
| Animalia | Mammalia | Primates | Lemuridae | Chordata | Hapalemur aureus |
The golden bamboo lemur, scientifically known as Hapalemur aureus, is one of Madagascar’s most endangered and amazing primates. Endemic to the island’s southeastern rainforests, this lemur’s survival depends almost entirely on one plant species – giant bamboo.
From its lush golden fur to fascinating adaptations, the golden bamboo lemur has captivated scientists and conservationists alike. However, these magnificent lemurs are on the brink of extinction due to extensive habitat loss over the past decades. Less than 1,000 remain today.
On this page, you’ll learn all about the magnificent golden bamboo lemur – from taxonomy and physical traits to behavior, reproduction, diet, and conservation status.
![]()

- Common Name: Golden Bamboo Lemur
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1987
- Monkey Size: 28 to 45 cm (11 to 18 in)
- Skin Color(s): Dark grayish-brown
- Habitat: Rainforest
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Native Countries: Madagascar
Golden Bamboo Lemur Distribution
Golden Bamboo Lemur Characteristics
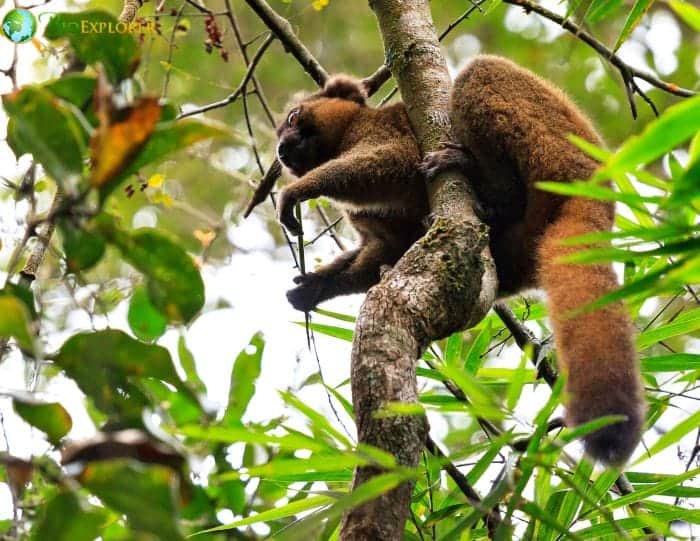

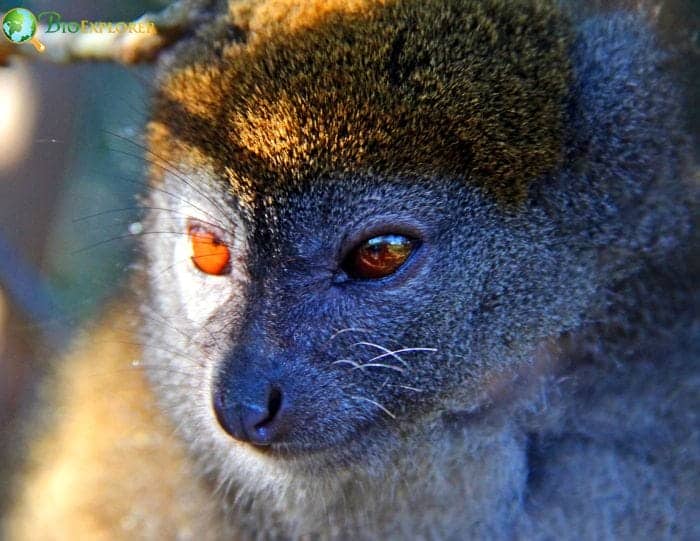
The golden bamboo lemur, Varibolomena or Bokombolomena in Malagasy, is a medium-sized bamboo lemur native to southeastern Madagascar.
- Golden bamboo lemurs are dark drab with underlying orange fur on the tail’s lower face, abdomen, and underside.
- Other identifying traits of the golden bamboo lemur include a small head size, total length of 11-18 inches, weight of 3.5 pounds, and hind limbs longer than the forelimbs, allowing for vertical clinging.
- The golden bamboo lemur derives its name from its beautiful, bright golden-orange fur. Juveniles have cream or gray fur instead, which darkens as they mature.
- They have large, round, desert ceramic-colored eyes and flat, black, hairy faces with pink noses. Their long fingers are used to grasp bamboo, and their tail is dense and non-prehensile.
- Both male and female golden bamboo lemurs are sexually monomorphic; that is, there are no physical differences between the two sexes beyond their genitals.
- Distinctive white fur encircles the eyes and muzzle, contrasting sharply with the rich gold coat. Their face is cat-like but with a pronounced lemur snout. Short fur covers the body and tail.
- Females have only one pair of breasts (mammary glands) located on top of the pectoral muscles. Golden bamboo lemurs are considerably larger than most other bamboo lemur species.
Golden Bamboo Lemur Habitat & Range
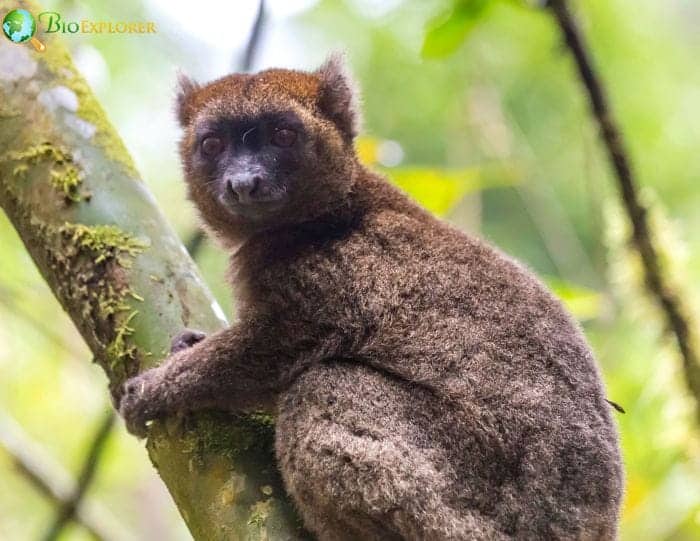

