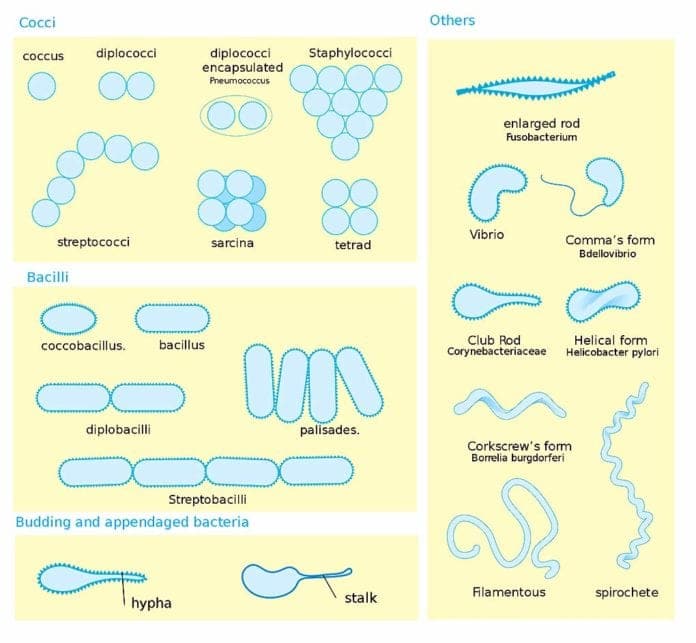
Shapes of Bacteria: Bacteriology (study of bacteria) is a major part in Microbiology. The prokaryotic kingdom consists of unicellular microscopic microorganisms called bacteria.
Bacteria or a bacterium (sing.) are simple single-celled organisms that lack organized nucleus and any chlorophyll pigments but they possess a rigid cell wall. The rigidity of its cell wall determines the shape of a bacterium. It also endows the bacterium with flexibility, and other added advantages.
Bacteria are grouped into 2 major groups, Gram +ve or Gram -ve, based on the response to Gram’s stain. There are several distinguishing features that Gram’s stain can identify.
The main difference is that Gram-positive bacteria contain single-layered cell walls whereas, Gram-negative bacteria contain double-layered cell walls.
The average size of a bacterium is about 2 µm (microns or micrometers). They can be found in various shapes and sizes. In this article, we will explore different shapes of bacteria, examples, and diseases caused by bacteria.
Shapes of Bacteria
Based on the shape of the bacterial cell, bacteria can be mainly classified into four major categories, namely:
- Spherical bacteria or Coccus
- Rod-shaped bacteria or Bacillus
- Spiral bacteria
- Filamentous bacteria.
Apart from these four main categories, there are other odd-shaped bacteria such as the following shapes, namely:
- Box-shaped bacteria (arcula) or rectangular
- Appendaged bacteria
- Pleomorphic bacteria
- Star-shaped
- Sheathed
- Stalked
- Spindle-shaped
- Lobed
- Trichome-forming
Considering the arrangement of bacteria, they may either be in pairs (diplo), in grape-like clusters (staphylo), or chains (strepto). On average, the diameter of a spherical bacterial cell ranges between 0.5 and 2.0 µm and between 0.25 and 1 µm for rod-shaped or filamentous bacteria.
![]()
Spherical Bacteria or Coccus
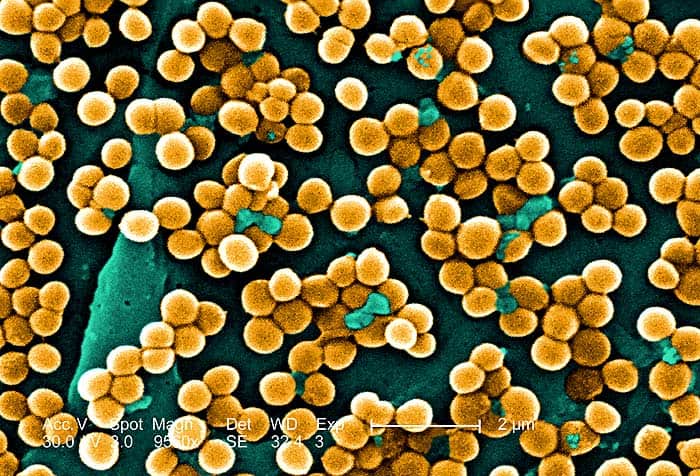
These bacteria are round, flattened cells adjacent to each other. They can be found in different arrangements, namely, diplococci (in pairs), tetrads (arrangement of groups of four), streptococci (in pairs), and staphylococci (in clusters).
