
| Animalia | Primates | Hominidae | Pongo | Pongo pygmaeus |

- Common Name: Bornean Orangutan
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1760
- Monkey Size: 97 to 97 cm (38.19 to 58.19 in)
- Skin Color(s): Orange-red
- Habitat: Rainforest
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Native Countries: Indonesia, China
Bornean Orangutan Distribution
Bornean Orangutan Characteristics
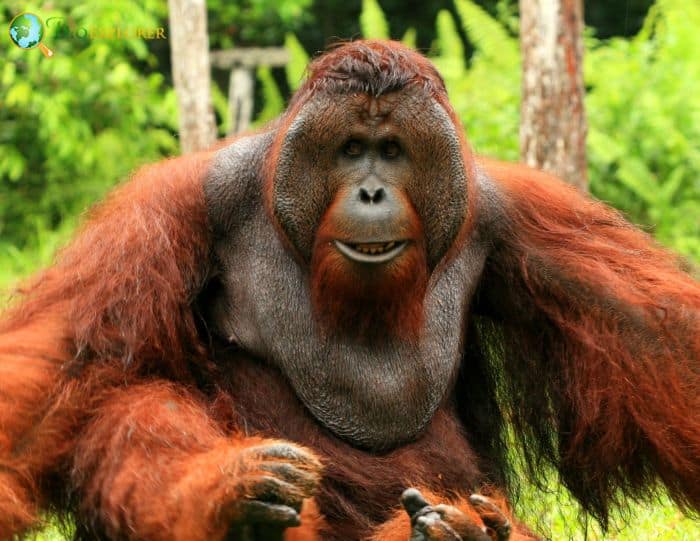

The Bornean orangutan[1] is native to the Borneo Island. Along with Pongo abelii (the Sumatran orangutan) and Pongo tapanuliensis (the Tapanuli orangutan), it belongs to the only genus of great apes endemic to Asia.
- They have thick, shaggy, orange-red hair and long arms, which are beneficial for traveling through the canopy.
- They grasp with their hands and feet, which suits their arboreal life. Unlike most mammals, their fur does not cover their faces.
- However, Bornean orangutans do have facial hair, including beards and whiskers.
- Also, they have sizeable fatty cheek pads called a harness and a drooping throat pouch.
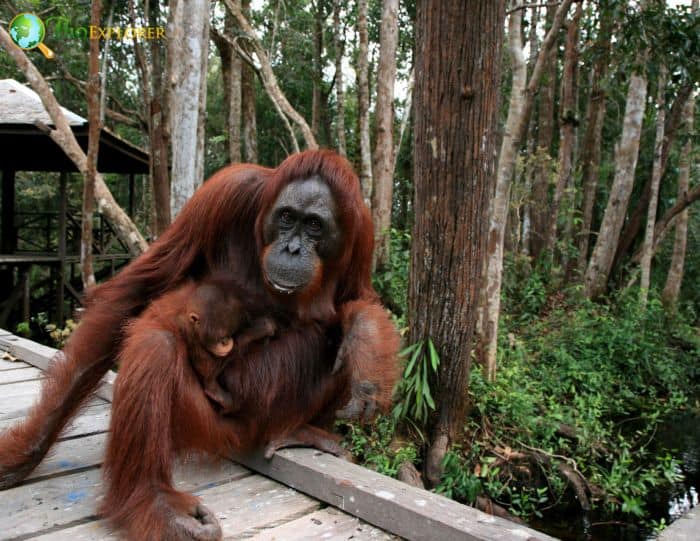

What Do Bornean Orangutans Eat?

The Bornean Orangutan consumes these plant matter[¶]:
- Clustertree (Ficus racemosa)
- Brown-Woolly Fig (Ficus drupacea).
- Pulasan (Nephelium lappaceum)
- Jacareuba (Calophyllum brasiliense)
- Oriental Trema (Trema orientalis).
- Cowa Fruit (Garcinia cowa).
- Ilang-Ilang (Cananga odorata)
- Javanese Treebine (Cissus nodosa).
- Bishopwood (Bischofia javanica)
- Weeping Fig (Ficus benjamina).
- Fig (Ficus)
- Council Tree (Ficus altissima).
- Myrobalan (Terminalia bellirica)
- Argus Pheasant Tree (Dracontomelon dao).
Bornean Orangutan Facts

- Although orangutans are not territorial, adult males exhibit threatening behavior when encountering other males and only socialize with females for mating.
- Like other great apes, orangutans are highly intelligent and display different tools and cultural patterns in the wild. In addition, orangutans share about 97 percent of their DNA with humans.
- The Bornean orangutan is an endangered species whose existence is seriously threatened by deforestation, hunting, and palm oil plantations.
- They travel more on the ground than their Sumatran counterparts despite being arboreal.
- The Bornean orangutan exhibits nesting behavior. Nests are built to be used during the day or at night.
Suggested Reading: Kinds of Apes
Cite This Page
APA7MLA8Chicago
BioExplorer.net. (2025, December 29). Bornean Orangutan. Bio Explorer. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/apes/bornean-orangutan/.
BioExplorer.net. "Bornean Orangutan" Bio Explorer, 29 December 2025, https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/apes/bornean-orangutan/.
BioExplorer.net. "Bornean Orangutan" Bio Explorer, December 29 2025. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/apes/bornean-orangutan/.











