These break-through news focus on various subjects related to cell biology 2021. In brief, they deal with cell organelle and their defects, the importance of stem cells in therapeutic purposes, the concept of nano-channels as artificial cell mimics, senescence in cells to combat cancer, the mechanism of cellular communication, and so on.
Table of Contents
- Top 15 Cell Biology News of 2021
- 1. Scientist discovers cell line that helps to treat mitochondrial diseases in children (USA, July 2021)
- Explore Mitochondria Functions & Their Importance
- 2. Researchers address the query as to how cell motility-inducing machinery gets recycled in cells (Finland, Feb 2021)
- Top Cell Biology News of 2020 – A Round Up
- 3. Scientists developed artificial cells that mimic the cellular behaviors of normal living cells (USA, Sept 2021)
- 4. Scientists discovered a new unnamed organelle that plays a vital role in cancer metastasis (USA, March 2021)
- 5. Understanding the fundamental processes underlying intestinal stem cell self-renewal and differentiation (Germany, Jan 2021)
- 6. Cell biologists decipher the mystery of how chromosomes are inherited down the cell line (USA, Jan 2021)
- Explore What Is Cell Theory & Parts of Cell Theory
- 7. Scientists have deciphered the rules of cell communication (Sweden, Feb 2021)
- 8. Scientists found new hope in stem cells that regenerate hair follicles (USA, March 2021)
- Top 25 Integumentary System Facts (Skin Fun Facts)
- 9. Researchers found novel synthetic genomic DNA that can replicate and evolve outside the cellular niche (Japan, 2021)
- 10. Cell biologists discovered a novel neural stem cell state that provides information about cancer (USA, June 2021)
- 11. Researchers have discovered a molecular pathway that prevents moving cells from wandering; potential implications in cancer spread (USA, March 2021)
- 12. Scientist predicts that the root cause of cellular disease lies in the cell cycle process (UK, July 2021)
- 13. Researchers claim that kidney damage may have an underlying cause of aging cells (USA, Dec 2021)
- 14. Scientists found a new cell that controls heart rate (USA, Nov 2021)
- 15. Cell biologists predict the mechanism of programmed cell death (Germany, Feb 2021)
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Overview, Properties, Functions & Therapies
Top 15 Cell Biology News of 2021
So, let’s glimpse these innovations with a broader view.
1. Scientist discovers cell line that helps to treat mitochondrial diseases in children (USA, July 2021)
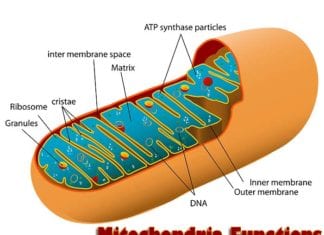
For its function as the “powerhouse of the cell“, the mitochondrion has developed quite a reputation. These minute but powerful organelles play a pivotal role, from operating our own cells and organs to firing chemical and biological processes, among other life-sustaining functions. But several uncommon diseases can develop when they aren’t functioning correctly.
- A group of severe genetic disorders known as mitochondrial diseases affects one in 5,000 people worldwide, most of whom are children.
- These illnesses come with numerous health issues, such as heart disease, learning and developmental disabilities, breathing problems, stunted growth, and even early death.
- The food we eat and the air we breathe provide our bodies with the energy they need to maintain life. The mitochondria are the final event for oxygen and nutrients like glucose as they travel through the body’s organs, tissues, and cells.
- The electron transport chain, a unique set of protein complexes, gets going when the nutrients enter the mitochondria’s inner membrane. Patients with mitochondrial diseases may have Complex I or Complex II defects.
- Complex I disruption patients frequently experience neurological issues like seizures and atypical brain activity. People with Complex II disruptions are more susceptible to multiple cancers and many other diseases.
These findings imply the treatment of mitochondrial dysfunction, cell models of mitochondrial Complex I and II defects have significant societal and economic significance.
