
| Animalia | Primates | Cercopithecidae | Cercocebus | Cercocebus lunulatus |

- Common Name: White-naped Mangabey
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1853
- Monkey Size: 40 to 67 cm (15.75 to 26.38 in)
- Skin Color(s): Slate-grey or brown-grey
- Habitat: Forest, rainforest
- Diet: Omnivorous
- Native Countries: Ghana, Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast
White-naped Mangabey Distribution
White-Naped Mangabey Characteristics
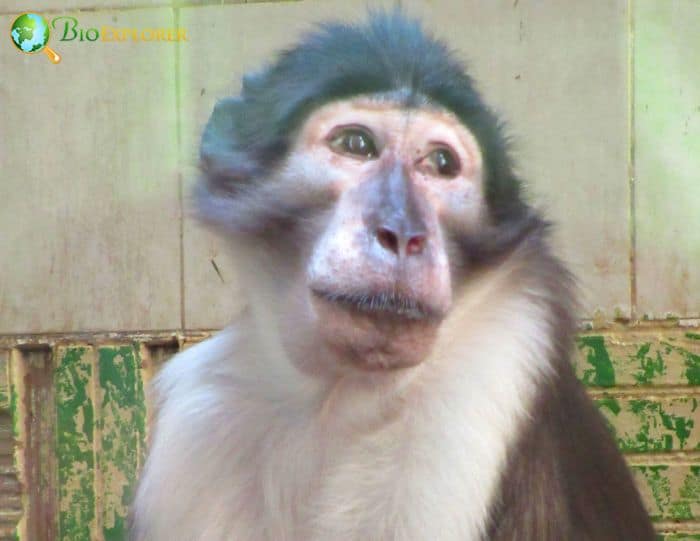

Cercocebus atys lunulatus,[1] now Cercocebus lunulatus, is commonly known as the white-naped, white-headed, or white-necked mangabey (causing confusion with the Collared mangabey).
- This now distinct species is thought to have a geographic range from east of the Sassandra River to west of the Volta River in Ghana.
- White-naped mangabey is also reported as a forest dweller in northeastern Côte d’Ivoire and southwestern Burkina Faso.
- A member of the Cercopithecinae (pocket-cheeked monkeys), white-naped mangabeys are smoky, slate-gray, or brownish-gray monkeys with lighter white on their ventral side.
- It is known for a whorl or Crown on the head, a darker face, a more prominent dorsal stripe, and a black-edged white oval patch on the nape.
- The hands and feet of white-naped mangabeys are more similar in color to the body and have white undersides.
- The mass of these mangabeys ranges from 8.5 to 14 kg for males and 5 to 9 kg for females, with an average of 8, 593 kg.
- The head and body length is 40-60 cm in females and 47-67 cm in males, while the tail length is 40-80 cm in both sexes. The shoulder height is 38-42 cm for females and 40-45 cm for males.
White-Naped Mangabey Facts
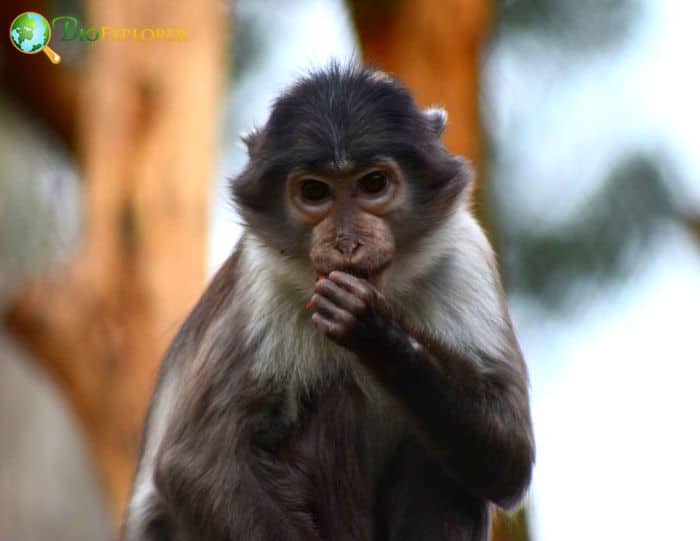

- White-naped mangabeys are diurnal, four-legged ground monkeys that live in groups of several males and females.
- They have sexually dimorphic behavior patterns: males are more likely to engage in social behaviors, and females are more likely to submit and receive agonistic behaviors.
- Unlike many non-human primates, white-naped mangabeys generally do not have a strictly matrilineal social structure. Their social structure has also been described as “contest competition” in which female species establish lineages based on matrilineal dominance.
- White-naped mangabeys have one of the lowest rates of agonistic behavior and contact aggression of any Old-World monkey. Most biting behaviors are harmless and involve a slight pinch on the tail or rump.
- These mangabeys can also distinguish between fruiting and non-fruiting trees and are more likely to approach fruiting trees.

Suggested Reading: Monkey Classification
Cite This Page
APA7MLA8Chicago
BioExplorer.net. (2025, December 27). White-naped Mangabey. Bio Explorer. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/white-naped-mangabey/.
BioExplorer.net. "White-naped Mangabey" Bio Explorer, 27 December 2025, https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/white-naped-mangabey/.
BioExplorer.net. "White-naped Mangabey" Bio Explorer, December 27 2025. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/white-naped-mangabey/.











