Lesser Spotted-Nosed Monkey

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Cercopithecidae | Cercopithecus | Cercopithecus petaurista |

- Common Names: Lesser Spot-nosed Monkey, Lesser Spotted Monkey, and Lesser White-nosed Monkey
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1774
- Monkey Size: 100.58 to 115.82 cm (39.6 to 45.6 inches)
- Skin Color(s): Olive green
- Habitat: Forest, rainforest
- Diet: Omnivorous
- Native Countries: Ivory Coast, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Togo, Guinea-Bissau, Senegal
Lesser Spot-nosed Monkey Distribution
Countries
Ivory Coast
Ghana
Guinea
Liberia
Sierra Leone
Togo
Guinea-Bissau
Senegal
Lesser Spotted-nosed Monkey Characteristics
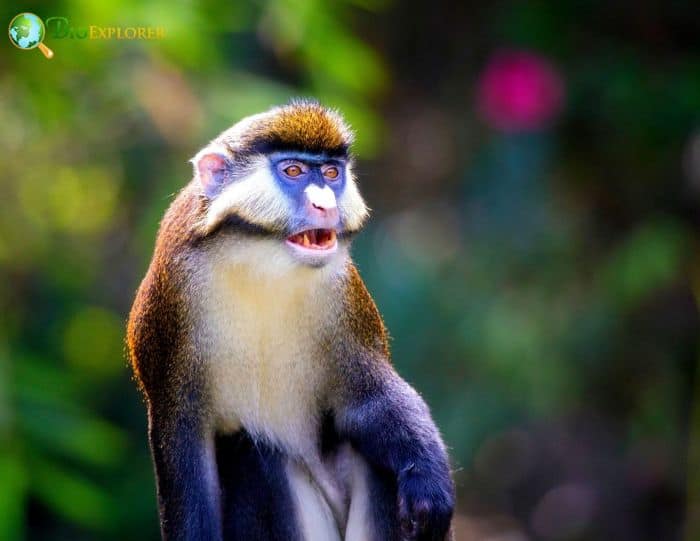

The lesser spotted-nosed monkey[1], lesser spotted monkey, or lesser white-nosed monkey (Cercopithecus petaurista) is a primate species in the Cercopithecidae family.
- It is a species of small monkey with a long tail. The face is black, with a white patch on the nose.
- A white stripe extends from the temple to below the ear. The Crown, back, outer limbs, and upper tail are olive or khaki.
- In some species, the middle and lower back have a reddish tint. The individual hairs, especially on the Crown, are mottled with black and yellow.
- The underparts, the limbs’ inside, and the tail’s underside are white or cream.
What Do Lesser Spot-nosed Monkeys Eat?
The Lesser Spot-nosed Monkey feeds on these food sources[¶]:
- Fig (Ficus)
- Chinalaurel (Antidesma)
- Leaf Flower (Phyllanthus)
- Hairy Rock Fig (Ficus glumosa).
- Persimmons (Diospyros)
- Ohia (Celtis zenkeri)
- Guanabanilla (Ouratea striata)
- Chinese Banyan (Ficus thonningii).
- African Nutmeg (Pycnanthus angolensis).
- Sacred Garlic Pear (Crateva religiosa).
- Boleko Nut (Ongokea gore).
- Raphia Palm (Raphia africana).
- African Oil Palm (Elaeis guineensis).
Lesser Spotted-nosed Monkey Facts
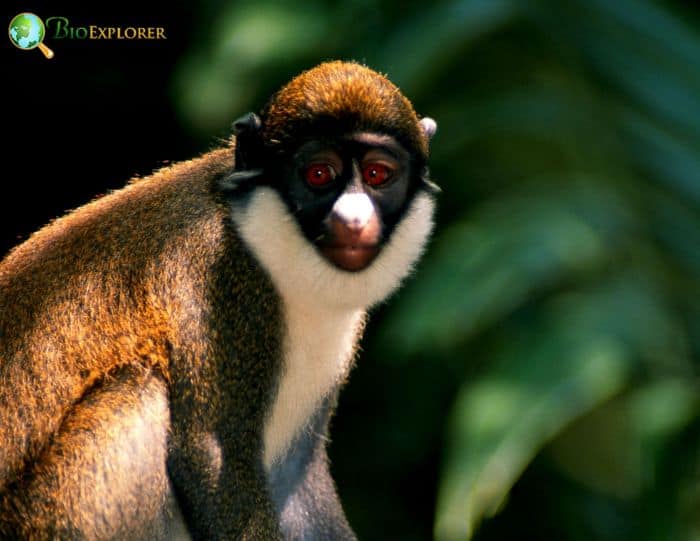

- The lesser spotted-nosed monkey is diurnal, arboreal, and cryptic; it moves cautiously through the forest, rarely climbing to high treetops but mostly visiting undergrowth and vines.
- It forms social groups of about 10 individuals, usually one adult male, several adult females, and their young.
- It feeds on fruits, leaves, flowers, and insects, collecting its food and storing it in the cheek pouches.
- Females give birth to single young after a gestation period of about 7 months. Therefore, breeding does not appear to be seasonal.
- The group’s male emits an alarm call similar to a cat’s purr, distracting potential predators so that the rest of the group can seek refuge elsewhere.
Suggested Reading: Types of Monkeys In The World
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 28). Lesser Spotted-Nosed Monkey. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/lesser-spotted-nosed-monkey/