Diplococci Bacteria: These bacteria are usually found in pairs as two joined cells. The name originates from the word diplo, meaning double, and coccus, meaning berry. One example of a diplococci strain is Neisseria gonorrhea. A typically gram-negative bacterium causes a sexually transmitted infection called gonorrhea. Another example of diplococcus strain is Moraxella catarrhalis that is a gram-negative bacterium that causes infections of the respiratory system.
Tetrad Bacteria: They are formed when the bacterium divides into two planes to form a square of four bacteria called a tetrad. Examples of tetrad-forming bacteria are Aerococcus, a urinary tract pathogen, Pediococcus, and Tetragenococcus, both of which ferment foods. Aerococcus urinae is an emerging cause of urinary tract infections, which was previously thought to be non-pathogenic (i.e., harmless) and a clinically insignificant urinary contaminant.
Staphylococci Bacteria: The term staphylococcus comes from the word Staphylo meaning grape-like clusters and coccus, meaning berry. The arrangement of staphylococci resembles cells aggregating in a grape-like structure. These are universally present on mucous membranes and the skin, usually as gram-positive facultative aerobes. An important example is that of Staphylococcus aureus, which is frequently implicated in food poisoning. It is found in the nose, respiratory tract, and skin. Another example of this species is Staphylococcus epidermis, which is normally found on the skin and is a part of the normal skin flora. It is known to be non-pathogenic but can be rendered pathogenic (i.e., harmful) in immunosuppressed individuals.
Streptococci Bacteria: The term streptococcus originates from the words “strepto” meaning chains and coccus, meaning berry. The arrangement of streptococcus resembles cells in chains attached. This species causes a variety of conditions in humans. An example of streptococci bacteria is Streptococcus pyogenes, known to cause rheumatic fever, tonsillitis, strep throat, and other respiratory infections. Another example of this bacteria is Streptococcus bovis, which causes urinary tract infections.
Sarcinae Bacteria: These bacteria are usually non-motile, with sizes between 1.8 and 3.0 µm in diameter. This arrangement is formed when bacteria divide into three perpendicular planes forming packets of 8 or more cells. It is pathogenic and is usually implicated in gastrointestinal disorders such as gastroparesis or gastric ulcers.
![]()
Rod-Shaped or Bacillus
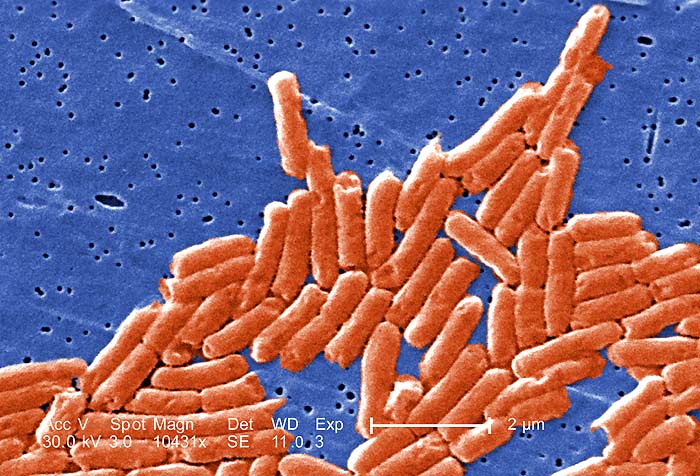
Rod-shaped bacteria can be found in several arrangements such as diplo (in pairs), strepto (in chains), cocco (oval), or in palisade arrangement.
Diplobacilli Bacteria: Diplobacilli are short rod-shaped bacteria that occur in pairs. As the name suggests, two individual bacilli are arranged side by side. An example of diplobacilli bacteria is Coxiella burnetii, an intracellular gram-negative pathogen that causes a disease known as Q fever. Another example is Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis, which causes chronic nasal infections in humans.
