RNA stands for Ribonucleic acid. The RNA is a polymeric molecule which when teamed with proteins and carbohydrates are considered as three essential macromolecules of life. RNA, just like DNA is described as a chain of nucleotides. However, a major difference between a DNA and RNA is its structure. While the DNA exhibits a pair of double-strand, the RNA continues to be a chain of nucleotide with a folded single strand. In the study of biology databases play a big-league role. Hence, RNA databases contribute major information to the study of genes and biological science.
Before delving deep into the subject, it is worth understanding a few crucial terminologies.
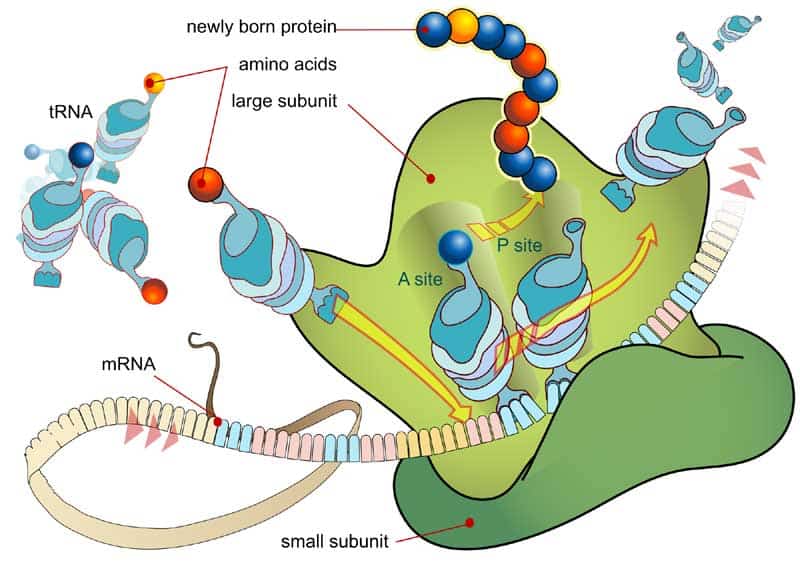
- Messenger RNA – We are pretty much aware that RNA is used for a wide number of biological roles. These include expression of genes, coding and decoding of genes and also regulation of genes. However, the question that arises here is what makes these RNA so functional in nature? This is where the mRNA or the Messenger RNA comes into limelight. Using nitrogenous bases like guanine, adenine, cytosine and uracil, the cellular organisms puts messenger RNA into use to convey important genetic information of a being. The mRNA also facilitates the process of protein synthesis. In this case, the mRNA successfully gathers proteins on ribosome. Further, using procedures of transfer RNA, the molecules drop amino acids onto the ribosome. Ultimately, rRNA or the Ribosomal RNA links along-with the amino acids to create proteins or the building blocks.
- RNA Sequencing – Popularly known as the Whole Transcriptome Shotgun Sequencing or the WTSS, RNA sequencing is a modern technology that puts the processes of next-generation sequencing into use to rack up evidences of RNA presence and their quantity in a genome in the form of snapshots. Performing RNA transcripts in a cell is quite a dynamic process. Other than expanding the nucleobase coverage of a DNA sequence, RNA-Seq transcripts can benefit multiple other functions like gene fusion, alternative gene spliced transcripts, mutations and post-transcriptional modifications. Living organisms when infected undergo varying cellular pathways. The RNA sequencing process maintains records of such changes and stores the information in the form of databases.
Examples of RNA Databases:
- BPS– This database contain experimental information on RNA Base-pair structures.
- Recode– It is a database filled with information about translational recoding events, the RNA molecular weights and DNA conversions.
- Poly A_DB– All details about mammalian polyadenylation is stocked in the Poly A_DB database.
- RefSeq– This is a rich database containing references of 30,900 sequences.

RNACentral.com is a new resource that provides unified access to the ncRNA sequence data supplied by the Expert Databases.
This site contains known RNA secondary structures of any type and organism. The ultimate goal of this database is to incorporate a comprehensive collection of known RNA secondary structures, and to provide the scientific community with simple yet powerful ways of analyzing, searching and updating the proposed database.
NAR Database Summary Paper Category List
Oxford Journals site contains a list of excellent collections of Nucleotide sequence databases, RNA sequence databases, Protein sequence databases, Structure databases, Genomics databases, Metabolic and signaling pathways, Human & other vertebrate genomes, Human genes and diseases, Microarray data & gene expression databases, Protemics resources, Molecular biology databases, Organelle databases, plant databases, Immunological databases and cell biology.
Database of RNA-binding Protein Specificities
This University of Toronto site page provides a database of RNA-binding protein specificities where you can browse by domain such as RNA Recognition Motif, K Homology, CCCH Zinc Finger and more. Also you can browse by species such as Homo Sapiens, Mus Musculus, Drosophila Melanogaster and Caenorhabditis Elegans.
lncRNAdb.org site has a searchable database which provides comprehensive annotations of eukaryotic long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). All entries are manually curated from referenced literature and each entry contains references information about the RNA including: Nucleotide sequences, Genomic context, Gene expression data derived from the Illumina Body Atlas, Structural information, Subcellular localization, Conservation, Function with referenced literature.
The purpose of this database is to provide information on nucleotide sequences of 5S rRNAs and their genes. The sequences for particular organisms can be retrieved as single files using a taxonomic browser or in multiple sequence structural alignments.
GtRDB: The Genomic tRNA Database
This genomic tRNA database contains tRNA identifications made by the program tRNAscan-SE on complete or nearly complete genomes.
Noncoding RNAs Database.
Database of validated primer sets for quantitative PCR.
The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) provides ribosome related data services to the scientific community, including online data analysis, rRNA derived phylogenetic trees, and aligned and annotated rRNA sequences.
RNABase is an annotated database of all publicly available RNA structures.
The European ribosomal RNA database.
Database of siRNA target sequences and other resources for RNA interference studies
Small RNAs are broadly defined as the RNAs not directly involved in protein synthesis. Small RNAs are usually in the 75-400 nucleotides range, although some are as long as thousand base pairs. They are synthesized by either RNA Polymerase I, II or III. The sequences reported here are based on actual sequence determinations and not on the basis of oligonucleotide catalogs.
The RNA modification database provides a comprehensive listing of post transcriptionally modified nucleosides from RNA.
The uRNADB is a tool in the study of the structures and functions of various U RNAs. It provides aligned, annotated and phylogenetically ordered sequences. The alignments of the sequences represent conserved secondary structure elements where each base pair is proven by comparative sequence analysis.
















