The current biotechnological innovations provide deep insight into developing drugs with a cell-free vaccine, genetically engineered yeast for rectifying metabolic disorders, the involvement of synthetic biology, and the generation of new genome editing techniques with the rise of retros.
In 2021, there were several advancements in the field of biotechnology. So let us glance at various research outcomes from a broader perspective.
Top Biotechnology News of 2021
1. Cells can communicate with computers thanks to “Nanopore-tal” (USA, Aug 2021)
For the first time, scientists demonstrated using a commercial nanopore sensor device for studying protein expression levels other than DNA and RNA sequencing, for which it was initially intended.
- Biotechnology research’s mainstay is genetically encoded reporter proteins, which enable researchers to monitor gene expression, comprehend intracellular functions, and troubleshoot genetically constructed circuits.
- However, conventional reporting methods that rely on fluorescence and other optical techniques have practical drawbacks that can hamper the field’s future development. Now that researchers at the University of Washington and Microsoft have developed a “nanopore-tal” into what goes on inside these intricate biological systems, it is possible to view reporter proteins in a completely new way.
- The group developed a new class of reporter proteins that can help directly by a sensing device with nanopores used for barcoding that is now on the market.
- To be drawn into the nanopore sensors by an electric field, the researchers designed the Nanopore TER tagged proteins with charged “tails“.
- The team then classifies the electrical signals for each Nanopore TER barcode using machine learning to determine the output levels of each protein.
Nanopore TER is the name of the novel system that can considerably surpass the capability of present methods to identify various protein expression levels from bacterial and human cell cultures. This new technology using reporter protein can be used to gain greater insight into barcoding about protein expression levels and opens up an avenue for sequencing methods.
![]()
2. Base editing successfully reduced cholesterol levels over time (Switzerland, May 2021)

A novel gene editing technique called base editing allows for the precise modification of certain DNA sequence building blocks.
- An international research team led by the University of Zurich has successfully reduced high LDL cholesterol levels in the blood of mice and macaques by introducing such a point mutation in a particular gene. As a result, patients with inherited metabolic liver illnesses may now be cured.
- Researchers perform single-point mutation PCSK9. This protein helps LDL cholesterol enter cells from the blood and transport it. Any modifications in PCSK9 caused by base editors.
- This strategy is worked out by the researchers’ base editors as part of the gene editing technique. These proteins can switch out certain DNA bases. For instance, adenine base editors change adenine (A) into guanine (G).
This new approach could treat many patients suffering from inherited metabolic liver diseases, such as hypercholesterolemia, phenylketonuria, or urea cycle disorders. Although genome editing has the advantage over conventional medications in that the modifications it causes are long-lasting, this strategy can be a better therapeutic approach soon.
![]()
3. Wonder transient biocompatible pacemaker dissolves in the body without surgical intervention (USA, June 2021)
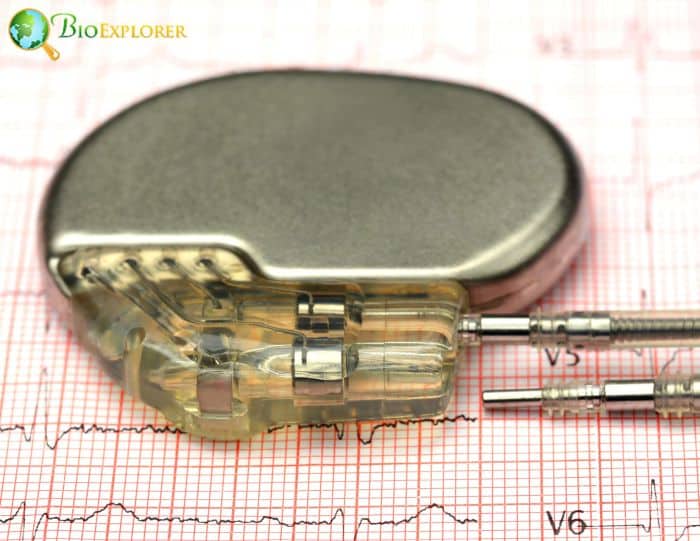
Researchers at Northwestern and George Washington (GW) universities have developed the first-ever transient pacemaker — a wireless, battery-free, fully implantable, bioresorbable pacing device without surgical extraction.
