
Top Cell Biology News in 2018: The diversity of cells in the world is astounding. A single cell can be both a fully functioning organism or a unit soldier with a specific role.
These complex entities can also act in a variety of ways in our bodies, influencing our overall well being and interacting with each other and the environment.
Modern cell biology intersects with multiple disciplines: computer science, biochemistry, medicine, and genetics, leading us to the ultimate conclusion – creating our very own artificial cell.
Table of Contents
- Top Cell Biology News in 2018
- 1. Producing cellular armor for transplants in diabetes patients.
- 2. New art of making nerve cells.
- 3. Looking inside immune cells-one at a time.
- 4. Stem cells help save feet in diabetic patients.
- 5. A novel approach allows making a 3D map of chromosomes.
- 6. New hope for spine injury sufferers.
- 7. Chinese fungal extract helps heal periodontitis.
- 8. Barcoding the brain cells.
- 9. Novel cell type that controls adipogenesis discovered.
- 10. Linking it all together: a novel multi-omics approach.
- 11. Scientists find more on how CTCs function
- 12. Inflammation helps fight cardiovascular diseases.
- 13. Thermogels for stem cells protection.
- 14. Making pancreatic cells regenerate by themselves.
- 15. Cell biology meets genetics: making new cells from scratch.
Top Cell Biology News in 2018
Here are the top 15 discoveries and breakthroughs in cell biology in 2018.
1. Producing cellular armor for transplants in diabetes patients.
 In type I diabetes, the patient’s own immune system attacks and destroys pancreatic cells.
In type I diabetes, the patient’s own immune system attacks and destroys pancreatic cells.
- These patients require transplantation. However, transplanted cells are bombarded with the immune system the same way the patient’s old cell used to be.
- In order to protect them, a device that encapsulates the implanted stem cells and protects them from the adverse reaction was developed.
- The device can be easily removed after the surgery and is safe for the patient.
![]()
2. New art of making nerve cells.
 Since it has become possible to force differentiated cells to revert to stem cells, the scientists came upon a treasure trove of possibilities.
Since it has become possible to force differentiated cells to revert to stem cells, the scientists came upon a treasure trove of possibilities.
- Autologous induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) are applied to various types of treatment.
- One of the most critical application is the treatment of nerve injuries and traumas. Novel protocols lead to induction of all known types of nerve cells, including neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglial cells.
- Nerve cells are now potentially replaceable!
![]()
3. Looking inside immune cells-one at a time.
 Adaptive immune cells have been unique, for they rearrange their own genes to make highly specific receptors to antigens.
Adaptive immune cells have been unique, for they rearrange their own genes to make highly specific receptors to antigens.
- In the course of immune response, very diverse immune cells are involved.
- Potentially, there can be multiple lymphocyte clones, and each one would be specifically reacting to a specific epitope.
- Single cell genomics enables scientists to grasp this incredible diversity. By sequencing each cell separately, one can find the role even of the smallest actor in the complex play of fighting against invasions of pathogens.
![]()
4. Stem cells help save feet in diabetic patients.
 One of the most debilitating complications of type 2 diabetes is diabetic foot ulcer.
One of the most debilitating complications of type 2 diabetes is diabetic foot ulcer.
- This condition often results in unavoidable amputation of the affected limb.
- It is now possible to use stems cells to promote wound healing and restoration in the affected foot, preventing the need for amputation.
![]()
5. A novel approach allows making a 3D map of chromosomes.
 Cells have a much more complex structure than we usually see in textbooks.
Cells have a much more complex structure than we usually see in textbooks.
- For instance, the inner structures of the nucleus are known to be organized in a sophisticated way that is a part of epigenetic control of gene expression.
- A novel technique called SNP-CLING combines CRISPR with the determination of the position of gene loci.
- It allows the researchers not only find the changes in the sequences but also to image the location of different alleles within the nucleus.
![]()
6. New hope for spine injury sufferers.
 Recent successful experiments on animals have shown that stem cell therapy can help in the restoration of the spinal cord injuries.
Recent successful experiments on animals have shown that stem cell therapy can help in the restoration of the spinal cord injuries.
- Stem cell therapies for spinal trauma are successfully transitioning to trials on human patients at present.
- Though the specialists do not expect stem cell implantation to provide a complete cure for their patients, there is a strong possibility that stem cell therapy combined with nanotechnology and physical rehabilitation therapy can bring significant relief to individuals that have suffered from the trauma of this type.
![]()
7. Chinese fungal extract helps heal periodontitis.
 Traditional Chinese herbs are now getting scientific backup.
Traditional Chinese herbs are now getting scientific backup.
- For instance, Coptidis rhizome – a preparation made from dried Coptis spp. Fungus native to China was praised for its assistance in wound healing and infectious diseases.
