water.
By definition, the cytoplasm[4] is the fluid that fills the cell up and is surrounded by the cell membrane. The cytoplasm is mainly composed of salts and proteins dissolved in water.
- In eukaryotes, the cytoplasm consists of materials (i.e., organelles) located in win the cell, excluding the nucleus.
- The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain any organelles is referred to as the cytosol.
![]()
4. Cell Wall
 The outer covering of cells (plants, fungi, algae, bacteria, and archaea) located next to the cell membranes is called the cell wall.
The outer covering of cells (plants, fungi, algae, bacteria, and archaea) located next to the cell membranes is called the cell wall.
- While the cell membrane is made up of phospholipids, the cell wall is made up of sturdier compounds – polysaccharides, usually cellulose (in plants) and peptidoglycan (in bacteria).
- Interestingly, throughout their life cycle, plants develop two types of cell walls: primary and secondary; Primary cell walls are usually thin and stretchable, but once the growth ceases, a secondary cell wall is produced. This secondary cell wall is tougher and more rigid due to the added polymer called lignin.
![]()
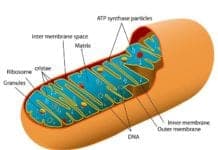
5. Mitochondrion
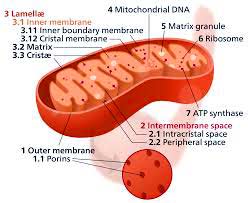 Known as the powerhouse of the cell, the mitochondrion (plural: mitochondria) is the double-membraned organelle where the process of cellular respiration takes place. During cellular respiration, precursor molecules like sugars and other carbohydrates produce a usable form of energy.
Known as the powerhouse of the cell, the mitochondrion (plural: mitochondria) is the double-membraned organelle where the process of cellular respiration takes place. During cellular respiration, precursor molecules like sugars and other carbohydrates produce a usable form of energy.
- In animals, the muscle cells contain the most number of mitochondria, which is justifiable because they need much energy for locomotion.
- Interestingly, the mitochondrion (together with the chloroplast) has a different genetic material than the nucleus. This phenomenon can be explained by the Endosymbiotic theory that states that the mitochondria and chloroplasts were once unicellular organisms that were engulfed by a larger cell.
![]()
6. Chloroplast
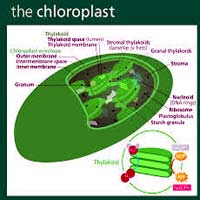 Specific to plant cells and algae, chloroplasts[5] are double-membraned organelles that can convert light energy, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O) to carbohydrates in a process called photosynthesis.
Specific to plant cells and algae, chloroplasts[5] are double-membraned organelles that can convert light energy, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O) to carbohydrates in a process called photosynthesis.
- Like mitochondria, chloroplasts are considered to have originated from the engulfment of cyanobacteria.
![]()
7. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
 Most cells contain two types of endoplasmic reticulum: the rough and the smooth. The rough endoplasmic reticulum[6] (ER) is the extensive and highly convoluted organelle that is involved in the production, folding, and regulation of proteins.
Most cells contain two types of endoplasmic reticulum: the rough and the smooth. The rough endoplasmic reticulum[6] (ER) is the extensive and highly convoluted organelle that is involved in the production, folding, and regulation of proteins.
- Basically, the rough ER is called as such because of the ribosomes that are attached to it (see smooth ER).
![]()
8. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
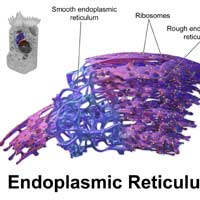 The more tubular type of the endoplasmic reticulum, the smooth ER forms an interconnecting network in the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi body.
The more tubular type of the endoplasmic reticulum, the smooth ER forms an interconnecting network in the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi body.
- Contrary to the rough ER, the smooth ER is called such because it is associated with slippery fat molecules, and there are no attached ribosomes.
![]()
9. Ribosome
 Ribosome are the sites where protein synthesis occurs. These proteins are important as they serve various purposes like catalyzing biochemical reactions, acting as structural support, and building blocks of some membranes.
Ribosome are the sites where protein synthesis occurs. These proteins are important as they serve various purposes like catalyzing biochemical reactions, acting as structural support, and building blocks of some membranes.
- Ribosomes are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.
- Inside the cell, the ribosomes are either found to be suspended in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER.
