Cell Biology News of 2022: Past news in 2021 was thrilling, with loads of innovation in stem cell research to cellular communication. These news topics focus on various subjects related to cell biology in 2022.
With inventions in molecular tools to design chromosomal segregation machinery, the role of transcription factors (NAC) as a gatekeeper in cell sorting, the role of mitochondria in cellular stress, and other 3D bioprinting tools to opt for therapeutic applications. So, let’s glimpse these innovations with a wider view.
Top 15 Cell Biology News of 2022
Here are the top 15 cell biology news and breakthroughs in 2022.
1. Scientists have found a molecular tool that is essential for creating artificial chromosomal segregation machinery (Japan, Dec 2022)
Most organisms undergo cell division with the help of kinesin proteins, which shorten microtubules and pull chromosomes to opposing spindle poles. Fission yeast doesn’t have these proteins but still undergoes the same process. According to a recent study, non-kinesin proteins of the TOG/XMAP215 family encourage microtubule shortening in fission yeast through a mechanism known as microtubule catastrophe.
- The transporter-opsin-G protein-coupled receptor (TOG) proteins were regarded as traditional microtubule stabilizers, and kinesin was thought to be the sole cause of microtubule shortening for chromosome transport.
- The team performth in vitro and in vivo experiments using yeast cells. Fluorescence microscopy was used to take pictures of yeast microtubules, and the effect of Dis1 on microtubule length was investigated.
- Images taken at five-second intervals showed that Dis1 encourages microtubule shortening through a process known as microtubule catastrophe, in which growing microtubules abruptly change into a rapidly shortening state.
The molecular device developed in this study can serve as a platform for synthetic chromosome segregation machinery, which could help develop treatments for illnesses brought on by chromosome segregation errors. Alternatively, it could be utilized to create artificial cells that can segregate genetic material into offspring.
Suggested Reading:
Top Cell Biology News of 2020 – A Round Up
2. Researchers unfold a twenty-five-year-old mystery on the mechanism as to how proteins in cells get sorted (Germany, Feb 2022)
Researchers have found the answer to an over-25-year-old mystery of how proteins are organized in cells. As a “gatekeeper” in protein synthesis, a protein complex called NAC (nascent polypeptide-associated complex) controls the transport of proteins inside cells. Molecular and cell biologists have now clarified the molecular mechanism underlying this function.
- NAC acts as a gatekeeper, ensuring only proteins with the endoplasmic reticulum as their destination are transferred to the protein transporter SRP (signal recognition particle).
- The transport of the “cargo” to the designated location is then mediated by SRP. On the other hand, the gatekeeper NAC prevents the protein transporter SRP from accessing a nascent protein with a destination other than the endoplasmic reticulum.
- The region of the ribosome where the developing protein exits the “protein factory” is where NAC binds.
- Part of NAC acts as a gatekeeper by positioning itself before the ribosomal tunnel, preventing SRP from accessing the ribosome and the developing protein.
- Only when a transport signal sequence for the endoplasmic reticulum, encoded in the developing protein, exits the tunnel during protein synthesis is access granted. This signal is recognized by NAC, which then relocates the ribosome.
Thus, the study reveals the molecular role of NAC as a gatekeeper, allowing SRP access only for those developing proteins with an endoplasmic reticulum destination. Future research must demonstrate whether NAC also serves other regulatory purposes at the ribosomal tunnel.
Suggested Reading:
Ribosomes Function: The Cell’s Protein Machinery
3. Scientists define the mechanism of how mitochondria report stress response (Germany, April 2022)
The method by which the protein DAP3-binding cell death enhancer 1(DELE1) detects organelle stress has been uncovered by researchers. This suggests a potentially novel method of treating neurodegenerative illnesses.
- This import-export process fails as a result of mitochondrial stress.
- When new DELE1 molecules try to enter the mitochondria, they are stopped and, depending on the cause of the disruption, either cut by Zn2+-dependent metalloendopeptidase (OMA1) or left outside the organelles uncleaved.