Suggested Reading:
Explore Mitochondria Functions & Their Importance
![]()
2. Researchers address the query as to how cell motility-inducing machinery gets recycled in cells (Finland, Feb 2021)
A new molecular mechanism that encourages cell migration has been identified by research teams. The discovery updates the “textbook view” of cell migration. In addition, it sheds light on the mechanisms that fuel the unchecked migration of cancer cells.
- For immune cells to patrol our tissues in search of bacterial and viral pathogens and for wound healing, cells need to be able to move around within our bodies.
- Conversely, unchecked cell movement indicates cancer invasion and metastasis. Actin-based proteins comprise a complex network of dynamic filaments that serve as cell migration engines.
- The rapidly lengthening plus ends of actin filaments face the plasma membrane. In contrast, the minus ends are oriented away from the plasma membrane in cells.
- During cell migration, the force needed to propel the cell’s leading edge forward is produced by the elongation of actin filaments at their plus ends against the plasma membrane.
- Actin filaments must be quickly disassembled in cells, which is thought to happen at their minus ends, to maintain a sufficient supply of monomeric actin subunits for filament elongation. Twinfilin, a conserved protein that binds to actin, effectively eliminates Capping Protein from the filament plus-ends ends.
- As a result, the filaments’ “aged” plus ends depolymerize and stop pushing the cell’s leading edge forward. As a result, Actin filament recycling is reduced, filaments move towards the cell edge forward less effectively, and cell migration is slower in the absence of Twinfilin.
These findings also lay the groundwork for future research into the pathogenesis of severe diseases and developmental disorders caused by anomalies in the actin disassembly machinery. In addition, many diseases, including the invasion of breast cancer and the development of lymphomas, are associated with Twinfilin’s unchecked expression. Thus, The research also sheds light on the molecular mechanisms that cause cancer cells to move uncontrolled.
Suggested Reading:
Top Cell Biology News of 2020 – A Round Up
![]()
3. Scientists developed artificial cells that mimic the cellular behaviors of normal living cells (USA, Sept 2021)
Researchers have created synthetic structures that resemble living cells using inorganic material that can autonomously take in, process, and expel material. Their article offers “cell mimics“, with potential uses in environmental science and drug delivery.
- The ability to live cells to gather energy from the environment to move molecules into and out of their systems is a fundamental characteristic of life.
- The process is active transport when energy moves these molecules from lower concentration to higher concentration areas. Cells can take in essential molecules like glucose or amino acids, store energy, and remove wastes via active transport.
- Researchers have attempted to engineer microscopic structures that mimic the characteristics and behavior of artificial cells. However, in most cases, these cell imitators cannot carry out intricate cellular functions like active transport.
- The cellular membrane, which regulates what enters and leaves a cell, is a spherical membrane that is the size of a red blood cell made by researchers using a polymer. They created a nano-channel through which matter can be exchanged by making a microscopic hole in the spherical membrane that mimicked a cell’s protein channel.
- The cellular membrane, which regulates what enters and leaves a cell, is a spherical membrane that is the size of a red blood cell made by researchers using a polymer.
- They created a nano-channel through which matter can be exchanged by making a microscopic hole in the spherical membrane that mimicked a cell’s protein channel. This movement of cargo proteins is regulated by reactive centers of nano-channels.
Scientists are still working on creating and studying cell mimics, including creating ones that can carry out various functions and discovering how various types communicate. Given that the cell mimics can release a preloaded substance when activated, drug delivery may be another potential use for them in the future.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Cell Biology Discoveries in 2019
![]()
4. Scientists discovered a new unnamed organelle that plays a vital role in cancer metastasis (USA, March 2021)
A new organelle, which has not yet been given a name, was found to be formed by the liquid-liquid phase separation process, which occurs when liquid blobs of living materials converge on one another. This organelle is involved in bone metastasis.
- The most recent discovery, which highlights the unnamed organelle, adds to our knowledge of the Wnt signaling pathway’s function.
- From tiny invertebrate insects to humans, the Wnt pathway is essential for embryonic development in various organisms. However, researchers found that cancer can take over this pathway.
