Table of Contents
Before we look into what is mitosis, let’s go over the basics first. Cells are often classified into two types. The first type is known as “Prokaryotes” while the second is termed as “Eukaryotes”. Cells that are smaller in size, usually about 1-10mm in diameter and reproduce by the process of fission are classified as prokaryotic cells.
Because the cells reproduce by fission, the offspring successfully culminate genetic information, absolutely identical to the parent cell.
The second type or the eukaryotic cells are distinguished by the only feature of a nucleus. Every eukaryotic cell consists of an individual nucleus that store genetic materials in the form of chromatin.
Check out the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes in detail here.
Let us now explore what is mitosis, where it occurs, mitosis stages and mitosis by different organisms (Animals and Plants).
What is Mitosis?
According to the Cell Theory, new cells are only created by the division of existing cells. In particular, mitosis is perhaps the most dramatic stage[1] of the cell cycle as it involves both the disintegration and reorganization of the components of the cell.
Mitosis, by definition is a type of cell division that involves only the somatic cells (any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells).
In this process, the growth of the organism itself and the repair of any damaged tissues are ensured by continuously dividing cells. Mitosis is also the process by which lower eukaryotic organisms multiply through asexual reproduction (i.e. budding and use of runners).
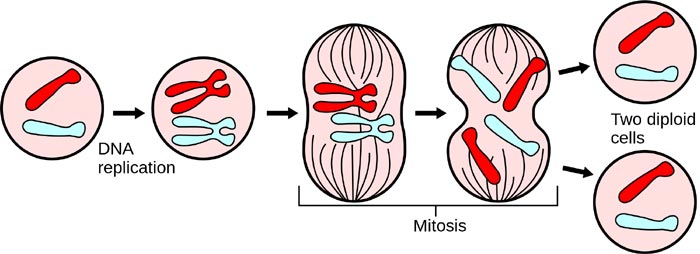
In simpler terms, during mitosis, a single cell gets divided into two identical daughter cells.
The main purpose of mitosis is to allow growth of new cells and also to replace the repaired or worn-out cells.
![]()
What Occurs Before Mitosis?
- For instance, the cell undergoes a process called the interphase as the preparatory phase before mitosis. Interphase is divided into three major stages: G1, S, and G2 phase.
- During the S phase of interphase, the chromosomes are duplicated in order to make sure that each daughter cell will receive one copy of every chromosome.
![]()
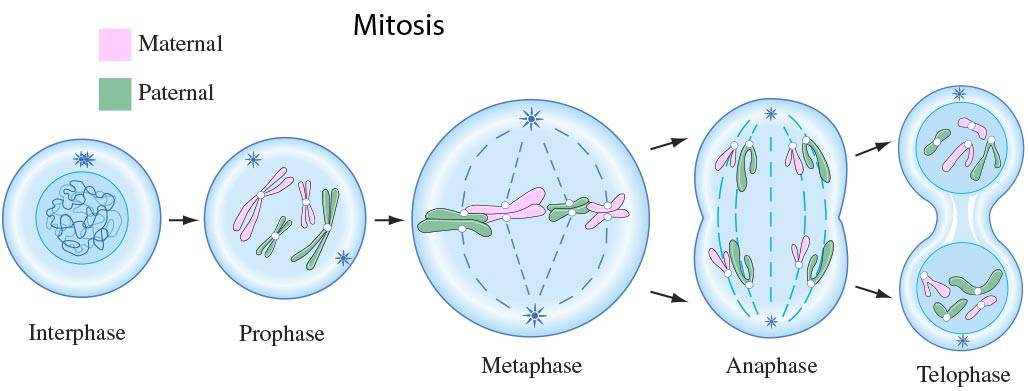
Four Stages Of Mitosis
While the process of mitosis is variable among living organisms, the fundamental actions of separation are highly conserved in eukaryotes. Mitosis, although a continuous process, is typically divided into four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
1. Prophase
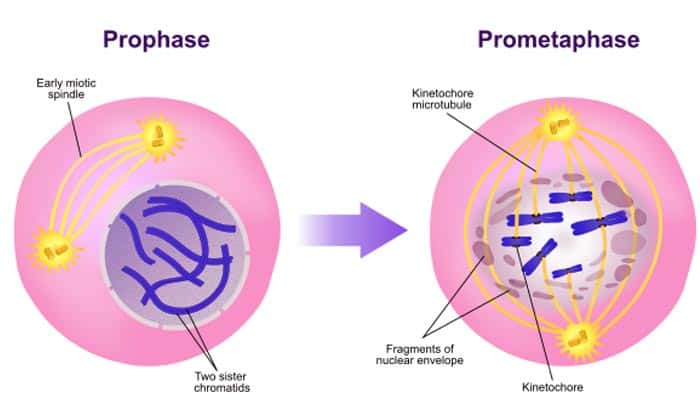
- During prophase, the chromatin coils into visible rod-shaped structures called the chromosomes.
