Last year’s 2021 biotechnological news dealt with cell-free vaccines, GMO yeast for rectifying metabolic disorders, synthetic biology, and more. The 2022 biotechnological innovations paved the way for stem cell therapies, cannabinoid trichomes’ roles in plant defense mechanisms, inventory methods to utilize human waste, the role of quick mRNA vaccines, therapeutic gene editing methods, cancer medicines, and other technological breakthroughs, and so on.
Table of Contents
- Top 15 Biotechnology News of 2022
- 1. Scientists develop a fresh approach to stem cell production (Australia, June 2022)
- 2. Biotechnologists have effectively defined how cannabis cells produce cannabinoids using high-efficiency “hacks” (Canada, Aug 2022)
- 3. Future biotech systems may rely largely on urine in various ways (UK, Oct 2022)
- 4. Production of vaccines is made quick and adaptable due to biotechnology platform advancements (USA, June 2022)
- 5. The recent finding of the DNA repair process could take biotechnology to the next level (USA, Mar 2022)
- Explore Mitochondria Functions & Their Importance
- 6. Scientists discover that sexual activity can help a deadly fungus proliferate, creating more drug-resistant, ferocious strains (Canada, June 2022)
- Top 10 Biochemistry News of 2020 – A Round-Up
- 7. To further the study of biofuels, researchers construct bioreactors and manipulate microbes (UK, Jan 2022)
- 8. Engineered microorganisms transform absorbed carbon dioxide into substances used in energy, textiles, and cosmetics (USA, Feb 2022)
- 9. A novel CRISPR-Cas method enables more accurate DNA cleavage (USA, Oct 2022)
- 10. Discovery makes it possible to produce cereal crops with less fertilizer and reduce nitrogen pollution (USA, Aug 2022)
- 11. Researchers have discovered the process behind the formation of fruit and seeds in flowering plants (USA, July 2022)
- America’s 15 Must-Visit Botanical Gardens: Discover Them Today!
- 12. A recently created radio-labeled chemical makes it possible to examine innate immune activation in real-time (USA, Feb 2022)
- 13. Using new technology, it is possible to fight the climate crisis (UK, Aug 2022)
- 14. Researchers use seaweed compounds to increase the success of bypass surgery (Canada, Dec 2022)
- 15. Researchers create face masks that fight viruses (USA, June 2022)
Top 15 Biotechnology News of 2022
1. Scientists develop a fresh approach to stem cell production (Australia, June 2022)
Researchers have created a novel 3D-printed method for collecting stem cells from bioreactors. This could lead to more affordable, high-volume stem cell production in Australia.
- Despite the potential of stem cells in treating illnesses and injuries, the current method of harvesting them is laborious and expensive. However, biomedical engineers collaborate with business partners to develop cutting-edge technology combining 3D printing and microfluidics.
- This innovative device aims to streamline the production process and make stem cell therapies more accessible to patients at a cost. Their work has focused on mesenchymal stem cells, a type of adult stem cell that can multiply and transform into tissue cells such as bone, cartilage, muscle, fat and connective tissue.
- Microfluidics may control Cells and other small objects precisely at microscopic scales. Recent developments in 3D printing have made it possible to create microfluidic apparatus directly, enabling quick prototyping and the production of integrated systems.
- Human bone marrow, adipose tissue, or blood are the first sources from which mesenchymal stem cells are isolated. Then, to enable the cells to multiply, they are delivered to a bioreactor in the laboratory and mixed with microcarriers.
- The mesenchymal stem cells are detached from the microcarriers using the new technology, which comprises four micromixers, one spiral microfluidic separator, and one microfluidic concentrator. The cells are then concentrated for further processing.
This approach has the potential to increase the accessibility of stem cell therapies to patients at a reduced cost, and scientists are presently collaborating closely with biotechnology firms to commercialize the technique. A closed system with no human interference is required for good production practices.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Biotechnology Discoveries in 2019
2. Biotechnologists have effectively defined how cannabis cells produce cannabinoids using high-efficiency “hacks” (Canada, Aug 2022)

Even though numerous biotechnology firms are actively working to engineer THC/CBD outside of the plant in yeast or cell cultures, little is known about how it achieves it in its natural state. Biotechnologists have, for the first time, identified the highly effective “hacks” that cannabis cells employ to produce cannabinoids (THC/CBD).
