These topics highlight the discoveries and innovations in ecology in 2022; the previous 2021 marks nature-based climate change solutions, carbon solutions towards climate change, and more. In 2022 paves the way towards discoveries in ecological consequences influenced by genetic factors, climate change in marine habitat, coral reefs, and plants having great adaptability to climate change, and the necessity towards conservation of biodiversity. Let’s glimpse research findings in this field with broader perspectives.
Table of Contents
- 1. Researchers discover how genetic factors simultaneously influence ecological consequences in species that interact (USA, Sept 2022)
- 2. According to a study, ecological systems are more frequently chaotic than previously believed (USA, June 2022)
- 3. Cellular mechanisms clarify biological distinctions between species and aid in our understanding of their evolution (Finland, Nov 2022)
- 4. Researchers claim that rewilding landscapes can help to restore ecosystems and provide high-welfare, high-quality food (UK, Sep 2022)
- 5. According to scientists, changes in marine habitats are not being noticed (Australia, Sep 2022)
- Explore 15 Remarkable Adaptations of Ocean Inhabitants
- 6. Scientists discovered that animal illness outbreaks brought on by humans have cascading ecological repercussions (USA, Mar 2022)
- 7. In Arctic Epishelf Lake, which is threatened by climate change, microbiologists research enormous viruses (USA, Aug 2022)
- 8. For the benefit of your cats’ health and the environment, keep your cats inside, suggests new research (USA, Nov 2022)
- 9. If given a chance to develop, coral reefs can adapt to climate change, claims research (USA, Sep 2022)
- 10. According to research, at least 44% of Earth’s land needs to be conserved to preserve biodiversity and ecosystem services (USA, June 2022)
- 11. Researchers have discovered more than 1,500 genes responsible for insect migration (UK, July 2022)
- 12. The world’s largest fish, the whale shark, may now be categorized as the largest omnivore according to marine experts (Australia, July 2022)
- 13. Scientists contend that shallow-water mining is not a viable substitute for deep-water mining (USA, Sep 2022)
- 14. Researchers discovered that a rare species of monkey had modified its food and level of activity to cope with life in a fragmented forest (USA, Mar 2022)
- 15. Using “chemically encoded” enzymes, a new study demonstrates that plants can modify their lignin to adapt to climate change (Sweden, Dec 2022)
- Conclusion
1. Researchers discover how genetic factors simultaneously influence ecological consequences in species that interact (USA, Sept 2022)

It’s not always apparent whether a result of an encounter, like whether a bacterium may infect a host, applies to all species members or depends on the individual genetics of the people involved. Researchers close this knowledge gap through a series of tests by utilizing the Melissa blue butterfly’s most recent host-range extension of lucerne.
- The variety of interactions between species, not the number of species, makes up the majority of the diversity of life.
- Researchers discovered that roughly half of the variation in caterpillar development and survival could be attributed to genetic variations among Melissa blue caterpillars and lucerne plants.
- The findings imply that individual variation matters and that numerous genes, most of which have additive or independent effects, contribute to the outcome of this plant-insect interaction.
- Moreover, variations in lucerne plant genetics have predictable impacts on caterpillar growth in numerous butterfly populations and species.
- The team’s findings, supported by comprehensive data gathered over several years at field plots in Utah and Nevada, are consistent with the idea that plant and insect genotypes affect caterpillar growth and survival roughly in equal measure.
Genetic variation within species may be crucial for other host-parasite interactions, aside from problems specific to insects and the plants that serve as their hosts. For instance, genetic variation in hosts and among pathogen strains affects how susceptible humans and other animals are to parasitic diseases. However, it is still unknown whether this theory is applicable generally.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Ecology News of 2020
2. According to a study, ecological systems are more frequently chaotic than previously believed (USA, June 2022)