- Aside from condensation, the mitotic spindle fibre, which will further help in the segregation of the chromosomes, is also formed due to various cytoplasmic changes in the cell.
- The centrosomes, which were previously replicated during interphase, begin to separate and migrate to the opposite sides of the cell. Here, the centrosomes will serve as the guide for the mitotic spindle (pairs of centrioles).
- The end of prophase is the breakdown of the nuclear envelope (in higher eukaryotes which will help for the easier release of the chromosomes. Note: The disintegration of the nuclear envelope is not a universal characteristic of mitosis[5] as organisms like yeasts exhibit a so-called “closed mitosis” where the envelope remains intact.
- Sometimes, biologist define a so-called intermediate phase between prophase and metaphase: prometaphase[6]. During this process, the microtubules alternately (and quickly) assemble and disassemble as they try to find their ways toward the kinetochores found at the centromeres of each sister chromatid.
![]()
2. Metaphase
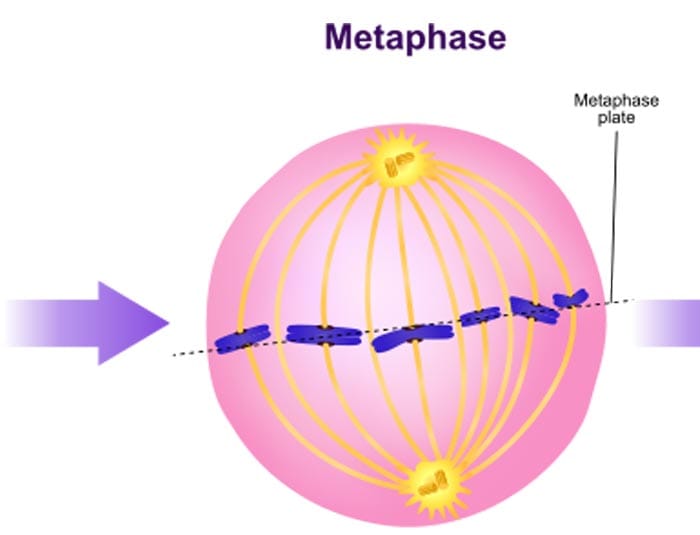
- Kinetochores (proteins associate with the centromeres) of the chromosomes are starting to be attached to the microtubules located at the opposite sides of the cell with the mitotic spindle fibres (The structures that facilitate the formation of spindle fibers are known as centrioles, and the organelle that organizes their creation is called the centrosome.).
- Most often, before proceeding to anaphase, cells undergo a so-called “spindle checkpoint” where they check to ensure that all the chromosomes have their kinetochores attached to the microtubules. If otherwise, the cell will have to stop mitosis until the problem is fixed. where metaphase only for a short period of time before going to anaphase.
![]()
3. Anaphase
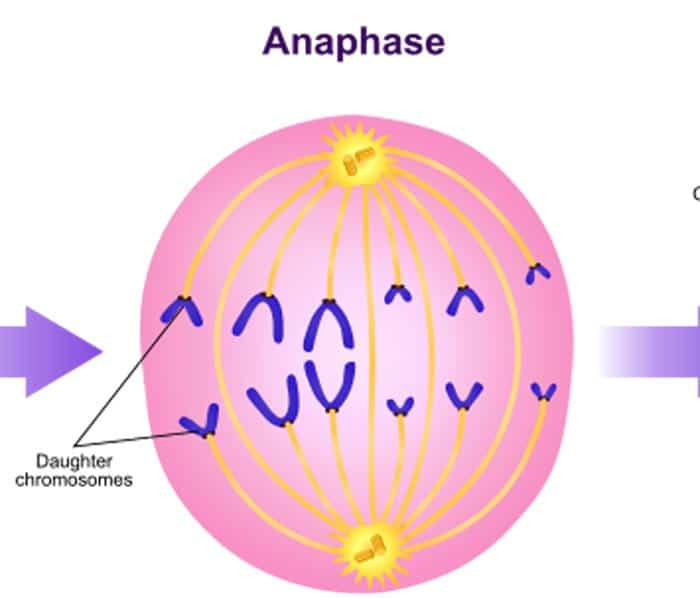
- To do this, the protein that holds the chromosomes together is broken; hence allowing them to be pulled toward the opposite ends of the cell.
- Along with this, the microtubules that are not attached to the chromosomes push each other apart, allowing the cell to be stretched further.