Streptobacilli Bacteria: Streptobacilli are gram-negative bacteria that occur as rods in chains. The name streptobacilli originates from the word “strepto” meaning chain and “bacilli” meaning “rod-shaped“. Species from this genus of bacteria are known to be pathogenic. An example of streptobacilli bacteria includes Streptobacillus moniliformis, the causative agent of rat-bite fever.
Coccobacilli Bacteria: Coccobacilli bacteria are called so because of their shape intermediates between rod-shaped and spherical. They are short rods that can easily be mistaken for spherical bacteria. The species of this genus are pathogenic, causing infections of the vagina, like Gardnerella vaginalis; or causing influenza-like Haemophilus influenzae. Chlamydia trachomatis, also a coccobacillus, is known to cause a sexually transmitted infection called Chlamydia.
Palisade Bacteria: This particular arrangement is formed during the process of cell division when the bacteria or bacilli bend at the area of the division-leading to the formation of a palisade-like arrangement. This bacteria resembles a picket fence or Chinese letters. A common example of a barrier bacteria is Corynebacterium diphtheria, which is the causative agent of diphtheria.
![]()
Spiral Bacteria
These bacteria are often found in helical or spiral arrangements such as Vibrio (comma-shaped), Spirilla (spiral), and Spirochetes (rigid helical body). Some spiral bacteria use flagella for movement.
Vibrio Bacteria: These are comma-shaped, usually gram-negative bacteria that are not completely bent or twisted. They are implicated in food-borne illnesses or diseases. The shape of the bacteria resembles a comma. A common example of this species is Vibrio cholera, the causative agent of Cholera. Other strains of Vibrio bacteria are non-cholera strains and cause other types of illnesses.
Spirilla Bacteria: This type of bacteria is a genus of spiral-shaped bacteria that are gram-negative and flagellated. Spirillum minus is an example of spirilla bacteria implicated in rat-bite fever. This genus consists of free-living aquatic forms of bacteria such as Aquaspirillum and Oceanospirillum.
Spirochete Bacteria: This arrangement of spiral bacteria resembles long helically coiled cells. They are pathogenic and are known to cause serious diseases in humans. An example of this type of bacteria is Treponema pallidum, which is known to cause syphilis. The borellia species cause Lyme disease in humans.
![]()
Filamentous Bacteria
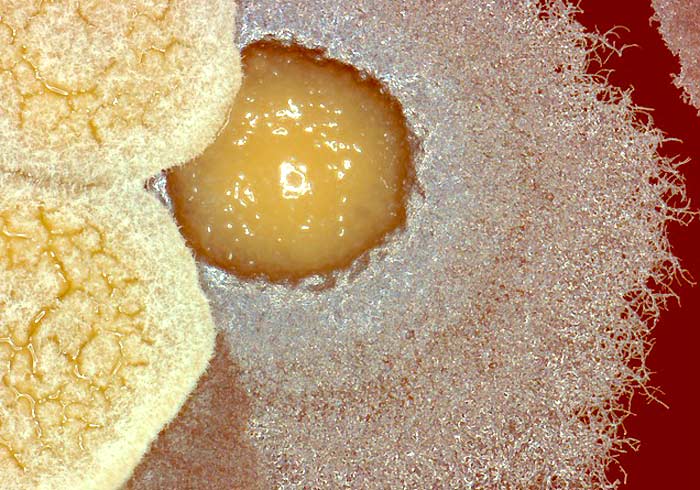
The Filamentous bacteria are long thin filament-like bacteria that can branch and form networks called mycelium. An example is Candidatus savagella that is found in the gut of animals like rodents or fish can be important to immune development.
![]()
Other Odd-Shaped Bacteria
The following odd shapes of bacteria also exist in the world of bacteria, which are enumerated below:
Rectangular Bacteria
The first odd shape bacteria is a rectangular-shaped bacteria, which is also known as an arcula. Bacterial species of this genus include Haloarcula vallismortis or Haloarcula marismortui. They are extremely halophilic and grow between 40 C and 45 C. They are not pathogenic and are not known to cause any diseases.