- The study provides light on numerous crucial points in the pathway of generating THC or CBD within the cell and uncovers the microenvironments in which THC is created and transported in cannabis trichomes.
- Scientists immobilized the plant’s cellular components and metabolites by rapidly freezing cannabis glandular trichomes. Due to this, they could examine the glandular trichomes of cannabis using electron microscopes, which showed cell structure at the nanoscale.
- They discovered that the metabolically active cells in cannabis create a “supercell” that serves as a miniature metabolic biofactory. Until now, synthetic biology methods have concentrated on improving the enzymes that produce THC and CBD, like establishing a factory with the most productive equipment to produce as much product as possible.
- These methods, however, have yet to create an effective means of transporting intermediate molecules between enzymes or from inside the cell to the outside of the cell, where final products can be gathered.
- This study contributes to the definition of the subcellular “shipping routes” that cannabis employs to build an effective pipeline from starting components to finished goods without accumulating toxins or waste.
This study greatly contributes to understanding how cannabis trichome cells can produce enormous amounts of terpenes and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), poisonous to plant cells in high doses, without poisoning themselves. This novel model can guide synthetic biology methods for producing cannabinoids in yeast, which are frequently utilized in biotechnology. These “tricks are necessary for them to have profitable output.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Biotechnology News of 2020
3. Future biotech systems may rely largely on urine in various ways (UK, Oct 2022)

Urine contains a common component that can be utilized to initiate the mass manufacturing of proteins required by biotech businesses, including hormones and antibodies. A technique that employs urea to start the manufacturing of these proteins in the massive amounts required by the biotech industry has been devised by researchers.
- In this method, little DNA snippets are inserted into bacteria like e.coli to induce them to overproduce particular proteins. It was initially developed in the 1970s and is now a well-known technology.
- However, ‘inducer’ molecules – expensive and frequently require careful handling, like refrigeration – typically cause overproduction. The researchers have created a less complicated, more affordable process that employs readily available components by substituting urea.
- In a recent study, scientists examined purified urea and the urea found in regular garden fertilizers. They demonstrated that any source could produce comparable results.
- The scientists also demonstrated that by adjusting the doses used, it was feasible to precisely control the levels of protein induced by the urea molecule. To prevent hurting or wearing out the host microorganisms, it’s crucial to do this.
- They discovered it was possible to maximize production to levels comparable to those generated with medium-strength promoters, which are currently the norm in the biotech sector.
- The research expands on earlier work in which the researchers showed that nitrate, a readily available, affordable, and stable inorganic ion, may also be employed as a trigger.
- Since nitrate is frequently present in many commercial fertilizers and even some garden fertilizers, it is always accessible, even in places where other promoter chemicals might not be.
These innovative methods will provide the biotech sector with fresh research opportunities. With the help of this technology, biotech companies will be able to streamline their operations and reduce costs.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Biotechnology News In 2017
4. Production of vaccines is made quick and adaptable due to biotechnology platform advancements (USA, June 2022)
Traditional manufacturing techniques could not match the demand when COVID-19 produced an urgent need for vaccines. As a result, biopharmaceutical firms turned to cutting-edge biotechnology platform-based manufacturing processes that could be more quickly adapted to manufacture and were more reliable, adaptable, and flexible than conventional methods.
- Vaccines created utilizing biotechnology platforms have ‘smart’ properties, making them more adaptable than vaccines created using conventional procedures.
- Biotechnology platform-based vaccine development entails developing a versatile foundation structure to produce new vaccines for related viruses. Researchers determine the alterations made by pathogen mutations and then apply them to the current structure.
- This strategy was already in place when the COVID-19 pandemic broke out, and the enormous worldwide demand sped up the wide-scale and pervasive adoption of the platform.
- Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna used one such messenger RNA-based platform to create their vaccines. The coronaviruses, which include the common cold and rapidly mutate, may be protected against using the mRNA platform, which had already been created for that purpose.
- The virus that causes COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, was sequenced within a year of the pandemic’s onset. Once they had the genetic information, researchers modified the existing mRNA platform to create a vaccine specifically for that variant of SARS-CoV-2.
- This process took less than a week. Johnson & Johnson employed a strategy referred to as a viral vector. Contrarily, conventional vaccine production, which entails growing disease-causing pathogens in culture and injecting some form of these pathogens, can take ten to fifteen years to create.
