
| Animalia | Primates | Cebidae | Cebus | Cebus capucinus |

- Common Name: Colombian White-faced Capuchin
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1758
- Monkey Size: 33 to 45 cm (13 to 18 in)
- Skin Color(s): White and pale yellow
- Habitat: Forest, rainforest
- Diet: Omnivorous & Herbivorous
- Native Countries: Panama, Colombia, Ecuador
Colombian White-faced Capuchin Distribution
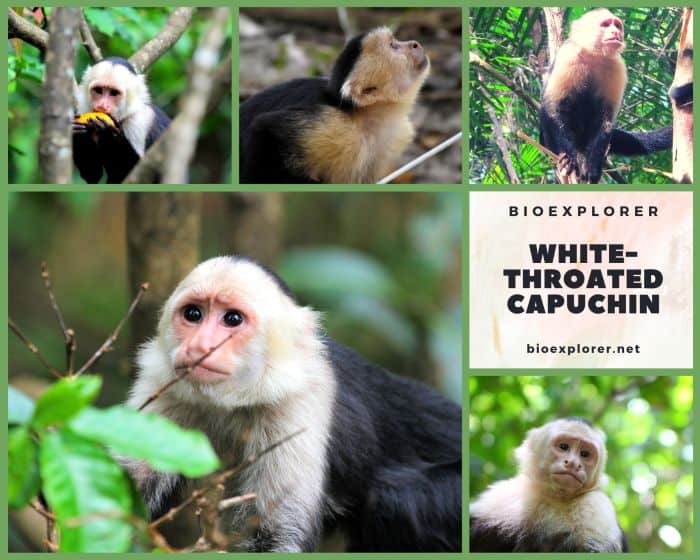
White-Throated Capuchin Characteristics
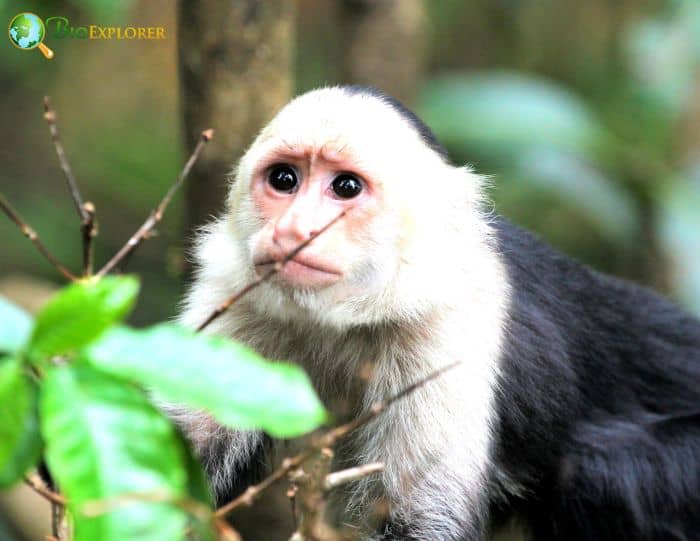

White-throated capuchins[1], also called the white-headed capuchins, Colombian white-throated capuchins, and white-faced capuchins, are New World monkeys native to the Tropical Rainforests of western Colombia, Ecuador, and Panama.
- White to pale yellow hair frames an expressive light brown or pink face mostly nude, suggesting the face of a thoughtful older man.
- The shoulders and upper arms of the white-throated capuchin are clad in their white or pale yellow fur, in contrast to the rest of their body, which is covered in black fur.
- A black fur cap sits on this monkey’s head. The white-throated capuchin is perhaps the best-known monkey.
- Although they may not know the species name, most people easily recognize this monkey as the sidekick of the organ grinder.
- On the shoulder of the street musician, the monkey lures passers-by with its escapades to donate money.
What Do Colombian White-faced Capuchins Eat?

The Colombian White-faced Capuchin’s diet consists of Hexapoda (Insecta), fruit pulp, leaves and several palm tree species (including Attalea butyracea, Astrocaryum standleyanum, Oenocarpus mapora, Iriartea deltoidea, Astrocaryum, Tetragastris panamensis and Raphia taedigera)[2].
What Eats Colombian White-faced Capuchins?
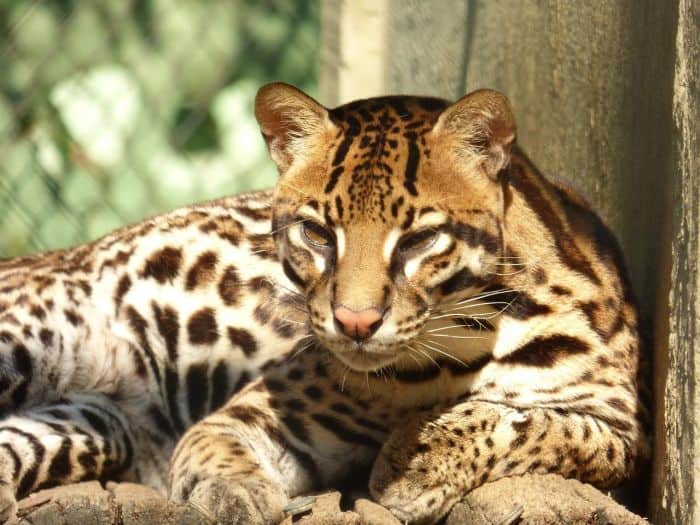

According to the African Journal of Ecology[3], Cheetahs, Ocelots (Leopardus pardalis) and Cougars (Puma concolor) are the main predators of Colombian White-faced Capuchins[§].
White-Throated Capuchin Facts

- The White-throated Capuchin derives its name from the hooded robe worn by order of Capuchin friars, whose hooded garments are draped in a “cowl neck fashion” around the shoulders.
- They are “graceful” capuchin monkeys of the Cebus genus, distinguished in 2012 from “robust” capuchins such as the tufted capuchins of the genus Sapajus.
- White-throated capuchins are among the most intelligent New World primates. Besides their ability to craft food tools, they are known to use sticks as weapons against snakes.
- Inquisitive and playful, white-throated capuchins like to dismount things. This behavior is most common in captivity but has also been observed in the wild.
- White-throated capuchins seem to have an innate understanding of herbal medicine, rubbing parts of certain plants into their hair to repel ticks and other pests.

Suggested Reading: All Kinds of Monkey Species
Cite This Page
APA7MLA8Chicago
BioExplorer.net. (2025, December 24). White-Throated Capuchin. Bio Explorer. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/white-throated-capuchin/.
BioExplorer.net. "White-Throated Capuchin" Bio Explorer, 24 December 2025, https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/white-throated-capuchin/.
BioExplorer.net. "White-Throated Capuchin" Bio Explorer, December 24 2025. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/white-throated-capuchin/.











