Carbon Cycle Steps: Overview & Importance in Biosphere
In this article, gain a deeper understanding of how carbon is cycled through the living & nonliving components of the biosphere – carbon cycle steps & more.
Carbon Cycle Steps: Most of the time, carbon[1] is called as the “chemical building block of life” because living organisms are made up of it.
Hence, if that is the case, identifying how carbon molecules work in an environment is an important indication of whether a certain environment can accommodate life.
It is important to note that the amount of carbon on earth itself and its atmosphere is fixed but always converted into different compounds, be it living or nonliving in nature.
In general, there is a constant amount of carbon present on the planet and in its atmosphere. However, that “constant” amount is always being transformed into other forms and being moved between both living and non-living things. How does this process actually work? What drives the carbon atoms to move? Scroll down to find out more.
Jump to:
- What is the Carbon Cycle?
- Carbon Cycle Steps
- 1. Entry of Carbon into the Atmosphere
- 2. Carbon Dioxide Absorption By Producers
- 3. Passing of the Carbon Compounds in the Food Chain
- 4. Return of the Carbon To the Atmosphere
- Two Types of Carbon Cyling
- 1. Short Term
- 2. Long Term
- Importance of Carbon Cycle
- 1. Essential For Life
- 2. Important For the Maintenance of the Balance in Ecosystems
- 3. Critical To Food Chain
- 4. Important For Climate Regulation
What is the Carbon Cycle?
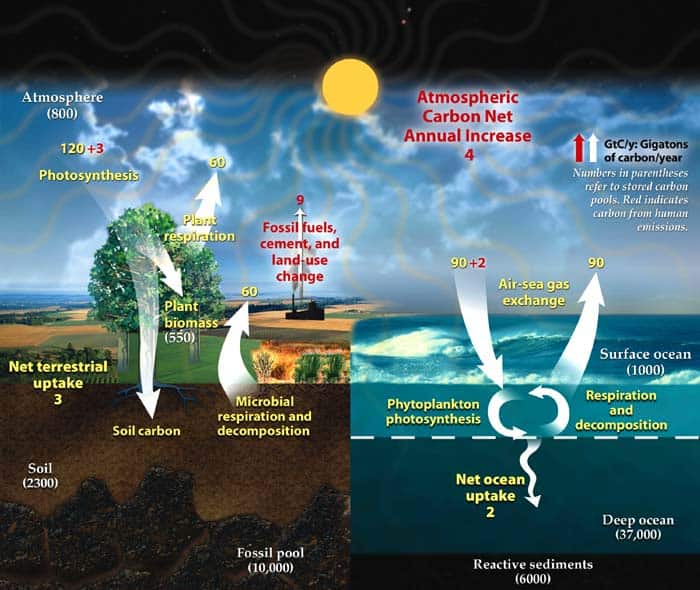
- Basically, three major carbon-bearing reservoirs[2] exist in the planet: the lithosphere (land), the hydrosphere (water), and the atmosphere (air).
- All of which are acted upon out by the biosphere (living organisms). Living organisms, in general, play an important role in maintaining the balance between the other reservoirs.
- By determining the interaction between these reservoirs and tracing the route through which carbon are transported from the source to the sink, the interconnected carbon cycles on Earth are described precisely.
