
| Animalia | Primates | Hominidae | Gorilla | Gorilla beringei |

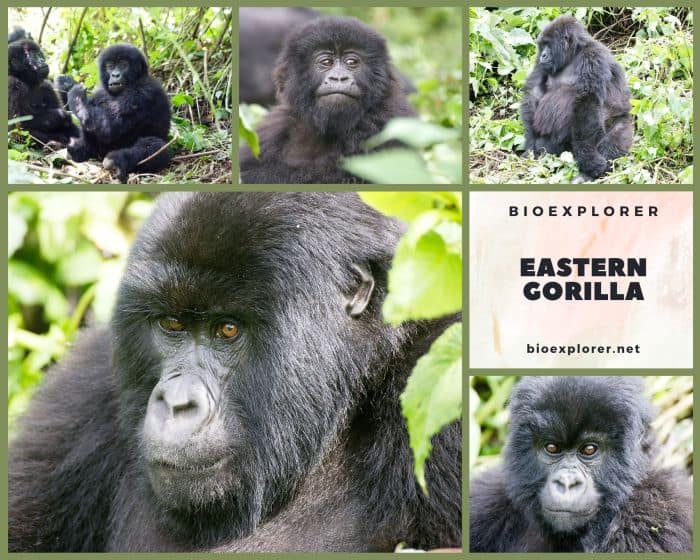
- Common Name: Eastern Gorilla
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1903
- Monkey Size: 150 to 185 cm (59.06 to 72.83 in)
- Skin Color(s): Blue-black to brownish-grey
- Habitat: Rainforest, mountains
- Diet: Omnivorous
- Native Countries: Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda, Uganda
Eastern Gorilla Distribution
Eastern Gorilla Characteristics
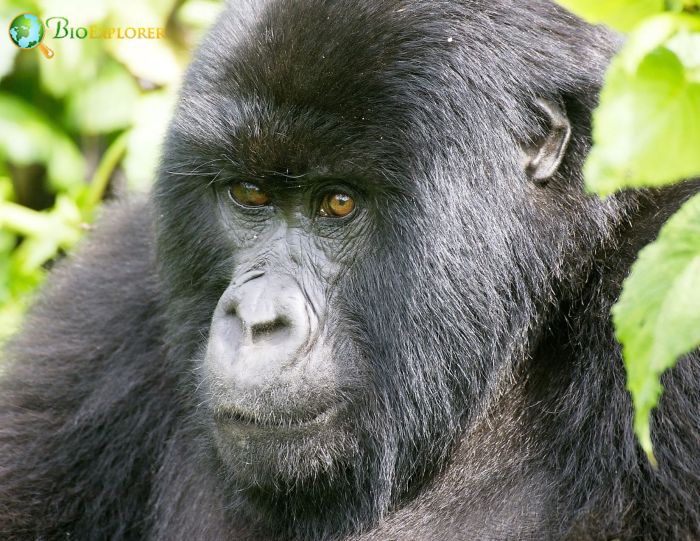

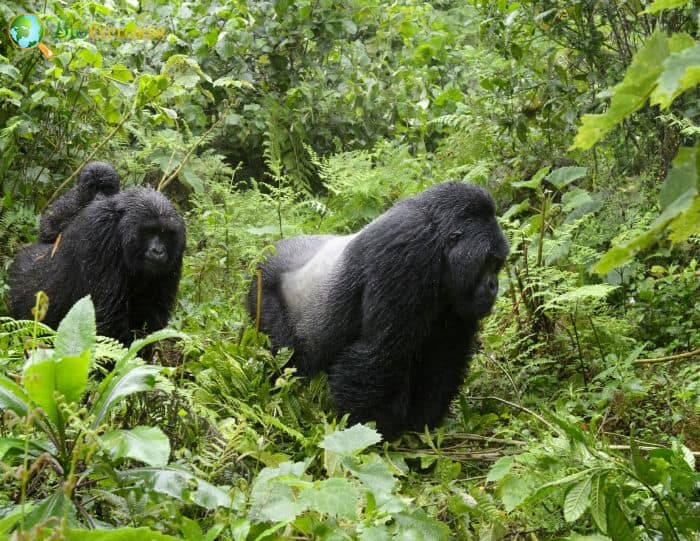
The eastern gorilla[1] is an endangered species of the Gorilla genus and the largest living primate, with an average length of 150 cm for females and 185 cm for males.
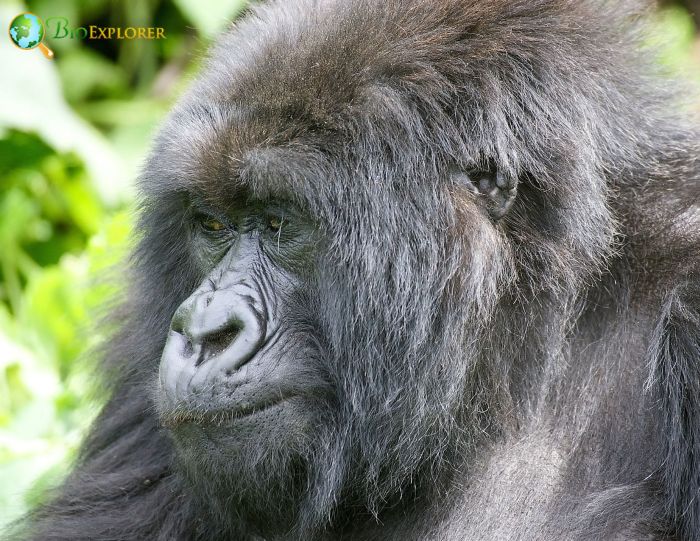