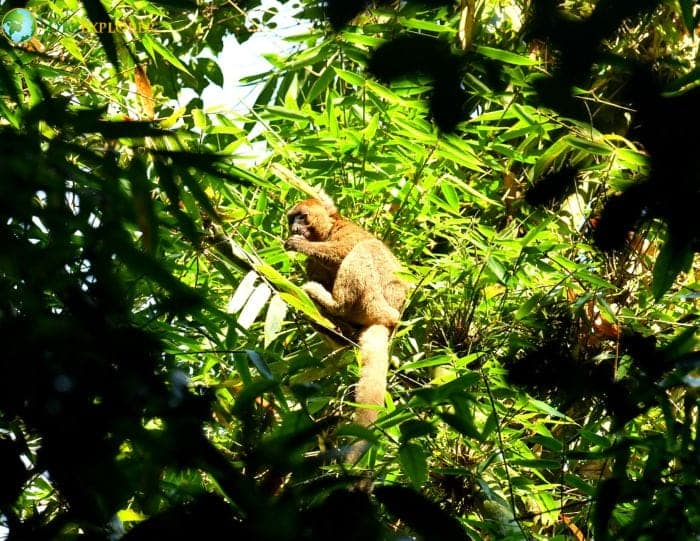
Golden bamboo lemurs exclusively inhabit tropical rainforests in southeastern Madagascar. They spend their lives in lowland to highland forests at 600–1,400 m (2,000–4,600 ft).
Within this narrow range, golden bamboo lemurs rely almost entirely on giant bamboo thickets of the species Cathariostachys madagascariensis for shelter and food. They are only found in areas with substantial stands of this bamboo.
Sadly, the population is declining to around 1,000 individuals remaining. Continued deforestation has fragmented their habitat, leaving many small isolated pockets. With no migration between populations, they are extremely vulnerable to local extinction.
Fascinating Bamboo-Adapted Behaviors
Golden bamboo lemurs have evolved a fascinating array of physical and behavioral adaptations for exploiting bamboo forests:
Mostly Nocturnal, Arboreal Foragers
Golden bamboo lemurs spend daylight hours sleeping in dense clumps of giant bamboo, emerging at dusk to feed. Their nocturnal lifestyle likely keeps them hidden from aerial and terrestrial predators.
They are highly arboreal, moving through the forest quadrupedally. Strong hands and feet allow them to grip onto bamboo stems. They often hang from their hind legs while reaching for shoots or grasping branches with their hands.
Small Family Groups with Defined Territories
Like other lemurs, golden bamboo lemurs are social animals. They live in small family groups averaging 2 to 5 members, usually containing an adult pair and offspring. A golden bamboo family shares a home territory of 20 to 80 acres.
Scent-marking behaviors reinforce territorial boundaries. Males vigorously defend territories by scent marking with arm and wrist glands.
Vocalizations such as periodic loud wailing calls also help regulate spacing between groups across the forest.
Reproduction Timing with Bamboo Cycles
Golden bamboo lemurs typically mate only once annually. Breeding seasons directly coincide with bamboo flowering and shoot production, reflecting an evolutionary adaption linking their reproduction to fluctuating food resources.
What Do Golden Bamboo Lemurs Eat?
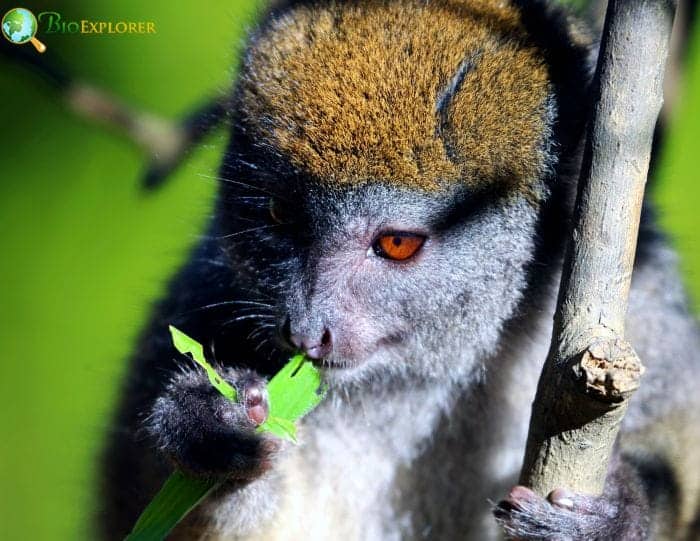