- In any case, the DELE1 protein’s activating portion is revealed in the cytosol.
- One of the sub-steps in the importing and processing of DELE1 comes to a halt because of all the different kinds of stress. This method is used to identify mitochondrial stress.
Researchers can now investigate a variety of scenarios because they have a better understanding of the mechanism. It would be dangerous if they didn’t figure out how a cell decides whether to enter a repair phase due to a stress response or undergo programmed cell death. As a potential method of treating neurodegenerative diseases, they also hope to be able to modify the signaling pathway so that it encourages cellular survival during times of mitochondrial stress.
Suggested Reading:
Top 15 Discoveries in Cell Biology for 2018
4. In cancer cells, RNA molecules regulate the repair of human DNA (Sweden, Feb 2022)
A recent study demonstrates how specific RNA molecules regulate the repair of damaged DNA in cancer cells. This finding may one day lead to more effective cancer therapies.
- All living things contain RNA molecules, fundamental molecules only involved in synthesizing proteins. However, recent studies show that RNA molecules serve a broader purpose and can be crucial in disease emergence.
- A contributing factor in cancer may be DNA damage to cells. DNA damage occurs and is continuously repaired, but in some circumstances, it can result in mutations that can cause cancer.
- Therefore, developing novel therapies requires a fundamental comprehension of how our cells repair DNA. In the current study, the scientists looked at how specific RNA molecules impacted the cancer cells’ capacity to fix radiation-damaged or frayed DNA strings.
- They discovered that the enzyme DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), which affected the DNA-repair mechanisms, was controlled by the interactions of two molecule types, small Cajal body-specific RNA 2 (scaRNA2) and WRAP53.
According to recent research, some RNA can bind to an enzyme that fixes damaged DNA and act as an “on-off” switch for the enzyme, regulating DNA repair. The findings, in the opinion of the researchers, will help us better understand how RNA contributes to DNA repair and cancer. This could lead to the development of novel cancer treatment strategies, such as using artificial RNA molecules to induce cancer cell death.
Suggested Reading:
Top 12 Cell Biology News in 2017
5. A recent study reveals the reason behind the failure of In vitro fertilization embryos (USA, July 2022)
According to new research, so many human embryos fail to develop normally may be due to spontaneous errors in the earliest stage of cell division.
- Cell division starts about 24 hours after fertilizing a human egg. The entire genome, which consists of 46 chromosomes and more than 3 billion base pairs of DNA, must be faithfully replicated during cell division.
- The duplicate chromosome sets must be divided, giving each daughter cell a full set. Errors within the double helix of the DNA appear to be the root of DNA copying errors in embryos.
- Even though the exact cause of these barriers is unknown, they cause DNA duplication to pause or even stop, which leads to DNA breakage and an abnormal number of chromosomes.
- The researchers discovered that spontaneous DNA errors could happen durihuman embryos’the first cell division cycos and subsequent cell divisions.
- The embryo cannot develop further if there are too many chromosomally abnormal cells in the early embryo. Most human embryos produced through IVF stop growing a few days after fertilization.
- The effectiveness of fertility treatments is hampered by the inefficiency of human development.
The researchers plan additional studies examining DNA damage during replication to comprehend normal and disease-causing variations in the human germ line. These investigations may eventually result in techniques to lessen the chance of genetic anomalies and embryo attrition in patients undergoing IVF.
Suggested Reading:
Top 25 Reproductive System Fun Facts
6. A new type of cell in the human lung is capable of regeneration (USA, April 2022)
A new type of cell has been identified that is found deep inside the human lungs and may be crucial in the development of lung diseases.
- The scientists examined human lung tissue to find the novel cells, called respiratory airway secretory cell, and published their findings in Nature Today (RASCs).
- Deep inside the lungs, close to the alveoli structures where oxygen is changed into carbon dioxide, the cells line tiny airway branches. The researchers demonstrated that RASCs have stem-cell-like qualities that allow them to regenerate other cells necessary for the healthy operation of alveoli.