A new analysis suggests that chaos in natural populations is significantly more frequent than previously thought. Ecologists frequently debate whether population variations in natural ecosystems are regular (changing around a supposedly “stable” equilibrium), random (totally unpredictable), or chaotic.
- Almost 30% of the populations in an ecological database examined showed signs of chaotic dynamics. In previous meta-analyses that looked at its occurrence, chaos was found absent or infrequent in natural field populations.
- The researchers used fresh and improved chaos detection algorithms for the new study and rigorously tested them on simulated data sets. They then used a 172 population time series dataset from the World Population Dynamics Database to apply the three most effective techniques.
- Interesting correlations between chaotic dynamics, lifespan, and body size were found through investigation. Plankton and insects had the highest levels of chaos, whereas birds and mammals showed the lowest levels, and fish exhibited a middle level of chaos.
- This demonstrates that many short-lived organisms frequently exhibit chaotic population dynamics, and these species also frequently exhibit boom-and-bust dynamics.
- The findings warn against using equilibrium-based approaches to conservation and management, particularly for short-lived species, and show that ecological forecasting may have inherent limitations.
We need to acknowledge the existence of chaos to avoid missing out on opportunities to foresee events in the short-term using techniques designed for chaotic systems and overestimating our capacity to predict events in the long run. For instance, this would enable us to forecast fish populations and establish harvest limits for fisheries.
Suggested Reading:
Explore Ecological Pyramid: 3 Major Types and Limitations
3. Cellular mechanisms clarify biological distinctions between species and aid in our understanding of their evolution (Finland, Nov 2022)
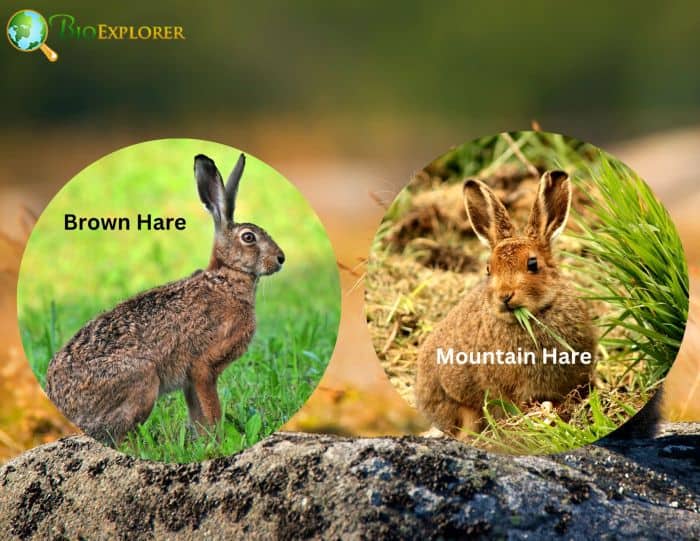

Researchers have thoroughly analyzed the relevance of species variations for the most important cell maintenance systems to comprehend evolution better. The mountain hare (Lepus timidus) and the brown hare (Lepus europaeus) served as the study’s model organisms.
- About 3 million years ago, the evolutionary lineages split between the mountain hare and brown hare. The mountain hare originated in the Beringian region, and the Americas and the Far East are home to its closest relatives.
- The mountain hare arrived in Europe before its time, settling there during the Ice Age. It continues to have a remarkable, uninterrupted spread from the Nordic nations to far-eastern Siberia.
- Four brown hare cell lines and four mountain hare cell lines were used for the investigation, and the researchers found significant variations in regulating numerous gene families. Several of these contributed to brown hare cells increasing more quickly than mountain hare cells, which was connected with the age and maturity of the species.
- The changes in cell cycle regulation may also cause variations in cell proliferation. Together with cell cycle control, there were disparities in energy metabolism, which show how the two species invest different amounts of resources in different aspects of their fundamental cell functions.
- The aging and reproduction of the two species are expected to exhibit the same disparities in resource investment.
The research contributes to our understanding of how genetic variations translate into adaptive phenotypic variations between species, how variations in life cycle strategies appear at the cellular level, and how species boundaries may form at the molecular level. The study of aging, metabolic illnesses, and human ancestry hybridization can all benefit from some of the findings from the hair cells.
Suggested Reading:
Cellular Organization: Exploring The Cell
4. Researchers claim that rewilding landscapes can help to restore ecosystems and provide high-welfare, high-quality food (UK, Sep 2022)