- After cardiac surgery or while waiting for a permanent pacemaker, individuals who require temporary pacing may utilize the thin, flexible, leadless, lightweight device.
- All pacemaker parts are biocompatible and gradually dissolve over five to seven weeks into the body’s biofluids without surgical removal.
- Through the use of near-field communication protocols, which are also used in RFID tags and smartphones for electronic payments, the device wirelessly collects energy from an external, remote antenna and maintains the cardiac rhythms naturally.
The device tackles the secondary issues of patient comfort, freedom of movement, and rehabilitation in addition to the fundamental issue of occasionally post-cardiac surgery patients needing temporary pacing due to blockages or arrhythmias. This technology seems promising and will significantly enhance the patient’s recovery rate.
![]()
4. Researchers construct one of the concise repositories of the human transcriptome as ‘RNA-Atlas’ (Belgium, June 2021)
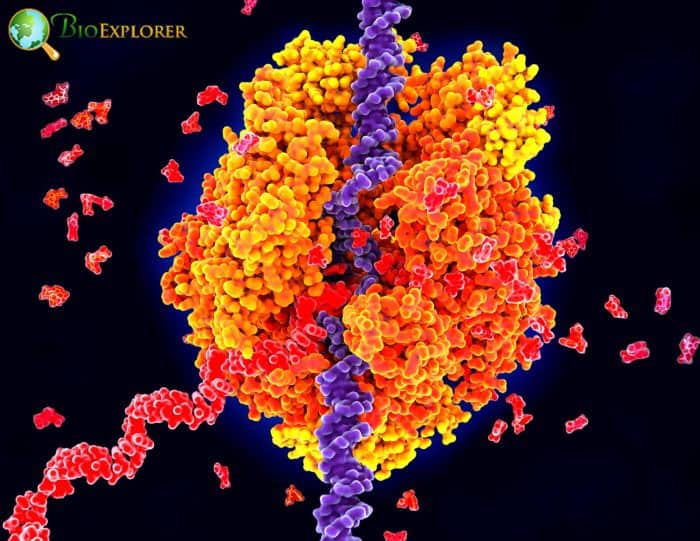
Researchers have found thousands of new RNAs and improved our understanding of the function of existing RNA molecules by combining complementary sequencing approaches. They discovered correlations between the abundance of various RNAs in various cell types that point to regulatory functions. They were able to determine whether this regulation occurs at the transcriptional level (by inhibiting or promoting the transcription of protein-coding genes) or post-transcriptionally (e.g., by breaking down RNAs).
- A novel class of non-polyadenylated single exon genes and numerous new circular RNAs were among the thousands of novel non-coding RNA genes found. Thanks to this most recent sequencing method.
- The abundance of each measured RNA transcript in the various cells and tissues, the presence or absence of a polyA-tail (for some genes, it appears that this can vary from cell type to cell type), and whether it is linear, or circular were all determined by trying to combine and comparing the results of the various sequencing methods.
- Additionally, the consortium discovered crucial hints for figuring out how some ncRNAs function.
So, to better understand disease processes and find novel genes that could be used as therapeutic targets or biomarkers, it is crucial to have a greater grasp of the complexity of the transcriptome.
![]()
5. Synthetic Biology, Approach identifies “Biological Dark Matter” with better clarity (Australia, Oct 2021)
Synthetic biology might well be able to help define complex microbial communities more thoroughly, unlocking their potential for use in industrial and medical biotechnology, according to a recent body of research published in Nature Communications.
- As most of the microbes are difficult to grow and study in the laboratory, and for most of scientific history, they have been a kind of ‘biological dark matter’, Metagenomics is the study of these complex microbial communities by comparing their DNA sequences to those of other described species in databases.
- This process was made possible by developing modern DNA sequencing tools. But certain constraints in the metagenomic approach can be overcome with synthetic biology. One can explore the possibility of reconstituting the entire microorganism at the theoretical feasibility level.