Beyond COVID-19, many more viruses may be the subject of future research thanks to biotechnology-based methods. Device connections could be facilitated by a smart manufacturing strategy that uses technologies to collect, store, and communicate high-quality process data-enabling biopharmaceutical companies to effectively identify and implement solutions, such as mass customization, modular manufacturing, automation, and knowledge management, to improve the development and production of vaccines.
Suggested Reading:
15 Wonderful Biotechnology Inventions In 2018
5. The recent finding of the DNA repair process could take biotechnology to the next level (USA, Mar 2022)
The blueprint for life, DNA, has a helix-like form but is unexpectedly vulnerable to harm. A group of researchers has discovered a feature to repair the DNA double-stranded breaks that were previously unknown.
- Ultraviolet light, various cancer treatments, ionizing radiation, and certain medications can harm DNA. Only one of the two strands can break in some cases.
- Cells can repair the DNA quickly because the second strand keeps the DNA together. The second strand’s information is copied by the cells.
- This new study characterizes two DNA-PK protein complexes, each playing a unique role in DNA repair that the other cannot. When both strands of DNA are damaged, it is more challenging for cells to repair the damage.
- Before the ends of the DNA are rejoined, information in the form of Nucleotides may be lost and need to be added back in. Multiple DNA double-strand breaks increase the likelihood of the DNA being joined incorrectly.
- Numerous cancers are frequently linked to this kind of error. If DNA-damaging chemicals lead to chemical changes at the DNA ends, double-stranded breaks may also be harder to fix. “Dirty” ends are commonly used to describe damaged DNA ends.
- One of two ways that DNA-PK can aid in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. It can target enzymes that add missing nucleotides to breaks where information is absent, like using a needle and thread to sew the DNA back together.
- To rejoin “dirty” ends, DNA-PK enlists enzymes that can chop off the harmed DNA. Two distinct DNA-PK complexes, known as dimers, were discovered in previous structural investigations published by the team and their partners.
- In their recent research, scientists found that the two separate DNA-PK dimers serve different purposes: one complex attracts enzymes that fill in gaps in the genetic code, while the other turns on cutting enzymes that cut off “dirty” ends.
- The group also found that the balance between the two dimers is necessary for effective repair.
This finding might affect therapeutic gene editing methods, cancer medicines, and other technological breakthroughs.
Suggested Reading:
Explore Mitochondria Functions & Their Importance
6. Scientists discover that sexual activity can help a deadly fungus proliferate, creating more drug-resistant, ferocious strains (Canada, June 2022)
Since its initial identification in 2009, Candida auris has spread to more than 50 nations, where outbreaks have been documented, and tens of thousands of people have perished from fungal infections. A lethal infection contributing to this superbug issue has an evolutionary puzzle that has been solved: it can reproduce through sexual activity.
- A fungus called C. auris frequently affects immunocompromised hospital patients, leading to fatal illnesses or even death.
- Although microorganisms of this kind typically reproduce asexually, researchers report that Candida auris may produce more drug-resistant and virulent strains that can spread quickly through sexual or recombinant reproduction.
- The genesis and mode of reproduction of this fungal pathogen in nature are two of the most difficult and perplexing problems.
- According to the research, this fungus can recombine in nature and has done so, allowing it to produce new genetic varieties quickly. Although that may sound terrifying, it has two sides.
- We can mimic the process in the lab because they can recombine in nature. This will help us learn more quickly about the genetic factors that affect virulence, treatment resistance, and possibly other characteristics that make this virus so hazardous.
- Through sexual activity, they may produce offspring resistant to both drugs if one strain develops a resistance to one drug and another strain develops a resistance to another drug.
- A chance for them to interact and mate is created by mixing strains in the same hospital, possibly in the same patient.
- The implications of sex in living things are highly varied. It implies that fungi can disperse genes that are advantageous to them through populations much more quickly than through asexual reproduction alone.
As a result of the discoveries, scientists can now reproduce such sexual behaviors in the laboratory, which will aid in subsequent research.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Biochemistry News of 2020 – A Round-Up
7. To further the study of biofuels, researchers construct bioreactors and manipulate microbes (UK, Jan 2022)

At a fraction of the cost of commercial systems, researchers have created tools that can be used to study the production of bacterial biofuel. Then, this technology was also employed to show how bacterial genetic engineering could be utilized to increase the production of biofuels.
- The researchers built their bioreactors because buying commercial equipment to investigate microorganisms that produce biofuel can be too expensive.