According to the researchers, agricultural rewilding can help ease worries about how rewilding will affect livelihoods and generate “win-win ” outcomes for both the ecosystem and people.
- Agricultural rewilding refers to recovering ecosystems through importing, managing, and producing livestock using domestic species as the equivalents of their wild counterparts (usually hardy, native breeds).
- Rewilding traditionally aims to lessen or eliminate human influence in a landscape to repair ecosystems that have been degraded.
- Through active human involvement in landscapes, the restoration of ecosystems, and the creation of financially and environmentally viable lifestyles, agricultural rewilding offers the possibility of win-win scenarios.
- Unlike more intense agriculture, extensive farming as part of agricultural rewilding allows animals to be raised under naturalistic conditions and in line with strict welfare standards.
- Domestic livestock can be part of the landscape, restoring biodiversity and regenerating ecosystem function while still assisting in agricultural production, provided that their lives are lived by high welfare and environmental standards and that their deaths result in high-quality meat.
- This helps promote food self-sufficiency and reduces food production outsourcing to systems with greater environmental impacts.
Since agricultural rewilding can produce and preserve habitats that may be lost in “hands-off” rewilding approaches and whose loss would pose a hazard to habitat-specialist species, it has the potential to boost biodiversity more than conventional rewilding.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Discoveries in Ecology 2019
5. According to scientists, changes in marine habitats are not being noticed (Australia, Sep 2022)

The consequences of ocean acidification cannot be detected in great detail by the methods currently used to calculate biodiversity dynamics. According to studies, biological communities in our oceans may still be reorganized even when measurements for biodiversity show little or no change.
- The team examined studies on how species populations near volcanic CO2 vents beneath the sea and in lab mesocosms react to climatic changes.
- In addition to 23 studies conducted in outdoor experimental settings or laboratories, they analyzed 58 papers that looked at communities in various temperate reefs, coral reefs, and seagrass beds.
- Marine animals are directly impacted by climate change brought on by human activities. It modifies species connections, abundance, diversity, distribution, eating habits, development, and breeding.
- One of the most frequently held notions is that global marine biodiversity will change due to climate change.
- Because new species replace lost ones, commonly employed biodiversity measurements miss the reorganization of marine communities brought on by ocean acidification. Even under severe habitat loss, there is little to no change in biodiversity when another replaces one community of marine species.
Several of the important ecosystems in the world, such as coral reefs and kelp forests, suffer long-term consequences due to rising water temperatures. Instead of looking for indications of habitat loss or biodiversity loss per se, future predictions of ecosystem change and stability should concentrate on spotting species replacements and changes to species abundance.
Suggested Reading:
Explore 15 Remarkable Adaptations of Ocean Inhabitants
6. Scientists discovered that animal illness outbreaks brought on by humans have cascading ecological repercussions (USA, Mar 2022)
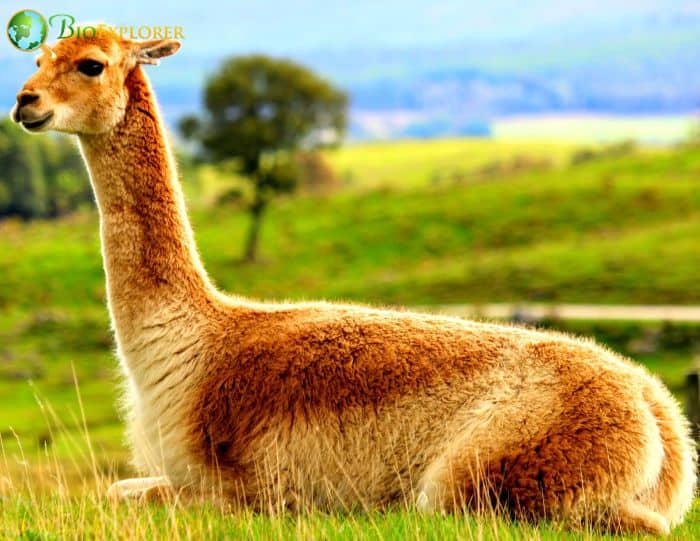