- Recent studies have shown that the Wnt signaling pathway plays multiple roles in healthy bone growth and cancer metastasis bones. When Kang and his colleagues discovered this new organelle, they examined the intricate interactions between Wnt, a signaling molecule called TGF-b, and a relatively unheard-of gene called DACT1.
- Bone tumors induce Wnt signaling to spread (disseminate) throughout the bone. The panicked shopping is then sparked by TGF-b, abundant in bones and inhibits Wnt signaling.
- Osteoclasts then develop in response to the tumors, removing deteriorated bone tissue. Osteoclasts remove a layer of bone, and osteoblasts then rebuild the bone with new material, regenerating healthy bones continuously.
- This leads to even more DACT1 hoarding and subsequent Wnt suppression, which is crucial for further metastasis, raising the TGF-b concentration.
This research sheds new light on how condensate biophysics interacts with cancer signaling pathways, leading to new therapeutic possibilities.
Suggested Reading:
Top 15 Discoveries in Cell Biology for 2018
![]()
5. Understanding the fundamental processes underlying intestinal stem cell self-renewal and differentiation (Germany, Jan 2021)

The gut regulates the body’s metabolism to a large extent, and disorders of the gut are linked to several illnesses, including obesity, diabetes, colitis, and colorectal cancer, which affect millions of people worldwide.
- A promising regenerative strategy for treating diabetes may involve focusing on endocrine dysfunction by promoting the development of enteroendocrine cells from intestinal stem cells.
- A thorough knowledge of the intestinal stem cell lineage and the signals governing the recruitment of various intestinal cell types is essential.
- The gut controls energy and glucose homeostasis as the body’s largest endocrine and digestive system. Specialized intestinal cells that are continuously produced and replaced every 3-4 days from intestinal stem cells perform various digestive functions.
- In addition, the production of defensins and defense against invasive pathogens by so-called Paneth cells, which are found in the gut, is another crucial function.
- Therefore, it should come as no surprise that intestinal dysfunction is linked to several conditions, including chronic inflammation, colon cancer, and diabetes, which affect millions of people worldwide.
- This study identified the role played by Wnt/planar cell polarity pathway, which controls intestinal stem cell self-renewal and lineage decisions, as a niche signaling pathway for intestinal stem cells.
- This is crucial because intestinal stem cells can regenerate and preserve gut function and tissue.
This study also gives us the property of intestinal stem cell self-renewal, heterogeneity, and lineage recruitment; this study challenges established paradigms. With this fundamental understanding, we can map intestinal stem cells’ lineage allocation and differentiation during chronic disease.
Suggested Reading:
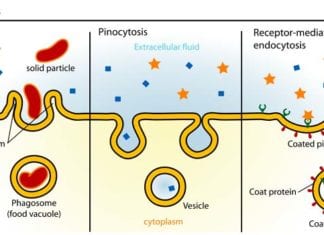
Pinocytosis: The Science of Cell Drinking
![]()
6. Cell biologists decipher the mystery of how chromosomes are inherited down the cell line (USA, Jan 2021)
According to cell biologists, the mystery of how chromosomes are correctly passed down each time a cell divides has a significant piece of information. They discovered how a “matchmaker” molecule prevents cell division until the parts are prepared to be split using a novel cell probe. A crucial component of healthy cell division is precise chromosome duplication. Congenital disabilities and some cancers may result from components that have been altered, even slightly.
- The “spindle checkpoint” pathway, a quality control mechanism ensuring accurate chromosome inheritance during cell division, was the focus of the researchers’ research.
- The kinetochore, a mechanical interface where protein fibers are coupled to pull chromosomes apart, is a location on the chromosome where the spindle checkpoint pathway is activated.
- To give time for attachments to form, kinetochores that are not attached to these protein fibers send out a “wait” signal, which stops the cell from dividing during mitosis.
- The cell ensures that every chromosome is attached correctly and prepared for separation before it divides, leaving no chromosome behind.