Golden bamboo lemurs feed almost exclusively on new growth of giant bamboo, including shoots, unfurling leaves, and leaf bases. This new growth is more digestible than mature bamboo.
- They supplement bamboo with occasional fruits and flowers. But overall, 99% of their diet comes from giant bamboo.
- Eating bamboo poses major challenges – it’s low in nutrients and high in toxins and abrasive silica. But golden bamboo lemurs have specialized adaptations allowing them to exist almost entirely on this difficult food:
- Stomach acid helps neutralize cyanide compounds.
- Slow digestive passage (over 24 hrs) maximizes nutrient absorption.
- Iron reinforcement on molar surfaces prevents excess wear.
- Golden bamboo lemurs could not survive on a bamboo diet without these remarkable adaptations. Tragically, they still face starvation risks when bamboo undergoes mass flowering and die-offs.
Golden Bamboo Lemur Reproduction and Life Cycle

Golden bamboo lemur females normally produce just one infant per breeding season. After a 138-day gestation period, they give birth to a single young.
Initially, the blind, helpless infant clings tightly to the mother’s belly for warmth and transportation as she moves through the forest. Within two weeks, the baby transitions to riding jockey-style on her back.
Weaning starts around 75 days old, but supplementation continues until over 5 months. Juveniles attain full independence after about 1 year with their mothers.
These lemurs reach full maturity between 2 and 3 years old and may live over 20 years.
Golden Bamboo Lemur Fun Facts

- The golden bamboo lemur, a unique species, was discovered in 1986 by Dr.Patricia Wrightin the area now designated as Ranomafana National Park. This discovery led to the park’s establishment in 1991, aiming to protect this rare lemur and its natural habitat.
- Adult golden bamboo lemurs consume approximately 500 grams of bamboo daily, which contains high levels of cyanide, amounting to about 12 times the lethal dose for most other animals of their size. Remarkably, these lemurs manage to avoid the acute and chronic symptoms of cyanide poisoning. However, the exact physiological mechanisms enabling this resistance remain unknown to scientists.
- They possess a toothed comb that is used for grooming. Still, they also have extra humps on their upper fourth premolars, which are believed to help grind up the tough, fibrous plant matter they consume regularly.
- Golden bamboo lemurs are vertical leapers and clingers, always landing their feet first, but are quadruped on horizontal surfaces.
- Golden bamboo lemurs produce a fatty secretion from their brachial glands, which they are believed to transfer onto their tails, aiding in dispersing their scent for communication and territorial purposes.
Conservation Status and Threats
The golden bamboo lemur is classified as Critically Endangered by the IUCN Red List, with less than 1,000 remaining in the wild. Their extremely limited, fragmented habitat renders them highly vulnerable.
Several key threats are driving dramatic population declines:
- Deforestation for timber harvests and subsistence agriculture directly destroys their forest habitat. An estimated 80-90% of their original range has been cleared in the past 50 years.
- Climate change brings more extreme weather like droughts and cyclones, reducing forest cover. Their restricted niche provides little climate buffering.
- Hunting still affects some forests, depleting lemur populations. Their loud calls, unfortunately, give away the location.
Comprehensive efforts focusing on forest corridors, habitat restoration, and community management offer the only hope for reversing the decline of these critically endangered primates in the coming decades.
Conclusion
In conclusion, through remarkable evolutionary adaptations, golden bamboo lemurs showcase a truly unique mammalian species specialized almost exclusively to bamboo forests. Tragically, the same deep ecological ties now threaten their very existence.
As Madagascar’s forests disappear in coming decades, so will the last of the island’s iconic bamboo lemurs. Urgent habitat conservation offers their only real salvation.
The next decade will determine whether organizations can connect remaining forest pockets to save these species from extinction. Their specialized niche gives no margin for error. Unless more habitat is protected soon, golden bamboo lemurs face a dire plight.