- These bioreactors are affordable for most research labs. The scientists then used this apparatus to confirm that one of their genetically altered Clostridium bacterium strains could quickly generate butanol.
- The results of this study demonstrate that a small alteration to a single gene can have profound effects on the biofuel production process.
- The researchers are especially eager to use their expertise to optimize processes that can convert waste products from food and agriculture into biofuels that are greener alternatives to fossil fuels.
- These exciting developments will aid in advancing research into bacterial biofuel production.
This effort is anticipated to make it easier to obtain less expensive bioreactors, which will encourage more studies into biofuel production from natural and artificial bacteria.
Suggested Reading:
Top 20 Biomass Energy Pros and Cons
8. Engineered microorganisms transform absorbed carbon dioxide into substances used in energy, textiles, and cosmetics (USA, Feb 2022)
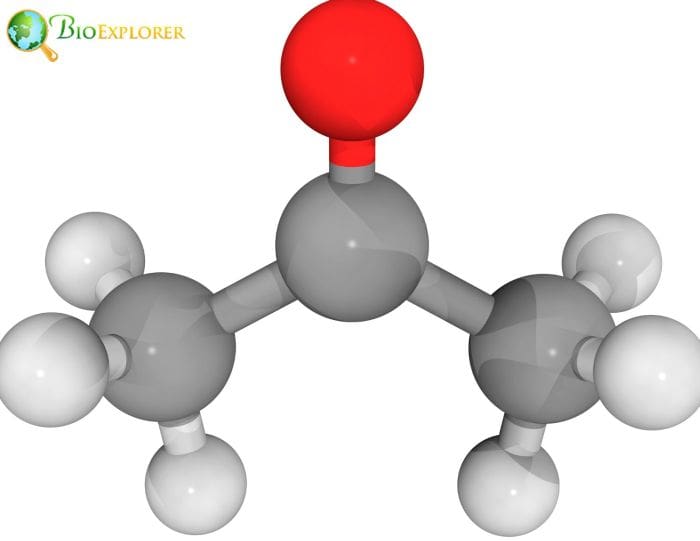
Researchers created a bacterial strain that can decompose carbon dioxide (CO2) and transform it into widely used, high-priced industrial compounds. The carbon-negative strategy avoids using fossil fuels to produce these compounds and removes CO2 from the atmosphere.
- The ability of a bacterium strain to convert CO2 into acetone and isopropanol (IPA) was successfully proved in a recent pilot study by the researchers after they carefully chose developed, and optimized the bacteria strain.
- This innovative gas fermentation method eliminates greenhouse gases from the atmosphere. It does it without fossil fuels, which are usually required to produce acetone and IPA.
- The researchers created a novel gas fermentation method to produce these compounds sustainably. They began with the LanzaTech-engineered anaerobic bacterium Clostridium autoethanogenum.
- The researchers then modified the bacteria using synthetic biology technologies to ferment CO2 and produce acetone and IPA.
- The team showed that the carbon-negative platform might cut greenhouse gas emissions by 160% compared to conventional procedures after undertaking a life-cycle analysis.
- These breakthroughs, driven by cell-free approaches that directed strain engineering and route enzyme optimization, cut the time to production by more than a year.
This revelation represents a significant advancement in climate disaster prevention. Closing the carbon cycle through the development of the acetone and IPA pathways may hasten the creation of other new products for application across various industries. The strategy might also be used to develop more efficient methods for producing other valuable compounds.
Suggested Reading:
How Are Viruses Different From Bacteria?
9. A novel CRISPR-Cas method enables more accurate DNA cleavage (USA, Oct 2022)
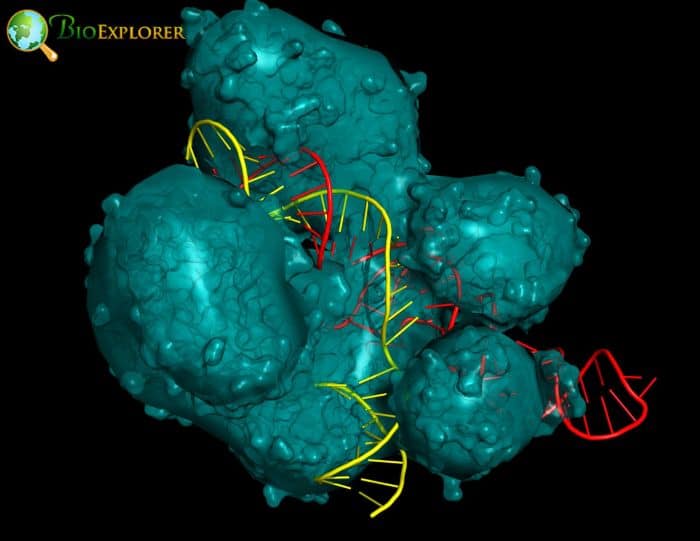
A significant barrier has been removed for using CRISPR-Cas enzymes and other technologies to cut and modify DNA. The most recent development will streamline and speed up molecular cloning methods and increase their usefulness.