This approach is a new doorway towards industrial fermentation in winemaking industries. Lastly, it can be commented that synthetic metagenomics could become a new scientific step not only on the dark microbial matter but paves its potential for industrial application and medical biotechnology.
![]()
6. Bacteria Can Sense Time With their Biological Clocks (UK, Jan 2021)

Now research reveals that bacteria, too, might have internal clocks that align with the 24-hour cycle of life on Earth.
- Circadian rhythms, also known as biological clocks, are exquisite internal timing devices found throughout nature and help living things adjust to the significant changes that occur from day to night and even across seasons.
- These molecular rhythms, which are present inside cells, enable biological clocks to be synchronized with their surroundings by utilizing environmental cues like temperature and daylight.
- Because of this, when we experience jet lag, our internal clocks are temporarily out of sync with the new cycle. The significance of these molecular metronomes to crucial processes, such as sleep and cognitive functioning in humans and water regulation and photosynthesis in plants, has been shown by a growing body of research over the past two decades.
The study explains a biological mystery that may have repercussions for biotechnology, the timing of drug delivery, and how we create effective crop protection strategies. Recently certain bacterial groups have been used in various applications, from laundry detergent to production to crop protection based on bioengineering biological clock.
![]()
7. Epigenetic information in cellular components can be mapped at scale using technology (Sweden, April 2021)
Histones are tiny essential proteins that bind to DNA and store data that can be used to turn specific genes on or off. With a method created by researchers at Karolinska Institute, it is now possible to simultaneously analyze how various histone variants bind to the genome in tens of thousands of different cells.
- The method was used on the mouse brain. It can be used to investigate single-cell epigenetics in other intricate tissues.
- Epigenetic information can take many forms, including histone modification. As “epigenetic stickers, ” histones are affixed to DNA like beads on a string, and which genes should be turned on or off is indicated by these stickers.
- These systems work together to ensure that thousands of genes are turned on or off at the appropriate time, location, and cell epigenetic knowledge.
In the human brain, single-cell CUT&Tag would be helpful for both normal development and investigation of various diseases. For instance, we’d like to investigate which epigenetic processes in multiple sclerosis led to neurodegeneration and whether we can control those processes to treat the condition.
Suggested Reading:
25 Mind-Blowing Biology Breakthroughs That Shaped Our World!
![]()
8. Age of Retrons is approaching with a promising gene editing tool (USA, April 2021)
Retron Library Recombineering (RLR), a new gene-editing technique developed by researchers, can produce millions of mutations simultaneously and “barcodes” mutant bacterial cells so that the entire pool can be screened at once. In addition, it produces better editing rates and can be applied when CRISPR is non-feasible.
- The conventional use of CRISPR Cas9 can be complicated to orchestrate. It can even be toxic to cells because Cas9 often cuts unintended, off-target sites.
- This bait-and-switch model may, at times, be harmful. Recombineering, an alternative gene editing, accomplishes this bait-and-switch by inserting a different piece of DNA while a cell replicates its genome.
- This effectively causes genetic mutations without damaging DNA. Furthermore, these techniques are straightforward enough to be applied to numerous cells to generate complex mutation pools for research.
- Retrons are bacterial DNA segments that undergo reverse transcription to construct single-stranded DNA fragments (ssDNA). One of two methods can incorporate ssDNA containing the desired mutation into an organism’s DNA when using recombination-based gene editing techniques.
- The mutant DNA strand and a single-stranded annealing protein (SSAP) can be introduced into a replicating cell so that the SSAP incorporates the mutant strand into the DNA of the daughter cells.
Thus, this RLR technique’ name tag’ system allowed building of a much more extensive library than currently used with CRISPR. Therefore, this proves to be a promising gene editing tool in future approaches.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Biotechnology News of 2020
![]()
9. Genetic Cloning Toolkits for Mammalian Synthetic System Design and Construction (UK, Oct 2021)

The advent of numerous cloning toolkits, which offer a wealth of standardized parts that can be put together and speed up the engineering of complex genetic devices, has been made possible by developing high-throughput cloning techniques. Although there aren’t as many cloning toolkits for mammalian synthetic biology as for bacterial and yeast, some are now made public.