These results contribute to understanding why kinetochores are the only locations in the cell where the “wait” checkpoint signal is generated. In addition, the results provide a framework for how certain disease states, such as cancer, can reduce the accuracy of chromosome inheritance.
Suggested Reading:
Explore What Is Cell Theory & Parts of Cell Theory
![]()
7. Scientists have deciphered the rules of cell communication (Sweden, Feb 2021)
Researchers found cell communication crucial to understanding many biological systems and diseases. A research team has now mapped cellular communication’s mechanism using a distinctive combination of techniques. Their research may help us comprehend the underlying causes of type 2 diabetes better.
- Using tiny culture chambers that allow for precise environmental control of the cells, researchers were able to map the mechanism underlying cellular communication in the metabolic process.
- The study focuses on glycolytic oscillations, a series of chemical reactions during metabolism where the concentration of substances can pulse or oscillate.
- The researchers chose to study yeast cells because they are similar to human cells.
- The research demonstrated how populations of cells that had initially oscillated independently became more synchronized.
The study may help us comprehend how pancreatic cells are controlled and how they secrete insulin, which may aid in our comprehension of the underlying mechanism causing type 2 diabetes.
Suggested Reading:
Top 17 Stem Cell Research Pros and Cons
![]()
8. Scientists found new hope in stem cells that regenerate hair follicles (USA, March 2021)
Scientists have discovered the biological process by which ongoing stress results in hair loss. They diagnosed that hair follicle stem cells remain in an extended resting phase without regenerating tissue due to the stress hormone corticosterone. The dermal cells surrounding the hair follicle were the first to detect the stress signal, which prevented them from releasing Gas6, a molecule that activates stem cells. However, when researchers added back Gas6, stem cells could regenerate hair even under stress.
- The hair follicle, one of the few mammalian tissues that can repeatedly regenerate throughout life, has developed into a paradigm for most of our fundamental understanding of mammalian stem cell biology.
- Powered by hair follicle stem cells, the hair follicle naturally alternates between growth and rest. Hairs lengthen daily during the growth phase as stem cells in the hair follicles become activated to regenerate the hair follicle and hair.
- However, the stem cells are dormant and more easily shed hair during the resting stage. Hair loss may result if the hairs fall out and the stem cells are not actively regenerating new tissue.
- Even though dermal papilla is essential for activating hair follicle stem cells, none of the previously identified factors secreted from dermal papilla were altered when stress hormone levels were changed.
- Instead, the researchers discovered that the stress hormone prevented dermal papilla cells from secreting Gas6. This molecule can activate hair follicle stem cells.
The Gas6 pathway may one day activate stem cells and stimulate new hair growth. It will also be fascinating to find out if the effect of the stress hormone on controlling Gas6 is connected to other tissue changes brought on by stress.
Suggested Reading:
Top 25 Integumentary System Facts (Skin Fun Facts)
![]()
9. Researchers found novel synthetic genomic DNA that can replicate and evolve outside the cellular niche (Japan, 2021)
Using only cell-free materials, scientists successfully induced gene expression from DNA and evolution through continuous extracellularly replicating for the first time. It may be possible to create artificial cells that can grow independently and produce effective, useful substances by including the genes required for transcription and translation in the synthetic genomic DNA.
- One of the defining qualities of living things is their capacity for reproduction and evolution.
- No synthetic materials with these properties have ever been produced. The information (genes) coded in DNA must be translated into RNA, proteins must be expressed, and the cycle of DNA replication with those proteins must continue over an extended period to create an artificial molecular system that can multiply and evolve.
- To date, it has not been possible to design a reaction system in which the genes essential for DNA replication are expressed, and the genes perform their respective functions.
- The team used circular DNA carrying two genes essential for DNA replication (artificial genomic DNA) and a cell-free transcription-translation system to successfully translate the genes into proteins and replicate the original circular DNA with the translated proteins.
It aims to clarify fundamental ideas regarding the composition and operation of genomes to develop a cell-use platform technology.