- Researchers’ capacity to modify DNA has changed due to CRISPR-Cas technology. In this most recent study, the team that created SpRY, a practically PAMless CRISPR-Cas9 variation, examined its efficacy as a general DNA cleavage tool.
- The researchers unexpectedly found that SpRY is PAMless in vitro and can successfully cleave DNA at any sequence programmed by the guide RNA (gRNA) by constructing SpRY and guide RNA (gRNA) complexes that targeted more than 130 DNA sequences in laboratory trials.
- Additionally, the researchers demonstrated how their technology can get around restriction enzymes’ drawbacks. They showed that SpRY DNA digests, also known as SpRYgests, allow DNA to be cut at virtually any sequence, including a large variety previously impossible to target with restriction enzymes or other CRISPR-Cas proteins.
- Researchers can cut DNA in a test tube at any desired DNA location with this new technique.
- SpRYgests’ new features will speed up and lower the cost of various applications for basic research, including some that might eventually impact patient care.
The researchers believe that SpRYgests could have many applications, including simplifying conventional molecular cloning methodologies, using more complicated cloning techniques, constructing next-generation sequencing libraries, and many more.
Suggested Reading:
Top 7 Pros and Cons of Cloning
10. Discovery makes it possible to produce cereal crops with less fertilizer and reduce nitrogen pollution (USA, Aug 2022)

Thanks to research, it is now possible to cultivate cereal crops with less nitrogen fertilizer. The discovery might reduce fertilizer costs for farmers by billions of dollars per year while also helping the environment.
- Chemical fertilizers are essential to agricultural activities because nitrogen is essential for plant growth. However, much of what is applied is lost and hurts the environment by leaking into the soil and groundwater.
- In addition, nitrogen fertilizers are incredibly costly. The goal of the study is to increase nitrogen fixation, the process by which soil microbes convert nitrogen gas in the atmosphere into ammonium.
- The scientists employed chemical screening and sequencing to find substances in rice plants that improved the bacteria’s capacity to fix nitrogen.
- They then determined the chemical production routes and applied gene editing techniques to boost the production of chemicals that induced the growth of biofilms. Bacteria in those biofilms have improved nitrogen conversion.
- As a result, the amount of ammonium in the soil for the plants and the bacteria’s ability to fix nitrogen increased.
This might lead to developing a sustainable substitute for the overuse of nitrogen fertilizers in agriculture. Other plants may use the route.
Suggested Reading:
What is Biotechnology?
11. Researchers have discovered the process behind the formation of fruit and seeds in flowering plants (USA, July 2022)

The growers need help producing food due to rising global temperatures and declining pollinator populations. Understanding this process is crucial because common food crops are exclusively made of fruits and seeds derived from flowers. It is essential to understand how plants “decide” to convert some of their blossoms into fruit and seed for agriculture and food production.
- A recent study tackles this matter and sheds light on the precise processes by which flowering plants produce their fruits and seeds.
- The team aimed to understand how pollination or fertilization causes a flowering plant to begin fruit development. Using strawberry plants, the scientists modeled fruit growth and pollination mechanisms.
- Strawberries are especially well-suited to fertilization modeling because of their distinctive structure and seed placement. They discovered that the AGL62 gene in every flowering plant causes a plant to produce fruit and seeds.
- Auxin is a crucial plant growth hormone that AGL62 stimulates. Auxin is produced as soon as the gene is activated, which causes the seedcoat, the endospermWhat is endosperm?An embryonic nutritive tissue formed during double fertilization by the fusion of a sperm with the polar nuclei., and the plant’s fruit to develop.
- The seed coat is the outer protective shell of the seed. For researchers, the role of auxin in controlling endosperm growth is very important because it affects the grain’s size and the fruit’s growth.