- Synthetic biology is centered on building DNA-encoded programs, and the time needed to design and construct for testing is frequently determined by the method used.
- This study describes and summarizes critical features of the available toolkits for DNA construction for mammalian cells. In addition, a comparison is made with the various cloning strategies according to their complexity and the time required to produce constructs of various sizes.
- It has been considered why Golden Gate cloning toolkits have gained popularity due to their modular Construction of the conventional type.
- Future developments are anticipated, such as cloning toolkit accessory packs that can help with editing, orthogonality, sophisticated regulation, and integration into the creation of synthetic chromosomes.
- But laboratory standardization is advantageous for synthetic biology. The field’s advancement depends on straightforward, low-cost, high-throughput techniques that shorten the design-build-test cycle.
Suggested Reading:
Woolly Mammoth Clone Project: Can It Be Resurrected?
![]()
10. HIV experimental vaccine made from mRNA is safe and effective in animals (USA, Dec 2021)
Scientists have found promising results in mice and non-human primates for an experimental HIV vaccine based on mRNA, the same platform technology used in two highly effective COVID-19 vaccines.
- According to their findings, the novel vaccine was risk-free. In addition, it successfully stimulated the desired cellular and antibody immune responses against an HIV-like virus.
- According to certain researchers at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), a division of the National Institutes of Health, an experimental HIV vaccine based on mRNA – the same platform technology used in two highly effective COVID-19 vaccines – shows promise in mice and non-human primates.
- Their findings, published in Nature Medicine, demonstrate that the novel vaccine was secure and elicited the desired cellular and antibody immune reactions against an HIV-like virus.
- Compared to unvaccinated animals, Rhesus macaques that had received a priming shot and a series of booster shots had a 79% lower per-exposure risk of contracting the simian-human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV).
This study provides insight into the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases. In addition, it develops better means of preventing, diagnosing, and treating these illnesses.
Suggested Reading:
How To Become An Infectious Disease Specialist?
![]()
11. DNA-like XNAs may have been the first forms of life on Earth (Japan, April 2021)
According to Nagoya University biomolecular engineer Keiji Murayama, it is widely believed that the RNA world represents a stage in the origin of life. The pre-RNA world may have previously been based on molecules known as Xeno nucleic acids before (XNAs). However, unlike RNA, XNA replication most likely didn’t need enzymes.
- Without enzymes, it could synthesize an XNA, providing strong evidence that there may have been an XNA world before the RNA world.
- XNA was formed of acyclic (non-circular) L-threoninol nucleic acid (L-aTNA) fragments. This molecule is thought to have existed before RNA.
- The association of shorter L-a TNA fragments linked up with longer ones was predicted to occur in the presence of a compound called N-cyanoimidazole, and a metal ion, like manganese, both of which were possibly present in early Earth.
Finally, this study exhibited an attractive system for experimenting with constructing artificial life and the development of highly functional biological tools composed of acyclicXNA.
Suggested Reading:
25 Reasons That Emphasizes The Importance of Biology
![]()
12. Researchers identify a promising new target for the treatment of diabetes (Germany, Jan 2021)

Diabetes complications, such as persistently elevated blood sugar, systemic metabolic failure, and multi-organ failure, place a significant financial and social burden on society and increase the risk of early death.
- Presently, there is no report of a drug on the market that can stop or revert disease progression. However, an innovative and treatable insulin inhibitory receptor known as an inceptor has been identified by researchers.
- The insulin signaling pathway in pancreatic beta cells becomes hypersensitive when inceptor function is blocked. This may enable the preservation and regeneration of beta cells to manage diabetes.
- Diabetes mellitus is a complicated disease characterized by loss or impairment of insulin-producing beta cells in the islets of Langerhans, named as “micro-organ” in the pancreas that controls systemic blood sugar levels.
Researchers have identified a molecular target that holds promise for therapies that protect and regenerate beta cells without having the unintended side effects of intensive insulin therapy.