According to a recent study, a mange outbreak that killed vicunas in a protected area in the Argentine Andes had particular implications on the area’s ecology. The published study is distinctive in that it followed the cascade consequences of the vicunas’ deaths from the disease on the environment and biodiversity in the area. Vicunas are wild South American camelids.
- The research team found that the impact of vicuna deaths due to disease was very different from vicuna deaths due to puma predation.
- They were able to trace the shift in ecosystem function from one where pumas served as the top predator to one where this disease predominated and conclude that they are not similar, which makes what they discovered so unique.
- The results had radically different consequences based on whatever source of death, for these vicunas were the dominant ones. The mange deaths caused increased vegetation and decreased condor populations, which feed on vicuna carcasses killed by pumas in the national park.
- The spread of diseases between domestic and wild animals can have disastrous effects on both parties, endangering local livelihoods and impairing natural processes in protected regions. Disease-dominated trophic cascades could eventually replace predators as the dominant top-down drivers in some systems as land use alteration and fragmentation continue to increase interactions between domestic and wild animals.
- According to the research, domestic llamas released outside the park were responsible for the mange outbreak.
- The study emphasizes the necessity of preparing for additional effects of human-induced epidemics of wildlife diseases and how it affects conservation. The study demonstrated how a large-scale disease outbreak could destabilize a persistent ecosystem.
To conserve ecosystems supported by intricately interconnected food webs and preserve human health and livelihoods, it will be essential to develop techniques for human-wildlife coexistence and protected area management that reduce the exchange and spread of disease.
Suggested Reading:
15 Leading Ecology News of 2018
7. In Arctic Epishelf Lake, which is threatened by climate change, microbiologists research enormous viruses (USA, Aug 2022)

The Milne Fiord Epishelf Lake is a rare freshwater lake that floats over the Arctic Ocean near the North Pole. Single-celled organisms, particularly cyanobacteria, predominate in the lake and are regularly infected by strange gigantic viruses. Scientists have made the initial estimate of the virus density in this lake.
- To identify the viruses and bacteria in the lake water, the study team took water samples and sequenced every piece of DNA.
- The research lays the groundwork for greater comprehension of viral ecology across various global habitats, notably in the high Arctic. The findings demonstrate the distinction between the viral population in the freshwater lake and the marine fiord water, especially in the halocline community.
- The halocline is a region where salinity rapidly decreases as the water column is raised. This ecosystem provides habitats for viruses and hosts not present in freshwater or uniformly salinity marine layers. The researchers claim that viruses likely play a significant role in biomass turnover because of the high bacterial richness and potential prevalence of the lytic lifestyle at this depth.
- The term “lytic lifestyle ” describes how daughter virus particles are released while the host microbial cell is obliterated. The Milne Fiord Epishelf Lake had several significant changes, but the most notable was a multiyear fall in cyanobacteria quantity.
- As cyanobacteria are extremely rare in the Arctic Ocean, the researchers blamed the decline on the growing marine influence in the freshwater lake.
The amount of time left for microbiologists to fully understand the biodiversity and biogeochemical cycles of these ice-dependent habitats, as well as the effects of the quick, irreversible changes in temperature, is rapidly decreasing due to rapidly rising temperatures. Every year, the ice shelf holding the lake in place deteriorates, and when it disintegrates, the lake will disappear into the Arctic Ocean.
Suggested Reading:
Top 15 Famous Marine Biologists
8. For the benefit of your cats’ health and the environment, keep your cats inside, suggests new research (USA, Nov 2022)
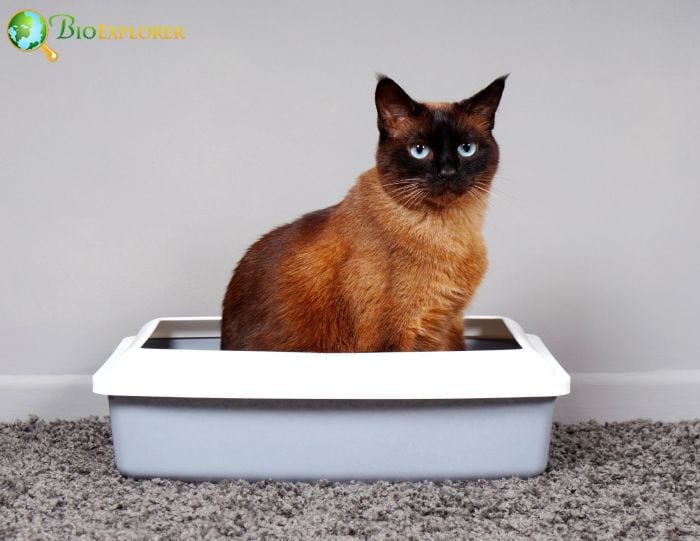