![]()
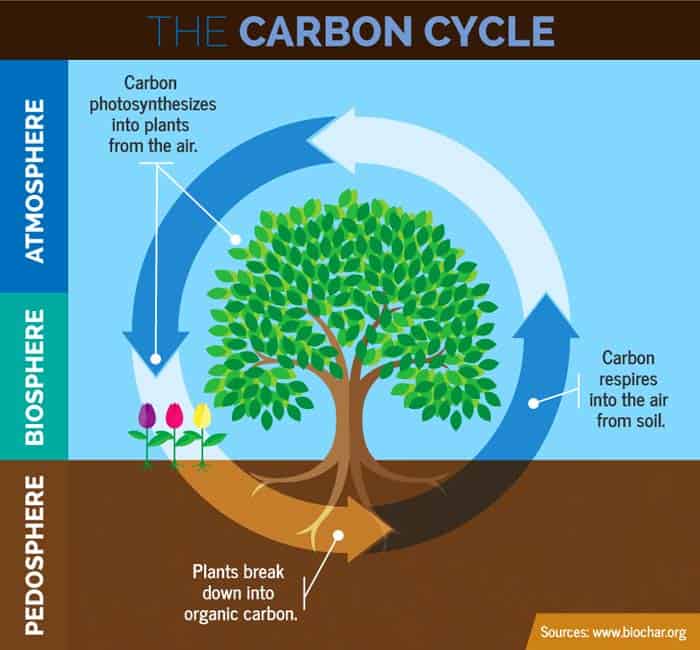
Carbon Cycle Steps
All in all, biological and geological processes are important in maintaining the carbon balance in the planet. The carbon cycle is divided[3] into the following steps:
1. Entry of Carbon into the Atmosphere
 The entry of carbon (in the form of carbon dioxide) in the atmosphere marks the start of the carbon cycle. Before this, carbon dioxide goes through the process of respiration[4] (process by which organisms release energy from their food) and combustion (process of burning). Such processes both involve the releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
The entry of carbon (in the form of carbon dioxide) in the atmosphere marks the start of the carbon cycle. Before this, carbon dioxide goes through the process of respiration[4] (process by which organisms release energy from their food) and combustion (process of burning). Such processes both involve the releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
![]()
2. Carbon Dioxide Absorption By Producers
![]()
3. Passing of the Carbon Compounds in the Food Chain
 Following the above step is the entry of the carbon compounds from the plants (producers) themselves to the food chain. When animals consume (hence consume) these plants, the carbon compounds are received by them.
Following the above step is the entry of the carbon compounds from the plants (producers) themselves to the food chain. When animals consume (hence consume) these plants, the carbon compounds are received by them.
![]()
4. Return of the Carbon To the Atmosphere
![]()
Two Types of Carbon Cyling
In general, the carbon cycle can be divided (depending on how long it takes to occur) into two types: short term and long term.
1. Short Term
 This type of carbon cycling involves the annual changes that occur within the atmosphere, terrestrial ecosystems, and the marine ecosystem.
This type of carbon cycling involves the annual changes that occur within the atmosphere, terrestrial ecosystems, and the marine ecosystem.
- This type of cycling is named as such because the movement of carbon across reservoirs only takes relatively short time (minutes, hours, days, months, or years).
![]()
2. Long Term
 This type of carbon cycling is the slower form since it takes thousands to millions of years to occur.
This type of carbon cycling is the slower form since it takes thousands to millions of years to occur.
- The excess carbons from the short term cycling are stored into the “long term” reservoir until they are removed after a long time.
![]()
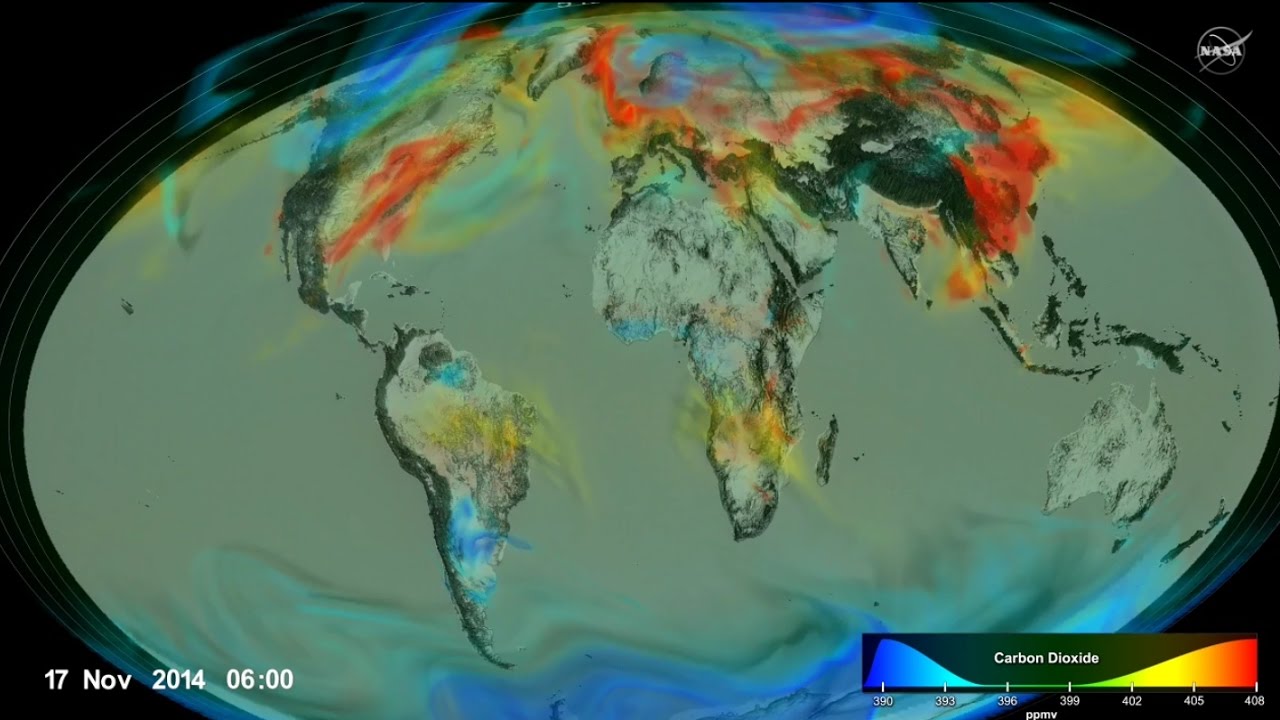
Here is the beautiful video produced by the NASA supercomputer project, which shows the CO2 emission from our earth by combining several Satellite images and earth system models. You can read more about this project here.