- Additionally, they discovered evidence that smoking cigarettes and the common smoking-related illness known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can impair the RASCs’ capacity to regenerate, which may suggest treating COPD by reversing this disruption.
- Alveoli typically experience progressive loss and damage due to COPD, which is made worse by ongoing inflammation. In some regions of the United States, it is thought to affect 10% of the population. It is thought to be responsible for 3 million fatalities annually worldwide.
- Oxygen therapy and/or steroid anti-inflammatory drugs are frequently prescribed to patients. Still, these therapies only slow the disease process rather than halting or reversing it.
The results suggest that RASC-to-AT2 differentiation can be restored to treat COPD or that the normal RASC population can be replenished in damaged lungs.
Suggested Reading:
Top 25 BEST Respiratory System Fun Facts
7. Researchers discover a gene that permits beta cells to communicate with one another, assisting the pancreas to secrete insulin in response to glucose (Germany, Nov 2022)
Diabetes, a disease that affects millions of people worldwide, arises when the body either produces insufficient amounts of the hormone insulin, which helps to keep blood sugar levels in check, or when the body cannot properly utilize the insulin produced. Not enough insulin is released when the number of beta cells is too low or not working properly.
To coordinate the release of insulin, beta cells talk to one another. The ability of beta cells to sense glucose and release the hormone insulin, which allows other cells in the body to store glucose, is now known due to the gene Wnt4. Future research on replacement beta cells for diabetes treatment may benefit from these discoveries.
- In beta cells, the Wnt4 gene is expressed as the cell matures. Wnt4-expressing cells stop proliferating and gain more functionality.
- They observed that beta cells secrete less insulin when Wnt4 levels are lower. The researchers discovered that despite the beta cells’ ability to detect blood sugar, they secreted less insulin in response to glucose.
- It was fascinating to learn about beta cell communication in the pancreas, how it is conserved across many animal species, and the mechanisms by which it functions, particularly the significant metabolic changes it causes in beta cells.
- Wnt4-expressing cells stop proliferating and gain more functionality. We observed that beta cells secrete less insulin when Wnt4 levels are lower. The researchers discovered that despite the beta cells’ ability to detect blood sugar, they secreted less insulin in response to glucose.
It was fascinating to learn about beta cell communication in the pancreas, how it is conserved across many animal species, and the mechanisms by which it works, particularly the significant metabolic changes it causes in beta cells. We do not know whether beta cells release Wnt4 routinely or only in certain situations. In the future, we’ll want to investigate this. The findings may support the creation of replacement beta cells for diabetes therapy containing Wnt4 to encourage maturation.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Cell Biology Discoveries in 2019
8. Researchers create a “prodrug” that targets glutamine, which cancer cells crave heavily while sparing healthy cells unharmed (USA, Nov 2022)
An anti-cancer medicine has been repurposed by researchers to target cancer cells while sparing healthy organs more effectively.
- The plan was to alter an old cancer treatment with a strong track record of effectiveness. Still, it couldn’t be clinically developed because it was excessively toxic, particularly to the gut.
- So, a prodrug strategy was adopted to achieve this. A novel chemical method to develop a prodrug that was simultaneously bio-activated in cancer cells and bio-inactivated in healthy organs like the gut. This makes their strategy distinct.
- This effective class of medications is being reevaluated safely in patients thanks to the payload’s preferred targeting of cancer cells.
- The newly altered prodrug takes advantage of a characteristic shared by cancer cells: a ravenous desire for glutamine, an amino acid essential for the synthesis of proteins, lipids, and Nucleotides, as well as for energy.
- The phenomenon known as “glutamine addiction” refers to excessive glutamine consumption by rapidly expanding cancer cells. However, other healthy cells with quick turnover, such as those lining the gut, also depend on glutamine.
- DRP-104 is a glutamine mimic medication termed DON (6-Diazo-5-Oxo-L-norleucine) that targets tumors and inhibits several glutamine-using enzymes in cancer cells.
- The development of DON was terminated because it was harmful to normal tissues, particularly the gut, despite numerous early tests showing it to be highly effective in humans and rats.