![]()
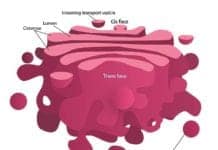
10. Golgi Body
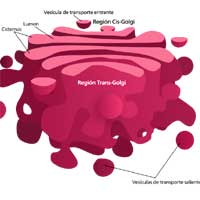 Inside the cell, the Golgi body (also known as Golgi Apparatus or Golgi Complex) is the organelle where the final modification and packaging of molecules like proteins occur. These molecules, when packaged, are either sent outside of the cell or stored in vesicles.
Inside the cell, the Golgi body (also known as Golgi Apparatus or Golgi Complex) is the organelle where the final modification and packaging of molecules like proteins occur. These molecules, when packaged, are either sent outside of the cell or stored in vesicles.
- The Golgi body is also responsible for the production of lysosomes.
- The Golgi body was named after the Italian biologist Camillo Golgi.
![]()
11. Vesicle
 As mentioned above, vesicles are membrane-sac that function for storage and transport of molecules within and outside of the cells. Usually, molecules are transported outside the cell through exocytosis and imported from the cell through phagocytosis and endocytosis.
As mentioned above, vesicles are membrane-sac that function for storage and transport of molecules within and outside of the cells. Usually, molecules are transported outside the cell through exocytosis and imported from the cell through phagocytosis and endocytosis.
- Vesicles are formed when a portion of the cell membrane is pinched off.
![]()
12. Vacuole
 The term “vacuole[7]” comes from the description of the morphology of this organelle – showcasing that the overall structure is “hollow” or “empty.”
The term “vacuole[7]” comes from the description of the morphology of this organelle – showcasing that the overall structure is “hollow” or “empty.”
- Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles that store food, nutrients, and non-nourishing chemicals. Aside from that, vesicles can also be temporary storage for waste products.
- In plant cells, vacuoles contribute to the rigidity of the overall structure by storing water to create hydro-static pressure.
![]()
13. Lysosome
 Lysosomes[8] are the membrane-bound organelles that are considered to be the “digestive system” of the cell as they contain a wide array of enzymes that can break down and degrade complex biological molecules (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids).
Lysosomes[8] are the membrane-bound organelles that are considered to be the “digestive system” of the cell as they contain a wide array of enzymes that can break down and degrade complex biological molecules (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids).
- Aside from digesting foreign materials and molecules, lysosomes can function to degrade the component of the cell itself.
- Sometimes, lysosomes are considered to be specialized vacuoles whose main function is digestion.
![]()
14. Centrioles
 Centrioles are minute cylindrical organelles found only in animal cells and some plant cells. They consist of a set of microtubules arranged in specific patterns. See the differences between centrosome and centriole here.
Centrioles are minute cylindrical organelles found only in animal cells and some plant cells. They consist of a set of microtubules arranged in specific patterns. See the differences between centrosome and centriole here.
- Centrioles play an important role in the development of spindle fibers during cell division.
![]()
Cell Shape And Size
Different cells have different shapes, and their unique morphologies are directly related to their function:
- Plant cells generally have rectangular, rigid walls and distinct edges. Such structure is contributed by the cell wall that forces the cell to have a definite shape.
- Unlike plant cells, animal cells tend to have more irregular body shapes due to the absence of cell walls in their overall structure.
- Microorganisms like bacteria have three types of cell shape: oval (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), spiral, star-shaped, and rectangular.
- See the differences between plant and animal cells here.
Like shapes, the size of cells is also linked to their functions. Depending on the type of organism, the size of the cell greatly varies.
- In particular, egg cells[9] are the largest cells that an organism has. This is very much related to their function, as the development of the zygote after fertilization requires huge amounts of energy. The human egg cell measures 0.12 mm in diameter.
- On the other hand, the smallest cell is that of the parasitic bacterium Mycoplasma gallicepticum. This bacterium thrives in the bladder, respiratory and reproductive tracts of mammals. This cell has an average diameter of 0.0001 mm.
![]()
To perform more efficiently, cells usually undergo a multi-cellular organization where similar cells form tissues. A group of tissues and similar structures which perform similar functions together constitute an organ. A group of organs performing physiological processes form an organ system, and organ systems that work together constitute an organism.
Isn’t it amazing how a single cell can be so complex?
![]()