- They successfully interfered with AGL62 function using the revolutionary gene-editing method CRISPR. As a result, the strawberry plants could not grow fruit and seed.
- In nature, pollination causes the AGL62 gene to start producing auxin, essential for the best possible fruit and seed development.
The team has established a foundation enabling agriculturalists to activate AGL62 utilizing biotechnology and completely avoid pollination by establishing this link between genes and hormones. These findings are especially significant since that global warming is having an effect on food production across the globe.
Suggested Reading:
America’s 15 Must-Visit Botanical Gardens: Discover Them Today!
12. A recently created radio-labeled chemical makes it possible to examine innate immune activation in real-time (USA, Feb 2022)
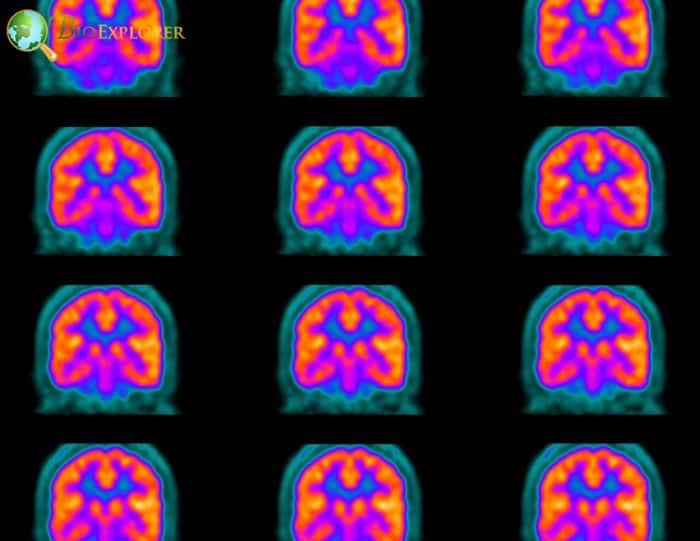
A novel radio-labeled molecule that can selectively react with specific high-energy radicals that are indicative of innate immune activation has been created by researchers. This molecule may provide a non-invasive method of real-time monitoring of inflammation using positron emission tomography (PET) imaging.
- The innate immune response is the body’s initial defense against invasive pathogens. The study team concentrated on MPO activity to create a redox-tuned reporter specific to the innate immune activity.
- The researchers created [18F]4FN as a labeled molecule to specifically attach adjacent proteins and cells after[18F]4FN has been oxidized by MPO + hydrogen peroxide, but not hydrogen peroxide alone, using newly developed chemical techniques.
- One aspect of the innate immune response substantially conserved among myeloid cells is myeloperoxidase.
- When hydrogen peroxide is utilized to activate this proinflammatory enzyme, several high-energy radicals are created that are employed to destroy infections.
- In several laboratory models of inflammation, the researchers assessed the[18F]4FN’s potential applications as an in vivo PET imaging tool. Acute toxic shock, arthritis, and contact dermatitis conditions whose inflammation is known to be mediated by innate immunity were all successfully brought to light by the molecule.
- Additionally, their findings imply that[18F]4FN is a more accurate and reliable reporter of inflammation than other clinically used PET imaging agents like fluorodeoxyglucose ([18F]FDG).
This PET imaging agent has to be tested in human research. Still, it has the potential to be used widely to help patients with a variety of illnesses and clinical conditions. The research team is in contact with clinical partners to test particular[18F]4FN uses.
Suggested Reading:
Top 17 Stem Cell Research Pros and Cons
13. Using new technology, it is possible to fight the climate crisis (UK, Aug 2022)

The recent rise in petrol costs in the UK, the advent of conflicts and civil wars in the Middle East, and the ecological and humanitarian threat posed by a nuclear meltdown in Fukushima, Japan, are just a few examples that have highlighted the vulnerability of the world’s energy supply. Therefore, finding alternative energy sources is crucial from a global perspective.
- A revolutionary technique developed by scientists can aid in the fight against climate change.
- The project uses a chemical process to create high-value fuels and chemicals powered by renewable energy from sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
- The project aims to reduce the increase in atmospheric CO2 levels, ensure vital green energy supplies, and lessen the world’s reliance on fossil fuels.
- The conversion can occur without the need for organic additives, the production of toxins, or electricity, thanks to bacteria grown on a synthetic semiconductor device known as a photocatalyst sheet.