Suggested Reading:
Top 14 Differences Between Serum and Plasma & Similarities
![]()
13. Probiotic yeast created using engineering to treat inflammatory bowel disease (USA, June 2021)

Human health may be significantly impacted by the variety of microbes in the human gut. The balance of these microbes is linked to several illnesses, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), raising the possibility that treating illness may involve reestablishing the proper balance. Today’s probiotics, which are living yeasts or bacteria, have evolved to be more effective in the context of a healthy gut.
- Using yeast is a common source of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a type used in brewing, baking, and winemaking.
- The scientists implanted genetic elements using the gene-editing method CRISPR/Cas9 that could detect and react to inflammation by secreting an enzyme that could break down a crucial molecule involved in inflammation.
- Depending on how much of the inflammatory signal is present at a specific location in the gut, the engineered yeast can secrete various enzyme levels.
However, a probiotic would need to perform a variety of tasks, such as being able to turn off inflammation, undo damages, and restore the gut microbiome, to treat complex diseases like IBD, so thereby by modifying probiotics is expected to develop more specialized, tightly controlled medications for the treatment of conditions affecting the gut and other organs.
Suggested Reading:
17 Major organs on left side of body
![]()
14. Researchers investigate a potential cure for the MRSA “superbug” (USA, Sept 2021)
Researchers at the Baker Institute for Animal Health, a division of the College of Veterinary Medicine, have discovered a new method using mesenchymal stem cells for treating wounds that significantly reduces the viability of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or MRSA (CVM).
- According to the most recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly 20 000 Americans passed away in 2017 due to bloodstream infections brought on by MRSA, which affected more than 119 000 people in the country.
- Since MRSA has developed a resistance to many antibiotics- the only treatments currently available to treat bacterial infections. These bacteria can become dangerous in certain situations, such as in immunocompromised patients or infected wounds.
- The researchers say this kind of fast genome sequencing could eventually form the basis for a regional or national infection surveillance program designed to head off MRSA outbreaks before they happen. It could also be used for outbreaks of food-borne infections like Salmonella or E. Coli.
The study might indicate a potential novel strategy for treating MRSA. While many people carry MRSA without severe consequences, this “superbug” can be fatal for those whose health is already compromised.
Suggested Reading:
Is MRSA Contagious? Explore the Etiology of MRSA Infection
![]()
15. Researchers discovered that enriching cell-free vaccine (USA, April 2021)
Researchers in synthetic biology have found a new method to amplify at least five-fold the production yields of protein-based vaccines, greatly extending access to potentially life-saving drugs.
- Scientists unveiled a new biomanufacturing platform that can efficiently produce shelf-stable vaccines at the point of care, preventing vaccine waste from mistakes made during storage or transportation.
- The team found that enriching cell-free extracts with cellular membranes-the ingredients required to make conjugate vaccines-significantly increased the yields of its freeze-dried platform.
- In bioconjugate vaccine expression (iVAX), the new manufacturing platform is made possible by cell-free synthetic biology, a technique in which researchers take out a cell’s outer wall (or membrane) and reuse its internal machinery.
- Conjugate vaccines are frequently used to prevent bacterial infections. They typically comprise an immunostimulatory protein carrier linked to a pathogen-specific capsular (CPS) or O-antigen polysaccharide (O-PS). Membranes naturally reassemble after being torn apart to form vesicles, spherical objects transporting significant molecular data.
- When these vesicles are more concentrated, it may be possible to create components for protein therapeutics like conjugate vaccines, which join a sugar unit specific to a pathogen to a carrier protein.
- By training the body to identify that protein as a foreign substance, it can mount an immune attack against it in the future.
So, in this present study, the cell membrane, typically discarded in cell-free synthetic biology, held the key to achieving that goal. In vitro, the conjugate vaccine expression platform offers a novel approach for both developed and developing nations to receive the protective advantages of a specific significant class of antibacterial vaccines.
Suggested Reading:
Top 10 Biotechnology Discoveries in 2019
![]()
Thus, these biotechnological events provide us with a thorough understanding of our most recent developments in the fields of Synthetic Biology, Stem cell and Tissue engineering research, Genome editing and decoding of the entire human transcriptomics, Construction of cell-free vaccine, and various other wonders. We anticipate more intriguing discoveries in 2022.
![]()