According to recent research, people who let their cats outside put them at significant risk of contracting and spreading disease, as well as causing a decline in the populations of native animals and the health of the ecosystem as a whole. According to the study, humans are mostly responsible for reducing these dangers by keeping cats indoors.
- Data from a survey in Washington, D.C., where 60 motion-activated wildlife cameras were placed across 1,500 sample sites, were used in the study’s analysis.
- The cameras documented the prey the cats consumed. They showed how they interacted with local animals, assisting researchers in understanding why cats and other wildlife are present in certain places but not others.
- The average domestic cat in Washington D.C., has a 61% likelihood of sharing an area with raccoons, the country’s most active rabies vector, a 61% spatial overlap with red foxes, and a 56% spatial overlap with Virginia opossums, both of which are rabies carriers.
- Outdoor cats endanger local wildlife and the possibility of exposure to illnesses that they could later transmit indoors to the people in their families (such as rabies and toxoplasmosis).
- The study showed that cats with outdoor access also interact with and hunt other small native animals, such as grey squirrels, chipmunks, cottontail rabbits, groundhogs, and white-footed mice, as well as share the same habitats. Cats can limit biodiversity and worsen ecological health by hunting these creatures.
These habitat correlations imply that human activity, rather than natural forces, is the primary driver of cat dispersal. Humans strongly impact where cats are found on the landscape, which means that they also control the level of risk these cats face and the damage they do to nearby wildlife.
Suggested Reading:
Top 15 Wildlife Biology Degree Programs In The USA
9. If given a chance to develop, coral reefs can adapt to climate change, claims research (USA, Sep 2022)
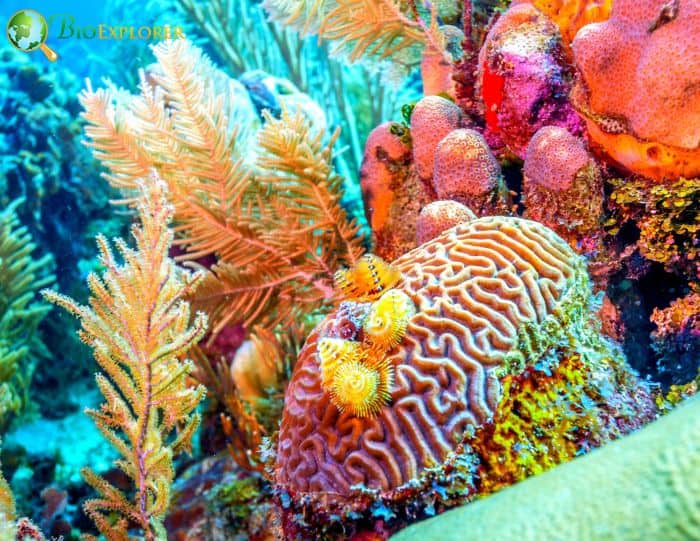

