
Biotechnology is the branch of biology that harnesses cellular and biomolecular processes to develop technologies and products that help enrich our lives and the well-being of our planet. In this article, we will explore the top 10 biotechnology news in 2017.
Table of Contents
- Top 10 Biotechnology News In 2017
- Clostridium botulinum’s Neurotoxin Role in Therapy
- New Study On Microbial Signal Recognition Systems
- Study Finds Prohibitin Protein Aids Virus In HFM Disease
- Plant’s Internal Clock Gets Regulated By A Protein
- Scientists Discover Nettles & Ants Help In Destroying Cancer Cells
- A breakthrough Study In Tissue Engineering
- Researchers Find Gut Bacteria Help Body Fight Off Infection
- Plant Protein SOBER1 Helps Plants From Infection
- Adeno-Associated Viruses Deliver Nanopeptide Drugs In Cells
- Bacterium’s Role in Destruction of Melanoma Cells
Top 10 Biotechnology News In 2017
Clostridium botulinum’s Neurotoxin Role in Therapy

Researchers at the Quadram institute have discovered genes that encode a new version of the botulinum neurotoxin produced by bacteria Clostridium botulinum. This toxin is known to be deadly, causing neuroparalysis once ingested. It is also used for medical and cosmetic procedures. The potency of this new toxin and its role in therapy is yet to be determined and quantified.
![]()
New Study On Microbial Signal Recognition Systems
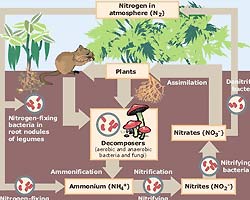
A recent study published in Nature Communications has provided insight on microbial signal recognition systems. The findings from the study shed light on a protein that enables microorganisms to absorb ammonium from their environment as a nutrient and energy source.
![]()
Study Finds Prohibitin Protein Aids Virus In HFM Disease
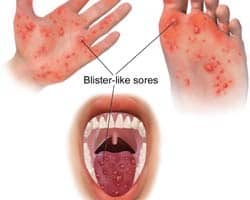
Scientists at the University of Singapore have discovered a protein called prohibitin that seems to aid neuronal infection by the virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease. Although the mechanism behind the infection is still unclear, researchers were able to elucidate the role this protein plays in aiding the virus.
![]()
Plant’s Internal Clock Gets Regulated By A Protein

Researchers at the Centre for Research in Agricultural Genomics have discovered how a protein involved in regulating the internal clock of the plant, sets the pace of plant growth throughout the day, thus ensuring that plant growth is limited until the end of the day. Findings from this study can help look at how plants regulate their growth under stressful conditions like high temperature and drought.
![]()
Scientists Discover Nettles & Ants Help In Destroying Cancer Cells

Scientists at the University of Warwick have discovered that a substance found in stinging nettles and ants can be used to destroy cancer cells. This compound is organic osmium based which gets activated by the non-toxic form of sodium formate. Sodium formate is the substance found in stinging nettles and ants.
![]()
A breakthrough Study In Tissue Engineering
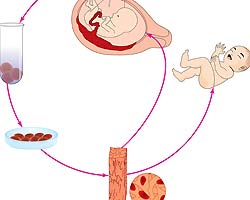
A recent study published in Nature Communications, led by a team of researchers at the Duke University, has shown promise and potential in the field of tissue engineering. Scientists were successfully able to grow functional human muscle cells from non-muscle cells. This discovery can make genome editing and cellular therapies easier.
![]()
Researchers Find Gut Bacteria Help Body Fight Off Infection
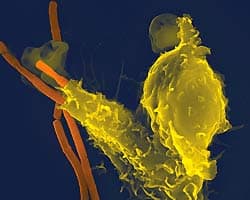
Researchers at the Babraham Institute have elucidated the mechanism by which gut or intestinal bacteria can control the genes in our cells. Upon digestion of fruits and vegetables in the gut by intestinal bacteria, certain chemical signals are released that can alter chemical markers across the human genome. This mechanism is thought to help the body fight off infection and cancer.
![]()
Plant Protein SOBER1 Helps Plants From Infection

Scientists at the Salk Institute have characterized different, unusual immune responses that plants display in response to infection. The team of researchers studied a specific protein called SOBER1, found in plants which seems to confer resistance to plants from infection.
![]()
Adeno-Associated Viruses Deliver Nanopeptide Drugs In Cells
A team of researchers at Rice University have successfully created adeno-associated viruses that can be programmed to deliver nanopeptide drugs into the cell. To make this possible, researchers created small versions of a specific protein found on the surface of the viral capsid of adeno-associated viruses.
![]()
Bacterium’s Role in Destruction of Melanoma Cells
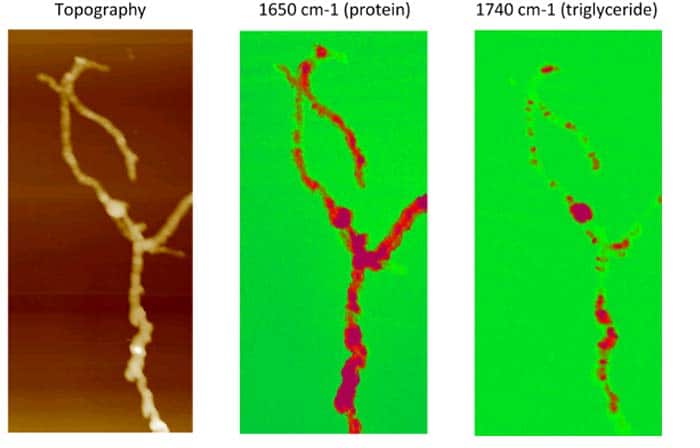

Scientists at the Oregon State University recently discovered the role of a bacterium that lives in the soil, in the destruction of melanoma cells. This bacterium produces a type of molecule that is a secondary metabolite and is naturally produced. The metabolite, known as mensacarcin, targets the mitochondria of melanoma cells. It has powerful anti-cancer and anti-proliferative effects, specifically against melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer.
![]()
