![]()
Appendaged Bacteria
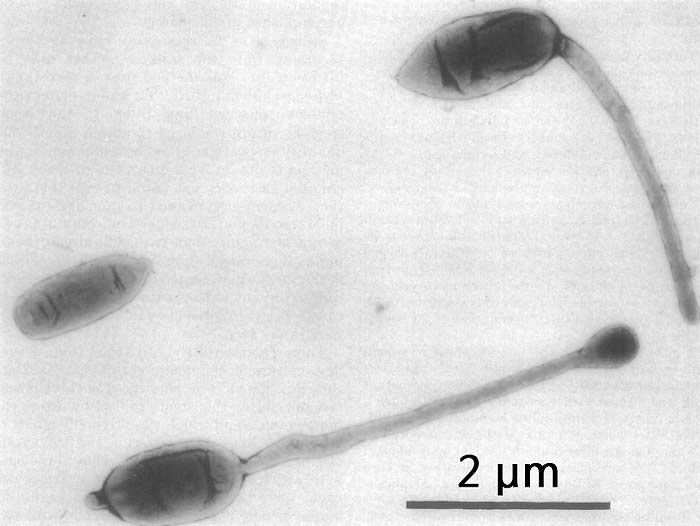
Appendaged or budding bacteria are a heterogeneous collection of microbes or bacteria. They differ from other bacteria in their mode of reproduction (i.e., budding). They can be non-motile. However, the motile forms are usually flagellated. The best examples of appendaged bacteria are Hypomicrobium and Rhodomicrobium.
![]()
Pleomorphic Bacteria
This term refers to the ability to change or alter the size and shape under the stress of pressure of environmental factors. One example is Mycoplasma pneumonia, which is the causative agent of pneumonia. Another example of a pleomorphic pathogen is Mycoplasma genitalium, found in ciliated epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tract that causes sexually transmitted infections.
![]()
Star-shaped Bacteria
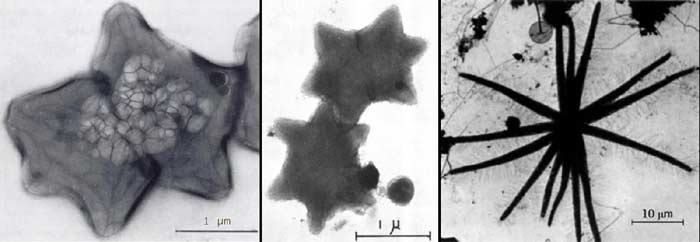
The star-shaped bacteria is an unusually shaped bacteria that resembles a flat, six-pronged star. An example of this species is Stella, found in freshwater, soil, and sewage. Examples include Stella humosa and Stella vacuolata. These are found in the soil when decomposition is underway.
![]()
Sheathed Bacteria
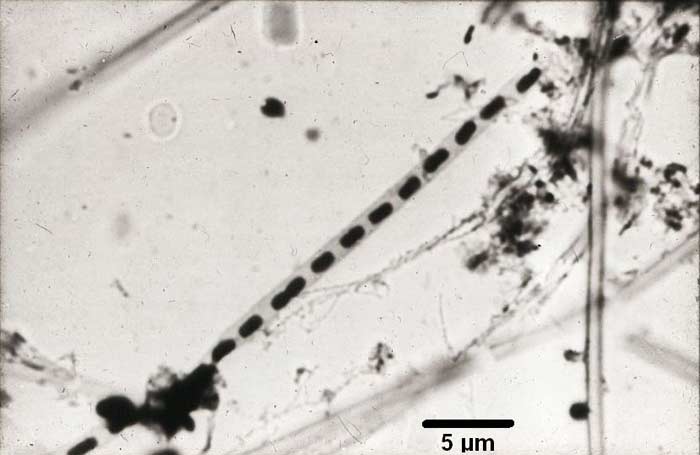

These bacteria are arranged in filament form, wrapped or covered in a sheath-like structure. They are aquatic bacteria found widely in nature, particularly in slow-running water. Examples of sheathed bacteria include Leptothrix, Crenothrix, and Clonothrix.