Without coordinated efforts to safeguard them, scientists predict that 99% of coral reefs will be gone by the end of this century. According to a recent study, coral reefs can modify and adapt to the consequences of climate change, but only if we preserve enough different coral reefs, especially those that are temperature-sensitive.
- Corals that have already adapted to new environmental conditions reproduce with corals that have not yet undergone the same process of evolution.
- For corals in hotter seas to breed and transmit their heat tolerance to other coral reef areas, we must maintain them healthy and protected as ocean temperatures rise.
- The study suggested that coral reef ecosystems may rebound over the next century and thrive if humanity takes quick and effective action to maintain coral reef health at local scales and addresses climate change.
- The nicest thing about these findings is that they highlight the significance of our local activities; we don’t have to stand by and let coral reefs suffer due to climate change.
We absolutely cannot allow coral reefs to disappear. If we don’t take action to safeguard coral reefs, we will be confronted with global economic, humanitarian, and biodiversity catastrophes.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Ecology News in 2017
10. According to research, at least 44% of Earth’s land needs to be conserved to preserve biodiversity and ecosystem services (USA, June 2022)

According to the study, we must save enough land to halt biodiversity disasters. In essence, it is a global conservation strategy.
- The study reveals that conservation efforts are needed to protect biodiversity on 44% of Earth’s terrestrial surface.
- Using cutting-edge geospatial techniques, the group mapped the world’s best locations for preserving terrestrial species and ecosystems. They employed spatially detailed land-use scenarios to determine how much of this area will be at risk from habitation by 2030.
- The amount of land that needs to be preserved to halt the biodiversity problem is currently best estimated by our study.
- It is an airplane conservation strategy. We must move quickly, the study demonstrates. The simulations indicate that by 2030, the habitat of more than 1.3 million km2 of this significant land-an area larger than South Africa-will likely be removed for human uses, which would be disastrous for wildlife.
- The work has significant policy implications since nations are presently negotiating a post-2020 global biodiversity framework under the Convention on Biological Diversity, with new goals and targets that should go into force later this year.
- Governments will be required to report on their progress towards these goals regularly, and this will shape the conservation agenda for at least the ensuing ten years.
Even though this is a fantastic beginning in the right direction, the study contends that more ambitious objectives and regulations are needed to protect ecological integrity above and beyond the 30% target. Nations must quickly increase their conservation efforts in scope, intensity, and efficacy if they are serious about preserving the biodiversity and ecosystem services that support life on Earth.
Suggested Reading:
Biological Weathering 101
11. Researchers have discovered more than 1,500 genes responsible for insect migration (UK, July 2022)