- The global energy issue and the effects of climate change are directly addressed in the study. We must create new technology to tackle these enormous problems without further harming the earth we live on.
This environmentally friendly technology can help the world attain net zero, secure more energy supplies, and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Suggested Reading:
Top 25 Immune System Fun Facts
14. Researchers use seaweed compounds to increase the success of bypass surgery (Canada, Dec 2022)
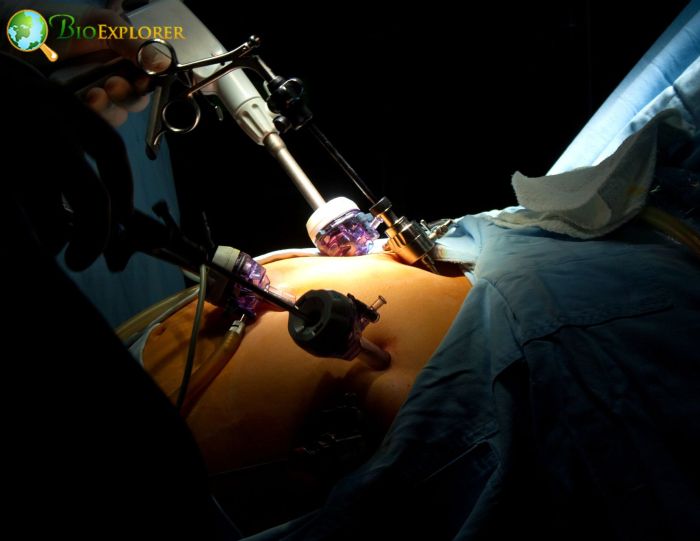
Researchers are employing a natural substance produced from seaweed to encourage vascular cell proliferation, minimize blood clots, and enhance the functionality of synthetic vascular grafts used in heart bypass surgery.
- The new method is crucial in situations involving small artificial blood vessels or those with a diameter of fewer than six millimeters, which are vulnerable to clots that can grow into complete blockages.
- Developing synthetic vascular graft materials is essential to accelerating long-term functioning. Fucoidan, a substance derived from seaweed, was added by researchers to alter synthetic blood vessels.
- The structure of Fucoidan is comparable to that of the anticoagulant medication heparin. Fucoidan encourages the proliferation of vascular cells surrounding the inner surface of the graft when used with a nanotechnology process called micropatterning, dramatically lowering the likelihood of clot formation.
- Patients may benefit from fewer problems, a higher quality of life, and a lower likelihood of blockages recurring and necessitating further medication or surgery.
- This useful, readily available, small-diameter vascular graft will aid in lifesaving procedures. The fact that they will endure much longer and provide free blood flow is crucial.
Fucoidan and micropatterning were used to test the novel method on small animals successfully, and the team now intends to go on to large animal testing before moving on to clinical trials.
Suggested Reading:
Top 25 Circulatory System Fun Facts
15. Researchers create face masks that fight viruses (USA, June 2022)

Researchers have found a practical approach to turn N95 face masks into on-contact germ assassins and efficient germ barriers. The antiviral and antibacterial masks may be worn for longer periods, resulting in less plastic waste since the masks would not need to be changed as frequently.
- A research team effectively grafted Broad-spectrum antimicrobial polymers onto the polypropylene filters used in N95 face masks. N95 masks include active filtration layers that are extremely sensitive to chemical alterations.
- They may no longer perform like N95s since it can make them less effective at filtering. They are constructed of polypropylene, a challenging material to alter chemically.
- The incredibly fine network of fibers in these masks presents another issue because doing so could make it more difficult to breathe through them.
- The group used ultraviolet (UV)-initiated grafting to covalently link antibacterial quaternary ammonium polymers to the fiber surfaces of nonwoven polypropylene textiles.
- This non-leaching polymer covering was created using a very basic chemistry procedure that may kill bacteria and viruses by essentially rupturing their outer layers.
- Only UV light and acetone were used by the team. Instead of needing to create fresh polypropylene filters, the technique can be used with ones that have already been produced.
- Wearing an unaltered N95 mask with another polypropylene layer with the antimicrobial polymer on top will prevent the reduction in filtration efficiency that occurred when the process was applied directly to the filtration layer of N95 masks.
- Future mask producers might include an antibacterial polymer in the top layer of the mask.
The research represents a first step towards more durable, self-sterilizing personal protective equipment, including the N95 respirator. In general, it might lessen the spread of airborne infections.