This prodrug (DON) was therefore made to target tumor cells and have less influence on healthy cells elsewhere thanks to this particular repurpose design.
Suggested Reading:
History of Immunology
9. Researchers unveil a novel method for treating aggressive cancer (USA, Feb 2022)
According to researchers, an enzyme called EZH2 that modulates chromatin has a novel function in the emergence of cancer. Next, using the proteolysis-targeting chimaera (PROTAC) technology, they created the new small-molecule MS177, which suppresses cancer growth by targeting both EZH2 and cMyc.
- EZH2 has two unique binding patterns in acute leukemia cells on chromatin, resulting in two separate gene-regulatory pathways.
- On the one hand, EZH2 interacts with cMyc to activate gene expression at genomic sites; on the other hand, EZH2 forms a classical protein complex known as PRC2, which causes gene repression at several genomic areas.
- According to the researchers, MS177 demonstrates substantial tumor-killing effects and has an on-target effect on cancer cells. “MS177 is more likely to act significantly better for treating patients with acute leukemias than the current enzymatic inhibitors.
- To our knowledge, no agent has ever been created to simultaneously target EZH2 and cMyc. In light of the preceding tumorigenic pathways, MS177 is a prospective option for the treatment of further malignancies.
Thus, this study shows how effectively the tiny chemical PROTAC targets cMyc and EZH2 in cancer cells at the same time.
10. Scientists discovered the mechanisms as to how the fat cells help combat acne (USA, Feb 2022)
Researchers have identified a particular antimicrobial skin cell and its function in the emergence of acne, which may lead to more focused therapeutic choices.
- It was once believed that hair follicles played the biggest role in the development of acne. They examined the cells outside of the hair follicle in this study. They discovered they had a significant impact on preventing the growth of germs and acne.
- These cells, known as fibroblasts, are in connective tissues all over the body. They create the antibacterial peptide cathelicidin in the skin, which is essential for the growth of acne.
- Reactive adipogenesis is when fibroblasts in the surrounding skin change into fat cells to fight infection inside a hair follicle. Cathelicidin is also created to battle the illness by inhibiting bacteria that can cause acne.
- In response to the acne-causing bacterium Cutibacterium acnes, these fibroblast cells were stimulated to create significant levels of cathelicidin, an essential antibiotic.
Thus, this discovery could assist in developing novel therapy options that directly target the fibroblast’s ability to make cathelicidin.
Suggested Reading:
Top 25 Integumentary System Facts (Skin Fun Facts)
11. TANGO2 (Transport and Golgi Organization 2 Homolog. is the focus of research on the iron-rich blood molecule (USA, Oct 2022)
Researchers have created novel instruments and methods to scan, monitor, and probe heme in biological systems to understand better how organisms manage this necessary but potentially deadly molecule.
- Life cannot exist without heme, the iron-containing molecule that gives blood its red color. Ironically yet, if not managed properly, it may be rather toxic.
- In fact, deficiencies in heme homeostasis are linked to a wide range of illnesses, including several malignancies and cardiovascular conditions. The study team uncovered a previously uncharacterized protein, HRG-ed TANGO2), that helps mobilize heme from production or storage sites for metabolism.
- In many illness scenarios, identifying a new protein that guarantees heme is bio-available may serve as a new therapeutic target, either to restrict heme, deprive cells of this vital nutrient, or promote excessive heme accumulation and make it poisonous to cells.
- A genetic condition caused by the TANGO2 gene is characterized by metabolic and developmental impairments.
The fact that TANGO2 is involved in heme homeostasis suggests that these disorders may be treated with heme-centered treatments. The researchers believe that comprehending the principles of heme trafficking will offer insights into the secure transportation of such “important poisons” inside the cell. Also, it might provide ideas for new treatment approaches to combat conditions, including anemia, porphyria, and a few cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases linked to heme dysregulation.