Millions of migratory hoverflies depart from northern Europe and travel far south every autumn. Scientists have discovered more than 1,500 genetic variations between these migratory and non-migratory hoverflies.
- The scientists read active genes in migratory insects as they flew across a mountain pass to establish which genes control migratory behavior. The genetic data was then compared to summer hoverflies that don’t migrate.
- They discovered 1,543 genes whose levels of activation varied in the migrants. Finding genes for metabolism was expected because migration is a very energy-intensive process.
- Still, we also discovered genes involved in muscle construction and function, hormonal regulation of physiology, immunity, stress tolerance, flight and feeding behavior, sensory perception, and extending life.
- When the scientists began classifying these genes based on their functions, they found that groups of genes were being activated simultaneously, including insulin signaling for longevity, immunity pathways, and pathways leading to the production of octopamine, the insect version of the hormone adrenaline needed for long-distance flight.
- Evolution has altered and integrated these pathways to enable long-distance travel in migratory hoverflies.
The study offers an effective genetic resource and a conceptual framework for future research on migration development. According to the research, a shared “migratory gene package” that regulates migration in other animals may exist, which has already identified several genes previously linked to migration in butterflies.
Suggested Reading:
Top 21 Facts About Blue Morpho Butterfly
12. The world’s largest fish, the whale shark, may now be categorized as the largest omnivore according to marine experts (Australia, July 2022)
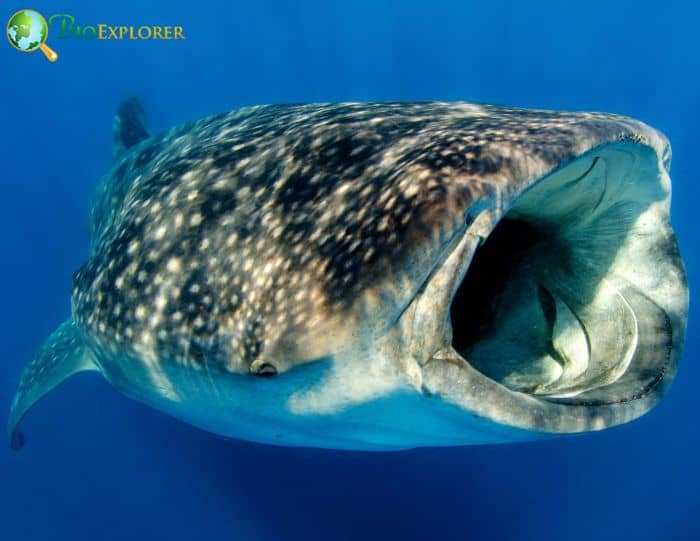

Filter feeders, whale sharks have long been seen consuming krill at Western Australia’s Ningaloo Reef. However, scientists found that whale sharks in the reef consumed a lot of plant matter when examining animal biopsy samples.
- The researchers gathered samples of potential food sources at the reef, ranging in size from tiny plankton to giant seaweed, to determine precisely what the whale sharks were consuming.
- Next, they compared the amino and fatty acids in the whale sharks to those in the plankton and plant matter.
- Compounds discovered in Sargassum, a common brown seaweed at Ningaloo that breaks off the reef and floats at the surface, were present in the whale shark tissue.
- It is believed that throughout development, whale sharks have developed the capacity to digest part of the sargassum that enters their digestive tracts.
- The fact that whale sharks travel to Ningaloo solely to feed on these little krill is only partially accurate. They are out there eating some algae as well.
The discovery makes whale sharks, measuring up to 18 meters long, the largest omnivorous globally. The largest creatures on land have always been herbivores. It has long been believed that in the water, larger animals, such as whales and whale sharks, eat smaller fish and creatures like shrimp, which are higher on the food chain. According to the findings, the evolution systems on land and water aren’t all that dissimilar.
Suggested Reading:
What Do Killer Whales Eat?
13. Scientists contend that shallow-water mining is not a viable substitute for deep-water mining (USA, Sep 2022)