![]()
Stalked Bacteria
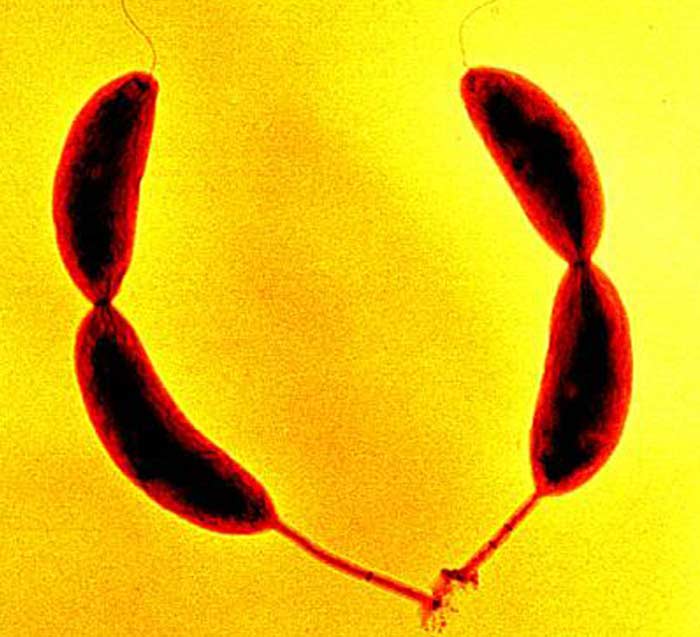
These are unusually shaped cells that have a stalk originating from one end of the bacteria. This arrangement is formed when the bacteria divide unevenly or asymmetrically. An example of this species is Caulobacter crescentus. It is a gram-negative bacteria that is found and lakes and streams and is used to study many aspects of microbiology like regulation of cell cycle etc.
![]()
Spindle-shaped or Fusiform Bacteria
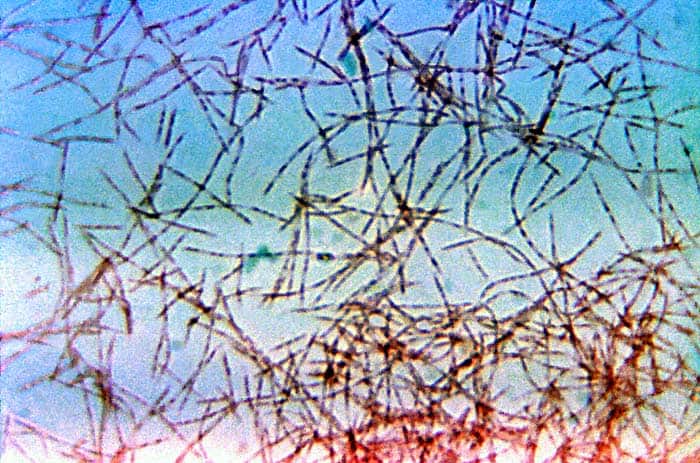

These bacteria have a streamlined or fusiform appearance, which is tapered at both ends and bulged in the middle. An example of this species is Fusobacterium necrophorum, the causative agent in Lemierre’s syndrome.
![]()
Lobed Bacteria
The arrangement of this bacteria species is lobe-like. Examples of lobed bacteria include the genus Sulfolobus. These are found mostly in volcanic springs and are acidophiles and thermophiles. The cell shape is irregular, and they are flagellated. Sulfolobus solfataricus was found and isolated from the Solfatara volcano. Sulfolobus acidocaldarius is another example of this type. These bacteria are also found in hot springs.