Importance of Carbon Cycle
Like any other naturally cycles, the carbon cycle is essential for living organisms and biological systems in general. Discussed below are some of them:
1. Essential For Life
 As alluded to earlier, all living organisms are made up of carbon or one way or another; hence, the mere fact of it is very essential for life itself. When the process fails, life may begin to disrupt, and may even cause the cessation of it.
As alluded to earlier, all living organisms are made up of carbon or one way or another; hence, the mere fact of it is very essential for life itself. When the process fails, life may begin to disrupt, and may even cause the cessation of it.
![]()
2. Important For the Maintenance of the Balance in Ecosystems
 The process of carbon cycle is very important in the maintenance of balance[6] in ecosystems due to the movement of carbon in various reservoirs. If ever imbalance happens, serious environmental disasters like global warming may occur.
The process of carbon cycle is very important in the maintenance of balance[6] in ecosystems due to the movement of carbon in various reservoirs. If ever imbalance happens, serious environmental disasters like global warming may occur.
- At present, scientists and researchers alike are still searching for novel methods of using other non-carbon sources for energy resource.
![]()
3. Critical To Food Chain
 The close relationship between carbon cycle and food chain boils down to the fact that all living organisms are made up of carbon.
The close relationship between carbon cycle and food chain boils down to the fact that all living organisms are made up of carbon.
- Through food chains[7] (and food webs), the carbon present in the producers migrate to the consumers that eat them. Consumers that eat other consumers as well receive the carbon from their food as well.
![]()
4. Important For Climate Regulation
 Carbon dioxide and methane[8] are the two carbon-based gases that significantly contribute to global warming. Since they are made up of carbon, the process of carbon cycle obviously determine the amount of these gases in the atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide and methane[8] are the two carbon-based gases that significantly contribute to global warming. Since they are made up of carbon, the process of carbon cycle obviously determine the amount of these gases in the atmosphere.
- When there is a huge amount of carbon released into the atmosphere, the level of greenhouse gases increases, and therefore trapping more heat in the Earth. Hence, the understanding of how carbon cycle occurs in the environment paves the way for the development of the understanding for world climate.
![]()
Humans, in general, have already disturbed the natural process of the carbon cycle since the start of the industrial revolution. Look around you. It is already becoming apparent how the atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations (and other greenhouse gases) are increasing due to domestic and other anthropogenic activities.
The disadvantages of such activities remain uncertain, but in the long run, we know for sure that it would sooner cause major drawbacks to life.
As a concerned human being on this planet, how can you contribute to mitigating the worsening of global climate change?
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2025, December 31). Carbon Cycle Steps: Overview & Importance in Biosphere. https://www.bioexplorer.net/carbon-cycle-steps.html/

 The next step is the entry of the carbon dioxide in the photosynthetic process[5]. Photosynthetic organisms like
The next step is the entry of the carbon dioxide in the photosynthetic process[5]. Photosynthetic organisms like  The next step is the return of the carbon to the atmosphere due to the decomposers (
The next step is the return of the carbon to the atmosphere due to the decomposers (