Although projects have been planned for Mexico, New Zealand, and Sweden, as well as shallow-water mining operations in Namibia and Indonesia, their consequences still need to be adequately analyzed.
- According to scientists, shallow-water mining requires a more thorough environmental assessment before it can be deemed sustainable and safe.
- The experts questioned the claim that the mining, which occurs at depths of less than 200 meters, is less harmful than mining on land and less dangerous than mining in poorly studied deep-water environments.
- Large volumes of silt must be dredged to extract valuable elements like gold, cobalt, copper, and phosphorites from the shallow ocean floor.
- The organisms that live in this silt, which takes thousands of years to build up, must also be removed. The researchers issue a warning that the loss of habitat and inhabitants will result in a decrease in biodiversity.
There are no socioeconomic or environmental arguments in favor of shallow-water mining because there are no objective assessments of the ecological effects of various mining processes.
Suggested Reading:
What Is Biological Magnification?
14. Researchers discovered that a rare species of monkey had modified its food and level of activity to cope with life in a fragmented forest (USA, Mar 2022)
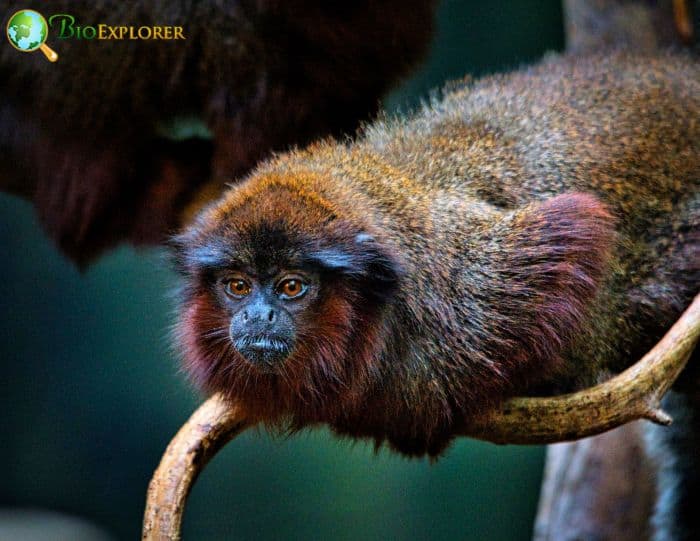

A group of researchers has discovered that a rare monkey species in Bolivia has learned to survive in a fragmented forest by reducing its activity and eating less during times of scarcity.
- The Olalla’s titi monkey (Plecturocebus Molalla), according to the research team, uses a strategy to conserve energy and minimize its use of space, which may allow it to live in a forest-savanna environment in the southwest corner of the Llanos de Moxos, the largest wetland in the Amazon.
- The researchers also saw a change in nutrition during the dry season, moving away from fruits and towards alternate meals, including seeds, lichens, and fungi.
- The monkeys also curtailed their mobility rather than increasing it while they searched for fruits and other higher-quality foods.
- According to the study, the range-restricted populations of these endemic and critically endangered primates are at serious risk from deforestation and growing range fragmentation, which must be addressed.
Given the growing deforestation and loss of forests in the research region, the study highlights the importance of knowing primate ecological flexibility in response to food shortages to create conservation efforts.
Suggested Reading:
Types of Rainforest Monkeys
15. Using “chemically encoded” enzymes, a new study demonstrates that plants can modify their lignin to adapt to climate change (Sweden, Dec 2022)

According to a recent study, plants use diverse combinations of the enzymes LACCASEs to build distinct lignin chemistries that allow them to grow tall and withstand climate fluctuations.
- Lignin stores around 30% of the planet’s total carbon, making it a significant environmental carbon sink. Thanks to it, plants may hydrate and grow to incredible heights of up to 100 meters.
- Various lignin chemistries modify the mechanical strength and waterproofing at the cellular level to assist plant development and survival.
- Researchers have shown that lignin contains a chemical “code” modified at the cellular level to serve various plant functions.
- The researchers demonstrated that several enzymes known as LACCASEs are utilized by each cell to modify its lignin “chemical code” to withstand challenges like drought or wind.
- The research demonstrates how each plant cell’s lignin is spatially regulated at the nanoscale scale. The process that enables plants to grow, hydrate, and withstand the pressures of climate change is ultimately the management of lignin chemistry at the cellular level.
The research could help farmers and foresters choose plants whose lignin composition will make them more resilient to changing climates. With the help of these findings, it will be possible to pick plants based on their lignin codes and increase the resilience of crops and trees to water scarcity issues.
Suggested Reading:
Are Enzymes Proteins?
Conclusion
This series of ecology news gives us a detailed overview of the recent development in this field. We are commencing with genetic variation based on ecological findings, chaotic relationship in ecological outcomes in nature, sustainable growth in living beings with vast ecological adaptability found in reefs and plants, new relevance of disease outbreaks due to climate change and habitat fragmentation, and awareness in terms of biodiversity conservation. With these developments as the foundation, we expect more exciting findings in 2023.
![]()