| Animalia | Primates | Cercopithecidae | Macaca | Macaca nemestrina |
Pigtail macaque Distribution
Pig-Tailed Macaque Characteristics

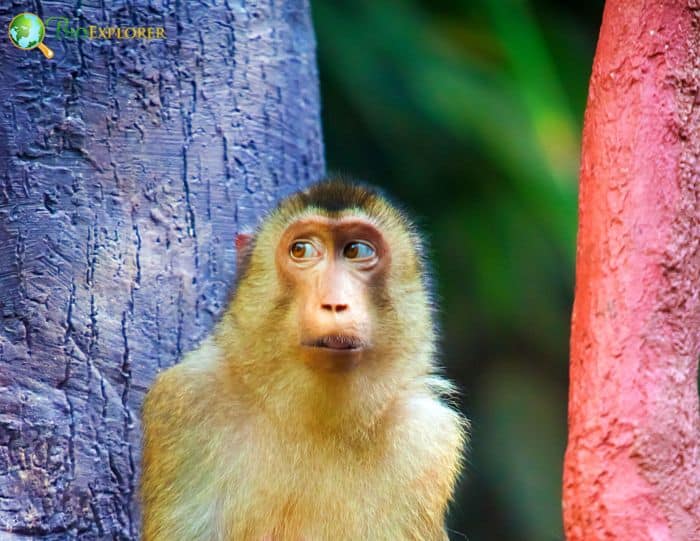
The pig-tailed macaque[1] (Macaca nemestrina), also called the Sundaland pig-tailed macaque and Sunda pig-tailed macaque is a medium-sized macaque native to southern Thailand, Indonesia, and Malaysia.
- It is locally known as Berok. Pig-tailed macaques have light brown hair that covers their body and a white belly.
- The hair on the crown is dark brown or black in color and grows as if it has a depression in the crown. Males have mane-like hair around their faces.
- Pig-tailed macaques also have long legs and hairless snouts.
- These macaques are born black in color and change their color during adulthood. They are sexually dimorphic, with males being larger.
- Females are about half the size of males.

What Do pigtail macaques Eat?
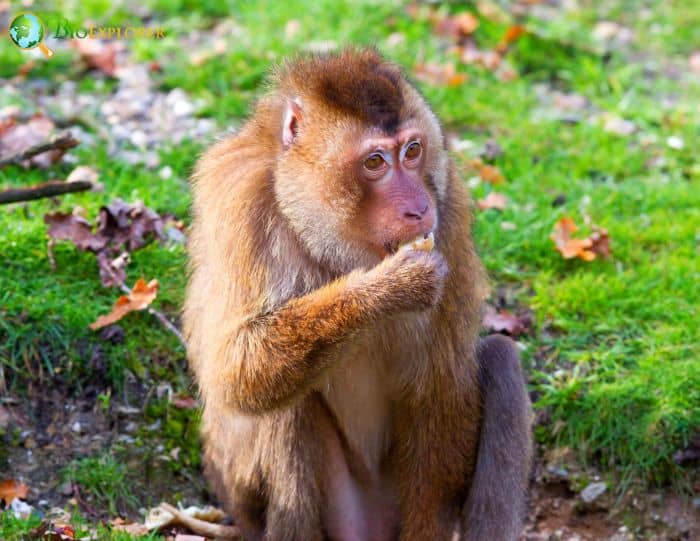

The Internal Journal of Primatology describes that the pigtail macaque feeds on[¶]:
- Weeping Fig (Ficus benjamina).
- Council Tree (Ficus altissima).
- Plum Mango (Bouea oppositifolia).
- Styrax (Styrax benzoin)
- Pulasan (Nephelium lappaceum)
- Fig (Ficus)
- Apel En Wai (Syzygium jambos).
- Mango (Mangifera indica)
- Langsat (Lansium domesticum)
- Malabar Melastome (Melastoma malabathricum).
- Duhat (Syzygium cumini)
Pig-Tailed Macaque Facts
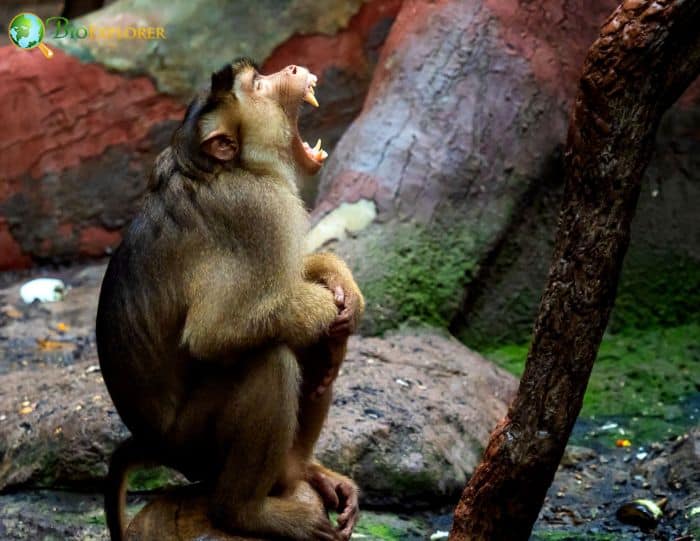

- Pig-tailed macaques get their name from their morphology. Their short, semi-erect tails resemble pigtails, earning them the nickname “pig-tailed” macaques.
- They live in groups with several males and females. The females stay with the natal troop, making it a female-bound society.
- Males are more socially dominant than females. However, groups of female species will gang up on a male species and attack him.
- Pig-tailed macaques are diurnal and spend most of their time in trees and only 8.4 percent[2] on the ground.
- Some researchers refer to these macaques as silent monkeys because they seem so quiet.
Suggested Reading: All Kinds of Monkeys
Cite This Page
APA7MLA8Chicago
BioExplorer.net. (2025, May 28). Sunda Pig-Tailed Macaque. Bio Explorer. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/pig-tailed-macaque/.
BioExplorer.net. "Sunda Pig-Tailed Macaque" Bio Explorer, 28 May 2025, https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/pig-tailed-macaque/.
BioExplorer.net. "Sunda Pig-Tailed Macaque" Bio Explorer, May 28 2025. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/pig-tailed-macaque/.