
| Animalia | Primates | Atelidae | Brachyteles | Brachyteles arachnoides |

- Common Name: Muriqui
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1806
- Monkey Size: 55 to 78 cm (21.5 to 30.5 in)
- Skin Color(s): Grayish-golden
- Habitat: Rainforest
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Native Countries: Brazil
Muriqui Distribution
Southern Muriqui Characteristics
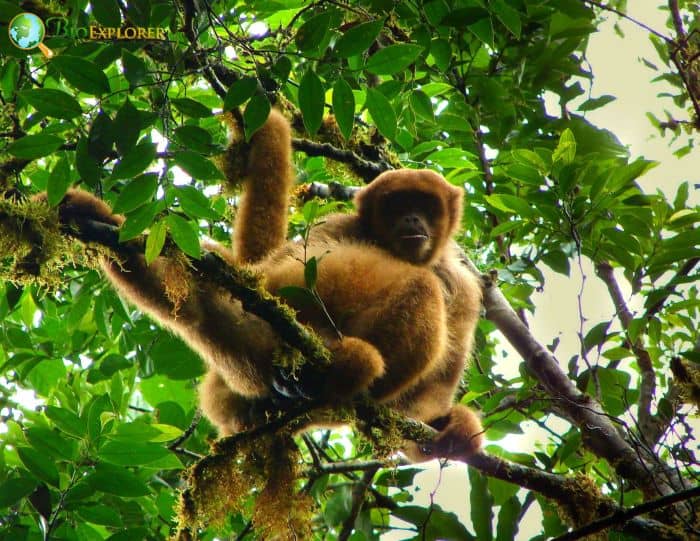

The southern muriqui[1] or woolly spider monkeys (Brachyteles arachnoides) are scattered across southeastern Brazil, from Bahia north to Sao Palo south.
- Southern muriquis have long prehensile tails that aid their arboreal existence.
- Due to the swinging nature of their movements, their thumbs were reduced in size and are believed to be vestigial.
- Both sexes have prominent bellies. The fur is golden gray except for the face, which appears to be covered in soot, and the area around the genitals, which tends to be much redder than the rest of the body.
- The genitals of this species are pretty noticeable.
What Do Southern Muriquis Eat?
The Southern Muriqui diet includes[¶]:
- Hollies (Ilex)
- Higuillo De Hoja Menuda <Piper er aduncum).
- Lyre Gurnard (Piper)
- Myrsine (Myrsine)
- American Black Nightshade (Solanum um americanum).
- Blolly (Guapira)
- Johnnyberry (miconia)
- Queen Palm (Syagrus romanzoffiana).
- Nightshade (Solanum)
- Higuillo (Piper dilatatum)
- Gumtree (Sapium glandulosum)
- Sweetwood (Ocotea)
- Attorney (Clusia)
- Mistletoe (Phoradendron)
- Black-Sage (Cordia polycephala)
- Hoja Menuda (Siphoneugena densiflora).
- Moena (Ocotea aciphylla)
- Winter’s Bark (Drimys winteri).
- Cedre Gris (Ocotea puberula).
- Wild Coffee (Psychotria)
- Bread And Cheese (Paullinia).
- Soldierbush (Tournefortia)
- Pearl Laceleaf (Anthurium scandens).
- Cargadera Blanco (Annona danforthii).
- Sweetleaf (Symplocos)
- Largeleaf Lantana (Lantana camara).
- Leathery Colicwood (Myrsine coriacea).
- Jamaican Nettletree (Trema micrantha).
- Cattley Guava (Psidium cattleianum).
- Abas (Psidium guajava)
- ‘Awapuhi-Ke’oke’o (Hedychium coronarium)
- Punchberry (Myrcia splendens)
- Sweetwood (Nectandra)
- Crackopen (Casearia sylvestris)
- Scratchbush (Urera baccifera)
- Sweetwood (Nectandra membranacea)
- Pricklyash (Zanthoxylum)
- Fuchsia (Fuchsia)
- Bay (Persea)
- Iguana Hackberry (Celtis iguanaea).
- Stinkingtoe (Hymenaea courbaril)
- Rodwood (Myrcia)
- Maricao Cimun (Byrsonima crassifolia).
- West Indian Cherry (Prunus myrtifolia).
- Langsdorf’s Copaifera (Copaifera langsdorffii).
- Philodendron (philodendron on imbe)
- Adanson’s Monstera (Monstera adansonii).
- Hairy Banana (Musa velutina).
- Privet Stopper (Eugenia ligustrina).
- Guavaberry (Myrciaria floribunda)
- Barbados Shrub (Pereskia aculeata).
- Sacky Sac Bean (Inga laurina).
- Guavas (Psidium)
What Eats Southern Muriquis?
Jaguars (Panthera onca), Águila Arpías (Harpia harpyja), and Ocelots (Leopardus pardalis) are the primary predators of Southern Muriquis[§].
Southern Muriqui Facts
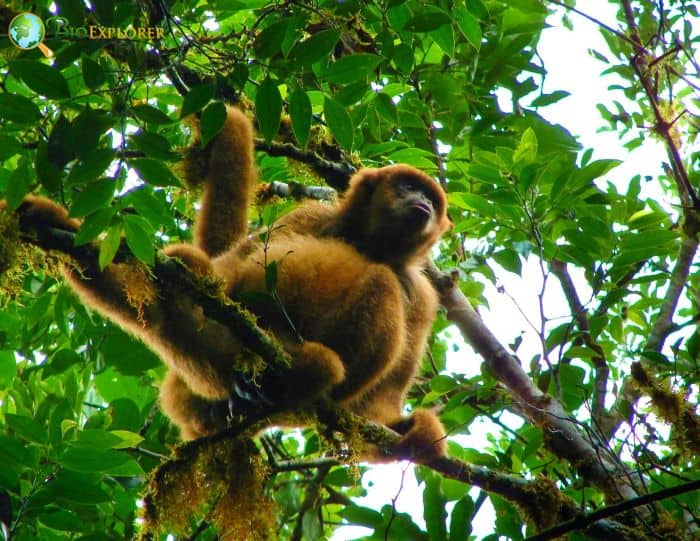

- The southern muriqui is one of the largest primates in South America, with males weighing around 15 kg and females around 12 kg.
- Muriquis are well adapted to arboreal living. Their vestigial thumbs and long arms allow them to lunge quickly from branch to branch.
- When moving from one feeding ground to another, a troop often moves in a line, with one monkey following the other through the forest.
- Unlike many other primate species, muriqui females control social interactions significantly.
- It is one of the few primate groups where the males stay with their natal group, and the females are the ones to join other troops.
Suggested Reading: Monkey Species List
Cite This Page
APA7MLA8Chicago
BioExplorer.net. (2025, April 14). Southern Muriqui. Bio Explorer. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/southern-muriqui/.
BioExplorer.net. "Southern Muriqui" Bio Explorer, 14 April 2025, https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/southern-muriqui/.
BioExplorer.net. "Southern Muriqui" Bio Explorer, April 14 2025. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/southern-muriqui/.