- It was proven that in cell culture of periodontal ligament stem cells Coptis rhizome extract does have a proven beneficial effect – it promotes stem cells differentiation into periodontal bone cells.
- This treatment is possible due to the active component of this fungal extract – berberine. Hopefully, berberine would become a novel remedy for periodontitis.
![]()
8. Barcoding the brain cells.
 During development, multiple lineages of brain cells emerge and disappear.
During development, multiple lineages of brain cells emerge and disappear.
- In order to understand how our brains, work, it is crucial to reconstruct the complex relationships between them.
- For that purpose, a novel method called single cell GESTALT was developed.
- The approach involves RNA sequencing of multiple cell types at the same time.
- Each cell is associated with a so-called barcode detected with the help of CRISPR-CAS9 technology.
- Testing the new approach in juvenile zebrafish has revealed more than 100 cell types present in the course of the CNS development.
![]()
9. Novel cell type that controls adipogenesis discovered.
 It was discovered that adipose tissue development is controlled by three distinct types of specific stem cells.
It was discovered that adipose tissue development is controlled by three distinct types of specific stem cells.
- While the first two types were responsible for adipocyte differentiation, the third type had unusual properties.
- Not only these cells do not develop into mature adipocytes; they prevented their neighboring cells from doing so.
- The protein these cells produce supposedly has inhibitory properties and requires further research.
- This discovery potentially opens a new field of research aimed at overcoming obesity.
![]()
10. Linking it all together: a novel multi-omics approach.
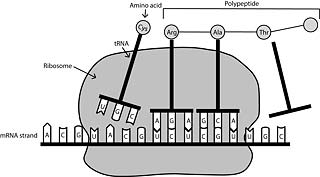 Many processes are going on in the cell namely transcription, translation, protein synthesis and metabolic cascades.
Many processes are going on in the cell namely transcription, translation, protein synthesis and metabolic cascades.
- Previously, each process was studied separately. However, when it has become possible to measure a particular cluster of processes in a single cell in real time and to use modern computers and statistical programs that assess enormous amounts of data, a new approach has become possible: multi-omics.
- Multi-omics techniques allow measuring the whole cell genome, chromatin structure, transcriptome and proteome of the single cell at the same time.
![]()
11. Scientists find more on how CTCs function
 It has been firmly established that a high quantity of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) is a risk factor of cancer metastasis development.
It has been firmly established that a high quantity of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) is a risk factor of cancer metastasis development.
- However, it is still unclear what makes a CTC robust enough to become a metastatic “seed“.
- Recent functional medicine studies are now providing specialists with insights into CTC biology and help them understand how they function.
![]()
12. Inflammation helps fight cardiovascular diseases.
 Inflammatory cells contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Inflammatory cells contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases.
- It is crucial to differentiate potentially harmful subsets and understand how they function.
- Novel sequencing technologies allow the determination of potentially pathological immune cells, especially subsets of monocytes and macrophages.
- The researchers hope that by looking into interactions between the cell types with different properties and mutations, they would find new insights into cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment.
![]()
13. Thermogels for stem cells protection.
 In many cases, scaffolds are crucial for successful tissue cultures. One of the ways to build them is using thermogels.
In many cases, scaffolds are crucial for successful tissue cultures. One of the ways to build them is using thermogels.
- Their structure can be very similar to the extracellular matrix, and it is also possible to create cultures in 3D using them.
- Thermogels are also good encapsulators, protecting the stem cells within from adverse factors such as higher temperature or free radicals.
- This combination of scaffolding and encapsulation makes possible effective transplantation of stem cell cultures into organs, where the gels can adapt to any shape.
![]()
14. Making pancreatic cells regenerate by themselves.
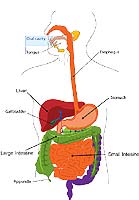 Cell transplantation is one of the options when β pancreatic cells are damaged.
Cell transplantation is one of the options when β pancreatic cells are damaged.
- However, this method requires surgery and possible immune suppression treatment.
- Specialists suggest another way: inducing development of new β pancreatic cells from neighboring ones through trans-differentiation or activating stem cell progenitors located in the pancreas.
- Both approaches have already been proven successful in preclinical studies.
![]()
15. Cell biology meets genetics: making new cells from scratch.
 Advances in genetics and synthetic biology have led to the creation of simple artificial genetic circuits.
Advances in genetics and synthetic biology have led to the creation of simple artificial genetic circuits.
- Now everything is ready for the next step: design of large-scale genetic circuits that perform crucial biological functions.
- Such circuits could potentially have application in all disciplines, from regenerative and transplantation medicine to environmental science.
![]()
Modern cell biology unites all the scientific and clinical fields, and next year discoveries, hopefully, would contribute even more to our knowledge how multicellular organisms’ function.
![]()

















Congratulations Coz New Ideas Are Upcoming So Lets Move Forward