![]()
4. Telophase
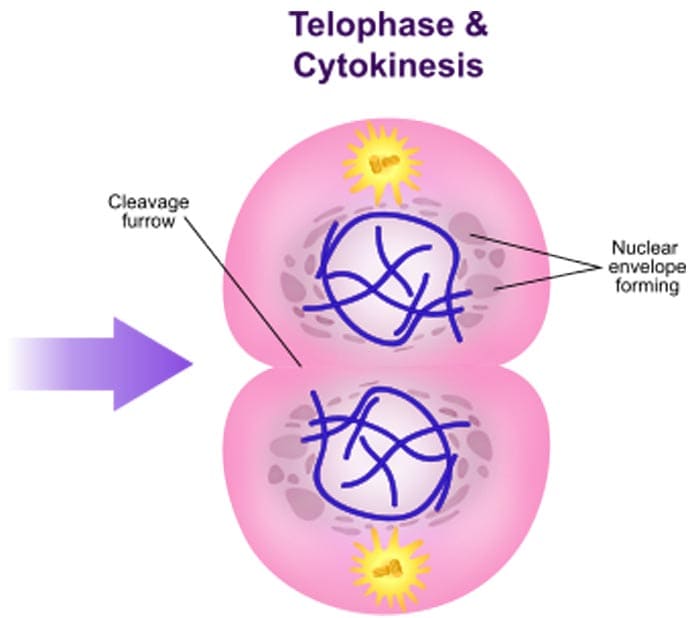
- Telophase is almost the opposite of prophase as it is when the set of chromosomes decondense back to chromatin.
- Also in contrast to prophase, the mitotic spindle is broken down as the nuclear envelope is re-synthesized.
![]()
Phases of Mitosis – Video Explanation
![]()
Mitosis by different types of organisms
As alluded to earlier, the process of mitosis is highly conserved among eukaryotes. However, different organisms still harbor unique mechanisms during the process.
Mitosis in Animals
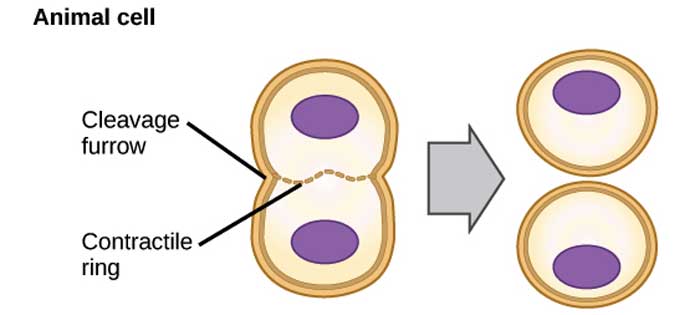
- This inward contraction then produces a depression known as the cleavage furrow.
- This characteristic is unique to animal cells as they are characterized by soft cytoplasm and easy to pinch cellular membrane.
![]()
Mitosis in Plants
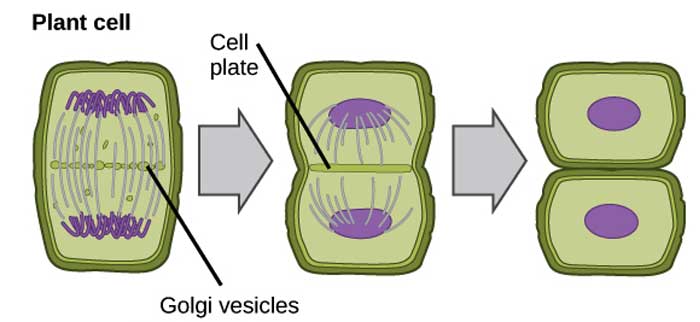
- In order to divide into two, plant cells start by creating a structure at the middle of the cell (called the cell plate). This cell plate, which is composed of nuclear membrane and other cell components is what helps the cell separate into two.
![]()
Summary
Perhaps, the most remarkable thing about the process of mitosis is its absolute precision and accuracy, that since its discovery is what have been intriguing biologists. At present, scientist have already known that this process is highly controlled as it involves a wide variety of cellular proteins and components.
While of course, the dynamic mechanism of mitosis is best appreciated when observed in living cells. But come to think of it, isn’t it weird that in biology, multiplication and division can mean the same thing?
![]()
Cite This Page
References
- [1] – “The Events of M Phase – The Cell – NCBI Bookshelf”. Accessed February 18, 2017. Link.
- [2] – “The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis”. Accessed February 18, 2017. PDF.
- [3] – “Phases of the cell cycle (article) | Khan Academy”. Accessed February 18, 2017. Link.
- [4] – “Mitosis I: The Mitotic Spindle – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com”. Accessed February 18, 2017. Link.
- [5] – “mitosis – The Cell – NCBI Bookshelf”. Accessed February 18, 2017. Link.
- [6] – “Cell Division: Stages of Mitosis | Learn Science at Scitable”. Accessed February 18, 2017. Link.
- [7] – “Telophase – The School of Biomedical Sciences Wiki”. Accessed February 18, 2017. Link.












thank you sir really its so nice now I well understand about mitosis