12. Researchers found unique defenses against infections and malignancies are provided by immune cells that are embedded in tissues (USA, June 2022)
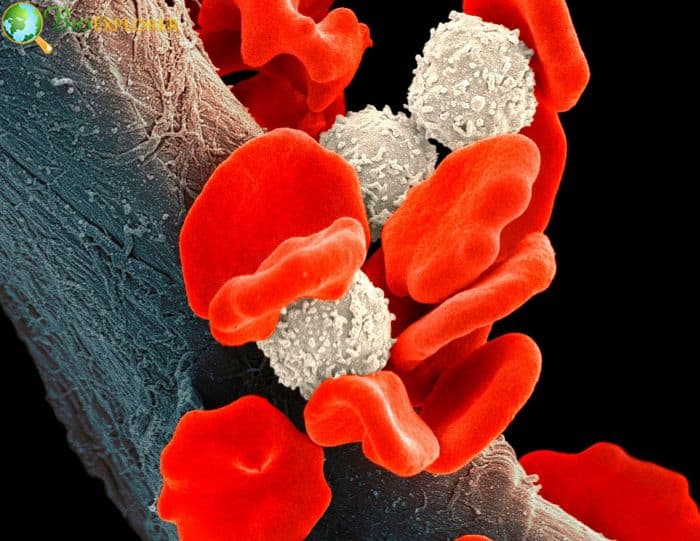
Researchers have achieved ground in comprehending special immune cells equipped to remember the names of dangerous intruders. The likelihood of developing immune defense techniques to strengthen immunity in places sensitive to infection has increased due to the researchers’ creation of a novel atlas that describes tissue-resident memory T cells in various tissue settings.
- CD8+ T cells, activated in response to infections and tumors and can recall the names of harmful invaders, are receiving more attention from researchers studying how the human immune system reacts to pathogens and cancers.
- These specialized cells, often called CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells, are the subject of a recent study undertaken by biologists at the University of California, San Diego.
- The likelihood of developing immune defense techniques to strengthen immunity in places sensitive to infection has increased due to the researchers’ creation of a novel atlas that describes tissue-resident memory T cells in various tissue settings.
- To find novel targets that guide the strategic design of vaccines to provide the highest protection among “first responders” in the tissues where infections and malignancies begin their growth by identifying the distinct transcriptional pathways and regulators of tissue-resident memory T cells.
These findings raise the possibility of “programming” tissue-tailored immune responses, where immune cells that promote or regulate inflammation could be transcriptionally engineered for trafficking to, retention in, and function within a particular tissue. Future extensions of this research could take the form of customized engineered therapies.
13. Researchers have developed constructs that resemble tissues and are capable of regulated, sophisticated shape modification (USA, March 2022)

Creating new cell-rich 4D bioconstructs that can change shape under physiological conditions is made possible by cell-laden bio-ink, which comprises densely packed, flake-shaped microgels and living cells.
- Scientists may manufacture complex structures and more accurately simulate the form changes during genuine tissues’ growth, healing, and normal function by using 4D bioprinting constructs.
- Creating a brand-new cell-fillbio inkink for bioprinting four-dimensional constructions of densely packed, flakes-shaped microgels and living cells.
- This novel technique makes it possible to create cell-rich bioconstructs that can transform under physiological demand. With the help of thbio inking system, it is now possible to priconstructscts that can undergo more complex architectural modifications over time.
- These cell-rich structures with pre-programmable and controllable shape transforming have the potential to resemble the body’s normal developmental processes, allowing researchers to understand tissue morphogenesis bettersis and make strides more closely in tissue engineering.
This is the first system that satisfies the stringent criteria for bioprinting 4D constructs, including loading living cells into bio-inks, permitting printing of large complex structures, inducing shape transformation under physiological conditions, supporting long-term cell viability, and facilitating desired cell functions like tissue regeneration.
Given the severe lack of available donor tissues and organs, this approach is extremely beneficial for clinical applications of tissue engineering.