![]()
Trichome-forming bacteria
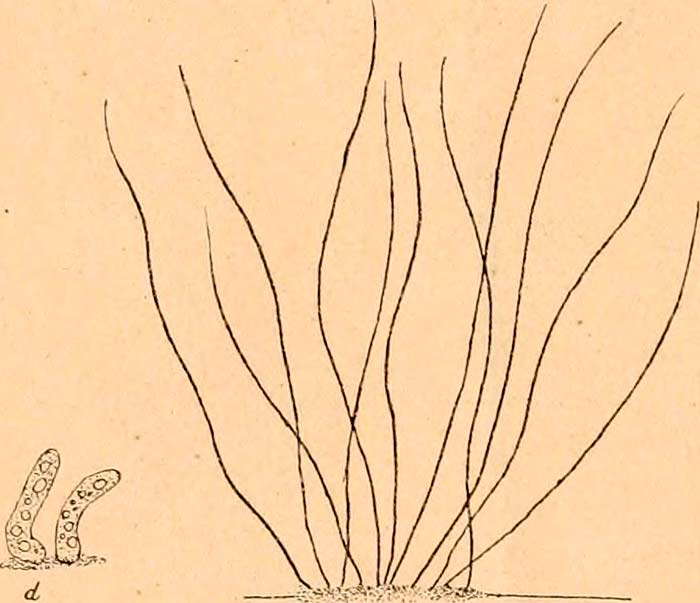
Some bacteria form structures called trichomes which are essentially a chain of vegetative cells. The trichome can sometimes be enclosed in a sheath-like structure. Examples of this type of bacteria include the species Thiothrix nivea, a sulfur-oxidizing bacteria.
![]()
Function of Shapes in Pathogenesis
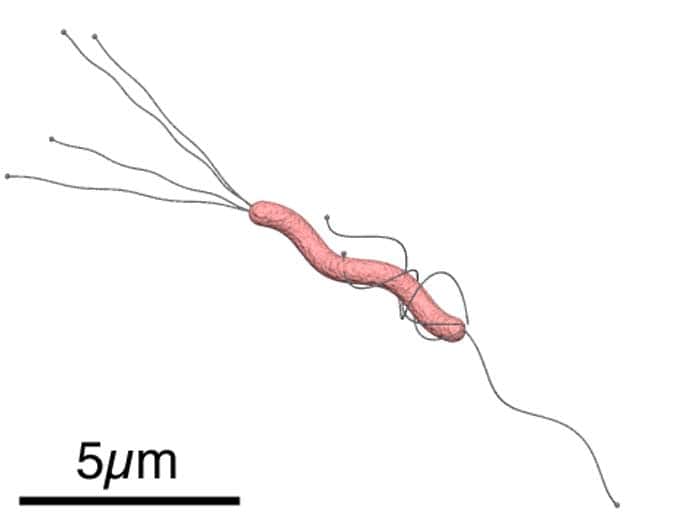
Peptidoglycan is essentially a polymer that contains repeated glycan strands composed of Beta-(1,4) linkages between N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) sugars that are covalently associated with NAM-peptides. Changes to this polymer configuration or thickness affect bacterial morphology and shape.
- By modifying the number of cross-linkages in the peptidoglycan layer, the curvature of the bacterial cell shape can be controlled. The peptidoglycan synthesis process also serves as an important checkpoint from where the bacterial cell assumes a particular shape. Processing of peptidoglycan polymer usually accounts for the rod-shaped bacilli-like shape.
- Genetic changes in proteins that form the peptidoglycan layer also leads to changes in shape and morphology of the bacterial cell. One example is the spiral bacteria Caulobacter crescentus. This bacterium is curved and not helical due to a mutation in the crescentin protein involved in peptidoglycan structure formation.
- Further studies have elucidated that bacterial shape affects the pathogenicity of the microorganism. One such hypothesis states the helical shape of Helicobacter pylori. H.pylori’s pathogenicity is hugely dependent on its motility. The helical shape of this bacteria is found to enhance its motility.
- Some bacteria can also change their morphology under environmental conditions, stress, or during the pathogenicity process. Therefore, shape and morphological traits are thought to be a selective factor in evolution. Bacterial shape, thus, is an important factor that decides not only the phenotypical features of the species but also its pathogenicity.
- The shape is not only a phenotypic feature but is affected by, and in turn, affects, pathogenicity, evolution and adaptability, nutrient uptake, motility, and perhaps a host of other features.
![]()
As we probe more into bacterial morphology and adaptations, can we one day correlate other important factors such as antibiotic resistance?
One of the current issues is the rapid development of antibiotic resistance toward some deadly strains of bacteria.
A dig into this subject could open new insights and provide evidence of a relationship between bacterial shape and drug resistance.
![]()