Suggested Reading:
Top 11 Cell Biology Textbooks of All Times
![]()
10. Cell biologists discovered a novel neural stem cell state that provides information about cancer (USA, June 2021)

Researchers in biomedical engineering have created a new cell classifier tool that provides a higher-resolution view of the neuroepithelial stem cells’ life cycle. This work identified and investigated a new resting phase known as Neural G0. This information might aid researchers in comprehending glioma brain tumors and creating new therapeutic strategies.
- The growth states of the tumor cells were frequently either neural G0 or G1. Additionally, fewer and fewer cells are still in the dormant Neural G0 state as tumors become more aggressive.
- This indicates that the tumor is growing and that more and more cells are reproducing. The prognosis for patients with glioblastoma, a particularly aggressive brain tumor, was correlated with this data.
- Less aggressive tumors were present in those with higher Neural G0 levels in tumor cells. They also discovered that the proliferation rate, or the rate at which a tumor’s cells divide and produce new cells, is unrelated to the quiescent Neural G0 state.
- Our findings revealed an intriguing possibility: quiescence may involve a distinct biological process. The goal of current cancer drug therapies is to eradicate cancer cells.
Nevertheless, when cancer cells are eliminated, they discharge cell debris into the vicinity of the tumor, which may make the remaining cells more resistant to the medications. Therefore, putting the cells to sleep instead of killing them may result in a much better outcome.
Suggested Reading:
History of Cell Biology
![]()
11. Researchers have discovered a molecular pathway that prevents moving cells from wandering; potential implications in cancer spread (USA, March 2021)
Scientists working with fruit flies claim to have discovered a new molecular pathway that aids in guiding moving cells in particular directions. The pathway’s network of connected proteins and enzymes is the steering and rudder system that directs cells to a destined location.
- According to researchers, Transepithelial migrationTre1 is essential for germ cell navigation. It was already known that the Tre1 gene encodes a protein that extends multiple times across the cell membrane and onto the cell surface.
- It belongs to a large group of G protein-coupled receptors that allow cells to communicate and react to signals from other cells and cues from light and odor.
- Inducing enzymes and proteins include WASp, PI (4,5) P2, dPIP5K, PI (4,5) P2, and phospho-inositol kinase.
- Tre1 activates the cell’s steering and rudder components. At the end of the molecular events, a protrusion of actin proteins forms at the cell’s leading edge to generate mechanical forces for movement.
The pathways surrounding Tre1 and the interactions between the proteins and enzymes that are a part of the pathway will be further studied by researchers. Knowing how moving cells move and spread could help scientists develop more effective ways to stop the spread of cancer cells.
Suggested Reading:
Types of Bone Cells
![]()
12. Scientist predicts that the root cause of cellular disease lies in the cell cycle process (UK, July 2021)
In humans, cell adhesion and division are coordinated by a crucial mechanism recently discovered by new research. Due to this discovery, significant progress could be made in understanding how cell adhesion signaling affects the growth and metastasis of cancerous tumors.
- All living things can function and regenerate thanks to the cell cycle, which links the mechanism for cell division, proliferation, and cell adhesion (which keeps cells in the right place within an organism’s structure).
- The cell must release its adhesions to the environment precisely when it begins to divide for cell division to occur inside humans.
- The proper functioning of cells in tissues and preventing uncontrolled cell division in processes like cancer depend on the synchronization of cell adhesion and the cell cycle.
- This discovery has enormous potential because it offers a fresh perspective on how cell division is managed within the boundaries of a complicated multicellular organism.
- Cell adhesion must be tightly coupled to cell division for cells to divide without compromising the stability of our tissues and organs.
This study is essential to comprehending how cancer spreads and other cellular diseases spread within the human body.