- They are very sexually dimorphic, with females weighing between 70 and 114 kg and males weighing, on average 160 kg.
- There are two sub-species of Eastern Gorilla: mountain gorilla (G. b. beringei) and eastern lowland gorilla (G. b. graueri).
- They have a stocky body, massive heads, long muscular arms, and short legs, and males have large, sharp canines.
- The eastern gorilla’s fur is long and silky, ranging from bluish-black to brownish-gray.
- Adult males develop a large patch of gray or silver fur on their backs, giving them the alternative name silverbacks.
- Eastern gorillas are distinguished from other gorillas by having shorter arms, a smaller nose, larger jaws and teeth, and longer hair.

What Do Gorillas Eat?
Gorillas are warm-blooded mammals occupy the forest floor layer of the tropical rainforests. What do gorillas eat? Are gorillas herbivores or omnivores? Explore the answers to all these questions & more.
What Do Eastern Gorillas Eat?

The Eastern Gorilla consumes these animals and plants including[¶]:
- Tail Grape (Artabotrys)
- Forest Newtonia (Newtonia buchananii).
- Chinese Banyan (Ficus thonningii).
- St. Johnswort (Hypericum)
- Fig (Ficus)
- Lemonwood (Xymalos monospora)
- Ceylon Spinach (Basella alba).
- Aframomum (Aframomum)
- Mistletoe (Viscum)
- Lyre Gurnard (Piper)
- Strawflower (Helichrysum)
- Blackberry (Rubus)
- Treebind (Cissus)
- Touch-Me-Not (Impatiens)
- Goldenleaf (Chrysophyllum)
- Boarwood (Symphonia globulifera)
- African Mammee-Apple (Mammea africana).
- Urera (Urera)
- Persimmons (Diospyros)
- Treefern (Cyathea)
- African Breadfruit (Treculia africana).
- Cane (Arundinaria)
- Rattlebox (Crotalaria)
Eastern Gorilla Facts
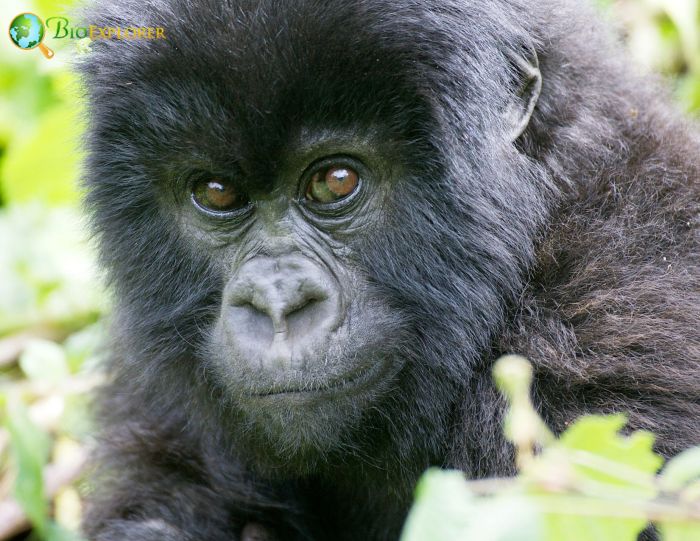

- Eastern gorillas live in stable and cohesive family groups led by a dominant silverback male.
- They tend to have larger groups than their western relatives, comprising up to 35 individuals.
- Males defend their females and young by using their size in intimidating displays of attacks and breast thrusts.
- They are diurnal, but most foraging occurs in the morning and late afternoon. At night, they build nests by folding in vegetation, typically on the ground.
- These primates are essential in structuring plant communities as they feed on vegetation.
Suggested Reading: All Other Types of Apes
Cite This Page
APA7MLA8Chicago
BioExplorer.net. (2025, December 29). Eastern Gorilla. Bio Explorer. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/apes/eastern-gorilla/.
BioExplorer.net. "Eastern Gorilla" Bio Explorer, 29 December 2025, https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/apes/eastern-gorilla/.
BioExplorer.net. "Eastern Gorilla" Bio Explorer, December 29 2025. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/apes/eastern-gorilla/.