Suggested Reading:
Top 25 Endocrine System Fun Facts
14. Scientists designed a new toolkit to develop safe and efficient therapeutic cells (USA, April 2022)
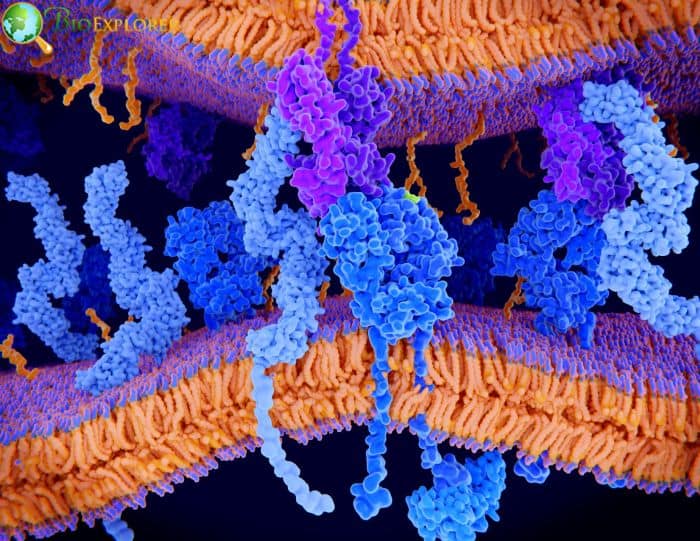
The molecular components employed to design therapeutic cells researchers thoroughly examineders. Their efforts produced a thorough set of guidelines for designing therapeutic cells with increased safety and specificity and for potentially customizing cell-based therapeutics.
- Most therapeutic cells contain a receptor molecule at their center. Large proteins that cross the cell’s outer membrane are called receptors.
- Their inner portion instructs the cell what to do when their outside portion recognizes a particular target (for example, a protein on the surface of a cancer cell).
- Inserting a synthetic receptor created by assembling bits of existing receptors into a cell – often an immune cell known as a T cell – is one therapeutic cell engineering method.
- SynNotch receptors can help T lymphocytes recognize and eradicate solid tumors more effectively.
- Since this early-stage research, Roybal’s lab has demonstrated how synNotch can be utilized in conjunction with CARs to provide next-generation cell treatments for ovarian cancer and mesothelioma.
These cell therapies can unleash robust therapeutic activity precisely where the disease is present, increasing the therapy’s effectiveness and lowering the risk of potentially fatal toxicities.
15. Scientists found a novel cell treatment strategy, tumors significantly diminish (USA, January 2022)

Researchers have created a novel method to combat cancer quickly and successfully by using tumor immune cells.
- Scientists at Northwestern University have created a new method to use immune cells from tumors to quickly and successfully treat cancer.
- There was a considerable reduction in tumor size compared to standard cell treatment techniques in mice. The scientists multiplied, sorted through, and collected hundreds of millions of cells using a unique microfluidic device that could be 3D printed, retrieving 400% more tumor-eating cells than was possible with earlier methods.
- Most cancer treatments include foreign substances and toxic chemicals that impair the body’s immune system and have negative side effects.
- Several disease therapies in regenerative medicine and cancer treatment have gained traction in the clinic because using tissue from one’s body can avoid adverse effects and the danger of rejection.
- Researchers can identify the more active cells using cell sorting methods made possible by nanotechnology by using a novel technology called microfluidic affinity targeting of infiltrating cells (MATIC).
Thus, the 3D-printed device might be brought into clinical settings rather than being restricted to a lab because it is compact and easily reproducible. The expense of research and development would be drastically reduced, and more patients could get cell therapy.
This 2022 news series on cell biology gives us a detailed overview of the recent advancements. Commencing with the construction of chromosomal segregation machinery to treat illness, the role of cell organelle mitochondria in combating stress response in cells, the contribution of RNA in DNA damage cells, the tiny chemical PROTAC targets cMyc and EZH2 in cancer cells at the same time, the role fattyose cells in therapeutic applications in acne, 3D-bio printed technique to use for cellular therapy. Thus, these key findings will show the path for more exciting news in 2023.
![]()