Suggested Reading:
Top 12 Diseases Caused By Protozoa
![]()
13. Researchers claim that kidney damage may have an underlying cause of aging cells (USA, Dec 2021)
Angiotensin II, a molecule known to raise blood pressure and stiffen the linings of blood vessels, has been linked to stress and tissue damage that results in cellular senescence, a process by which cell ages and permanently stop dividing but does not die. It’s significant to note that tissues returned to normal after removing senescent cells, despite a continued infusion of angiotensin II.
- The most effective method for inducing chronic stress was via angiotensin II because they could control how it was administered and achieve a measured stress level comparable to that of people whose blood pressure slowly increases throughout their lifetimes.
- Higher blood pressure is a common side effect of stress because it causes the blood vessel lining to become less flexible. However, unlike what they had anticipated when they began their experiments, the researchers found that these effects are more noticeable in the kidneys than in the brain or lungs.
- To address the senescence aspect of the disease, which has largely gone unexplored, it is essential to develop the biological foundation for a new therapeutic approach.
Senescent cell eradication with tolerable, brief therapy may ameliorate chronic cardiovascular disease and lessen lifelong therapy requirements.
Suggested Reading:
Difference Between Diffusion and Osmosis
![]()
14. Scientists found a new cell that controls heart rate (USA, Nov 2021)
Researchers have identified a novel type of heart cell that may regulate heart rate and hold the key to understanding certain congenital heart defects and other heart-related diseases.
- The nexus glial cells resemble the crucial glial cells in the brain, known as astrocytes.
- The heart rate increased when the newly discovered cells were eliminated. However, it beat erratically when they were denied access to a crucial gene that controls their glial development.
- Before, it was believed that astrocytes could only be found in the brain and spinal cord, which make up the central nervous system.
- Researchers had questioned why the peripheral nervous system, which includes all of the body’s remaining nerves, did not appear to have glial cells similar to astrocytes in the organs it supplies with nerves.
- They are vital for developing and maintaining neural circuits in the brain.
The future implication of this research proposes that these glial cells could play a pretty important role in regulating the heart, thus leading to an understanding of many different disorders.
Suggested Reading:
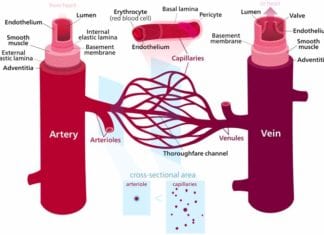
17 Differences Between Arteries and Veins
![]()
15. Cell biologists predict the mechanism of programmed cell death (Germany, Feb 2021)
A recent study demonstrates that Inhibitor of apoptosis (IAPs), proteins that can cause programmed cell death, are inhibited by a particular chemical modification. Furthermore, it demonstrates that they have a more extensive function in protein quality control than previously predicted.
- One of the most frequent modifications found in the protein complements of higher organisms is N-terminal acetylation, which is the direct attachment of an acetyl group (CH3-COO-) to a protein’s N-terminus.
- N-terminal acetylation prevents apoptosis, or “programmed death, ” and protects some proteins from degradation. However, these same proteins can cause apoptosis when they are not acetylated by interacting with IAPs, which are proteins.
- It is well known that IAPs take part in the control of programmed cell death.
- It has been demonstrated that IAPs can only bind to specific target proteins and inhibit the process if the N-termini of these targets is not acetylated. N-terminal acetylation thus guards against protein degradation.
These findings might have therapeutic ramifications for cancer treatment. Unfortunately, the signaling relays that cause apoptosis are damaged due to a mutation in many cancer types. This eliminates one potential course of treatment. The authors propose blocking N-terminal acetylation pathways could activate IAP activity and increase apoptosis sensitivity in tumor cells.
Suggested Reading:
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Overview, Properties, Functions & Therapies
![]()
This news series in cell biology gives us a detailed overview of the recent advancements. Starting from therapeutic implications in cancer treatment and the role of programmed cell death, glial plexus in regulating heart and other disorders, Senescent cell eradication could be an answer to brief therapy, identification of cell protein in cancer metastasis, the role of stem cells in regenerative medicine with its application. Thus, these key findings pave the way for more exciting news in 2022.
![]()